Unit 3: Direct and Indirect Speech – Reporting What Was Said
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding Direct Speech
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're going to explore *Direct Speech*. Can anyone tell me what it is?

It's when we quote exactly what someone said!

Exactly! We enclose the quote in quotation marks. For example, "I'm happy" is direct speech. What comes after the quote?

We usually follow it with a reporting verb and sometimes a comma!

Right! And remember, a comma goes before the opening quotation mark. Can anyone give another example?

He said, "I will come tomorrow."

Fantastic! Let's remember to always include the exact words of the speaker. In this case, we used the reporting verb 'said' and correctly formatted the speech.
Understanding Indirect Speech
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, shifting gears to *Indirect Speech*. Who can explain what that is?

It’s when we tell what someone said, but not using their exact words.

Correct! We also don't use quotation marks. Instead, we may change the verb tenses. For example, "I am happy" turns into "He said that he was happy." Why do we change the tense?

Because the reporting verb is in the past tense!

Exactly! Transforming the tense is essential for correct indirect speech. What about pronouns?

They also change! Like, "I" becomes "he" or "she".

Well done! It’s all about ensuring clarity and understanding when reporting speech.
Tense and Pronoun Changes
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s dive deeper into *tense changes*. When we report speech, the original present tense often changes to the past. Can someone give an example?

If someone says, 'I eat apples', it changes to 'He said that he ate apples'!

Perfect! And what about pronouns, how do they change?

Like, 'you' might become 'I' or 'he/she'.

Exactly! It's important to adjust them depending on who is speaking and who they are speaking to. Can anyone think of any time markers that need to change?

'Now' would change to 'then'!

Yes! These changes help us accurately convey what someone else has said.
Reporting Questions
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Next, let's focus on how we report questions. What do we do differently compared to statements?

We don’t just repeat the question. We change it into a statement.

Correct! If someone asks, 'Where are you going?', we report it as 'He asked where I was going.' What do we use for yes or no questions?

We use 'if' or 'whether'!

Exactly! Understanding these rules helps in effective communication when reporting speech.
Practice Exercise Recap
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's recap what we've learned today with some practice. If I say, "He said, 'I can swim'", how would that change into indirect speech?

It would be, 'He said that he could swim.'

Excellent! Now, let’s do one more. How about, "She asked, 'Are you coming?"

That would be, 'She asked if I was coming.'

Fantastic! Great job everyone! Always remember the key points about tenses and pronouns in these conversions.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
In this section, students will learn how to report speech through direct and indirect forms, along with key rules, examples, and practice exercises to solidify their understanding of reported speech.
Detailed
Unit 3: Direct and Indirect Speech – Reporting What Was Said
Understanding how to report what was said, using direct and indirect speech, is crucial in mastering English. This section focuses on two primary forms of speech: Direct Speech, which quotes the exact words of a speaker, and Indirect Speech, which paraphrases what was said without quoting verbatim.
Key Concepts:
- Direct Speech:
- Involves quoting the exact words spoken, using quotation marks.
- Example: She said, "I am going to the park."
- The format typically includes a reporting verb followed by the quoted speech.
- Indirect Speech:
- Paraphrases what someone has said, without quotation marks.
- Key rules include changing verb tenses, pronouns, and expressions of time or place.
- Example: She said that she was going to the park.
Basic Rules for Changing from Direct to Indirect Speech:
- Tense Changes: When the reporting verb is past tense, shift the tenses:
- Present Simple → Past Simple (e.g., "I eat" → he ate).
- Present Continuous → Past Continuous (e.g., "I am eating" → he was eating).
- And so on.
- Pronoun Changes: Adjust pronouns depending on the speaker and listener.
- Time and Place Adjustments: Modify time indicators appropriately (e.g., now → then).
- For questions, use 'asked' and convert to a statement format (e.g., He asked, "Where are you going?" → He asked where I was going).
Understanding these rules is essential for clear communication in both writing and speaking.
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
What is Direct Speech?
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Speech is how we report what someone has said. There are two main ways to do this:
- Direct Speech:
- Reports the exact words spoken by a person.
- These words are placed within quotation marks (" ") and are separated from the rest of the sentence by a comma.
- Example: She said, "I am going to the park."
- Example: "What are you doing?" asked Rahul.
Detailed Explanation
Direct speech is a way to convey exactly what someone has said. This form of speech uses quotation marks to show the exact words. It allows the reader to feel the original emotion and tone in the speaker's words, as it captures what was said verbatim. For instance, when someone says, 'I love ice cream,' it reflects their feelings directly. Including a comma before the quotation helps separate the speaker from their speech.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a friend saying, 'I am excited about the concert!' If you share this with another friend, using direct speech by saying, 'John said, "I am excited about the concert!"' keeps the original excitement and clarity of the message, just as hearing the friend say it in person would.
What is Indirect Speech?
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Indirect Speech (Reported Speech):
- Reports what someone said without using their exact words. The meaning is conveyed, but the original words are not quoted.
- Quotation marks are not used.
- Tenses usually change (shift back in time).
- Pronouns often change.
- Time and place expressions often change.
- Example: She said that she was going to the park.
- Example: Rahul asked what I was doing.
Detailed Explanation
Indirect speech conveys the meaning of what someone said, but it does not quote their exact words. Instead of using quotation marks, you change the structure slightly and often shift tenses to reflect the time of reporting. For example, if someone said, 'I am happy,' you would report this as, 'She said that she was happy.' This reflects the time and context of the statement.
Examples & Analogies
Think of it like sharing news about someone else's experience. If your friend told you, 'I have a pet dog,' and you want to tell another friend, you might say, 'He told me he has a pet dog.' You change the sentence to fit your context while still sharing the essence of what your friend meant.
Basic Rules for Changing from Direct to Indirect Speech
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Basic Rules for Changing from Direct to Indirect Speech:
- Reporting Verb: If the reporting verb (e.g., said, told, asked) is in the past tense, the tense of the verb in the reported speech usually changes.
- Present Simple → Past Simple (e.g., "I eat" → he ate)
- Present Continuous → Past Continuous (e.g., "I am eating" → he was eating)
- Past Simple → Past Perfect (e.g., "I ate" → he had eaten)
- 'Will' → 'Would' (e.g., "I will go" → he would go)
- 'Can' → 'Could' (e.g., "I can swim" → he could swim)
- Pronoun Changes: Pronouns change according to the speaker and listener.
- "I" becomes "he/she."
- "My" becomes "his/her."
- "You" becomes "I/he/she/they," etc.
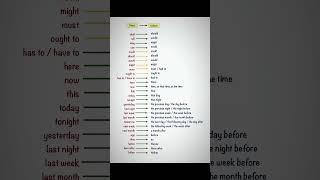
- Time and Place Changes:
- Now → then
- Today → that day
- Yesterday → the previous day/the day before
- Tomorrow → the next day/the following day
- Here → there
- This → that
- These → those.
Detailed Explanation
When converting direct speech to indirect speech, several rules apply. The main rule involves changing the tense of the original statement if the reporting verb is in the past. For example, if someone said, 'I am tired' and you want to report this later, you would say, 'He said he was tired.' Besides tense changes, pronouns may need adjustment based on who is speaking or being referenced. Additionally, expressions of time or place might change to fit the reporting context.
Examples & Analogies
Picture overhearing a conversation. If Alice says, 'I will go to the store tomorrow,' and later you tell Bob, you would say, 'Alice said she would go to the store the next day.' The change from 'tomorrow' to 'the next day' adapts the information to your context while keeping the meaning intact.
Changing Questions in Indirect Speech
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Questions:
- Use 'asked' or 'enquired'.
- If a 'wh' word (what, where, why, when) is used, repeat it.
- If no 'wh' word, use 'if' or 'whether'.
- Change the question form to a statement form.
- Direct: He asked, "Where are you going?"
- Indirect: He asked where I was going.
- Direct: She asked, "Are you well?"
- Indirect: She asked if I was well.
Detailed Explanation
When changing questions from direct to indirect speech, you first identify the type of question. For 'wh' questions (like what, where, when), you repeat the question word in the reported form. If the question is yes/no, you use 'if' or 'whether' to introduce the statement. The sentence structure changes to that of a statement rather than a question.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a teacher asking a student, 'What do you need to complete your project?' If the student later tells a friend about this, they might say, 'The teacher asked what I needed to complete my project.' Notice how the question 'What do you need?' was turned into a statement about what the teacher asked.
Key Concepts
-
Direct Speech:
-
Involves quoting the exact words spoken, using quotation marks.
-
Example: She said, "I am going to the park."
-
The format typically includes a reporting verb followed by the quoted speech.
-
Indirect Speech:
-
Paraphrases what someone has said, without quotation marks.
-
Key rules include changing verb tenses, pronouns, and expressions of time or place.
-
Example: She said that she was going to the park.
-
Basic Rules for Changing from Direct to Indirect Speech:
-
Tense Changes: When the reporting verb is past tense, shift the tenses:
-
Present Simple → Past Simple (e.g., "I eat" → he ate).
-
Present Continuous → Past Continuous (e.g., "I am eating" → he was eating).
-
And so on.
-
Pronoun Changes: Adjust pronouns depending on the speaker and listener.
-
Time and Place Adjustments: Modify time indicators appropriately (e.g., now → then).
-
For questions, use 'asked' and convert to a statement format (e.g., He asked, "Where are you going?" → He asked where I was going).
-
Understanding these rules is essential for clear communication in both writing and speaking.
Examples & Applications
Direct: She said, 'I will go to the store.' Indirect: She said that she would go to the store.
Direct: What time is it? Indirect: He asked what time it was.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Direct speech quotes, listen with care; Indirect speech paraphrases, shows you care.
Stories
Once, a girl named Mia had a friend Sam. Mia would report what Sam said, making it her own. She said: 'Sam loves pizza' and changed it to: 'Sam said he loved pizza'.
Memory Tools
Use 'T.P.' for Tense and Pronoun when switching to indirect speech.
Acronyms
R.P.T. - Remember Pronoun and Tense changes for reporting speech.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Direct Speech
Quoted words of a speaker, enclosed in quotation marks.
- Indirect Speech
Paraphrased version of what someone said, without quoting their exact words.
- Reporting Verb
A verb used to report speech, such as 'said' or 'asked'.
- Tense Shift
Changing the tense of a verb when converting from direct to indirect speech.
- Pronoun Change
Modifying pronouns according to the speaker and listener in indirect speech.
- Quotation Marks
Punctuation marks used to enclose direct speech.
- Time Expressions
Words or phrases that describe when something happens, which may change in reported speech.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
