Life Cycle Inventory (LCI)
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding Life Cycle Inventory
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're diving into the Life Cycle Inventory, or LCI. It's an essential method in sustainability that tracks all inputs and outputs associated with a product throughout its life cycle. Can anyone tell me what they think an 'input' might be?

Is it things like materials and energy used during production?

Exactly right! Inputs include materials, energy, and even water. Now, what do you think 'outputs' are?

I think outputs would be waste products and emissions.

Correct! Outputs encompass emissions, waste, and any by-products. Understanding both categories is essential for LCI.

How do we collect all this data?

Great question! Data is sourced from both primary and secondary methods, like industry databases and environmental reports. Remember, LCI is all about comprehensive data collection!

In summary, the LCI tracks inputs and outputs from a product's life cycle, providing critical data for sustainability assessment.
Role of Life Cycle Inventory in Sustainability
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now that we've covered what LCI is, let’s discuss its significance. How does tracking these inputs and outputs help in sustainability efforts?

It might help identify which stages of production are the most wasteful, right?

Absolutely! By identifying resource-intensive processes, companies can focus on improvement. Any other thoughts?

Could it also guide companies in reducing their ecological footprint?

Yes! LCI promotes sustainable practices by highlighting areas for reduction in waste and energy use. How do you think this affects consumer choices?

Consumers might choose products that have lower environmental impacts.

Exactly! LCI not only aids in corporate decision-making but also informs consumers, fostering a market for sustainable products. To recap, LCI is crucial for identifying wasteful practices and promoting sustainability.
Challenges in Life Cycle Inventory Data Collection
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

As we explore LCI, let's address some challenges in collecting data. What do you think might make data collection difficult?

Maybe access to reliable sources? Some companies might not share their data.

That's a significant challenge! Proprietary information can limit data access. What else could be a barrier?

I guess the processes involved can be complex, making it hard to track everything accurately.

Exactly again! The intricacies of production processes can complicate tracking. Overcoming these barriers often requires collaboration and innovative data management strategies. Remember, accurate data collection is critical for effective LCI.

In summary, challenges such as data access and complexity of processes can hinder effective LCI, but solutions exist.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
LCI systematically collects data about the resources consumed and waste generated during each phase of a product's life cycle. This comprehensive inventory forms the basis for evaluating environmental impacts and is essential for informed decision-making in sustainability practices.
Detailed
Life Cycle Inventory (LCI)
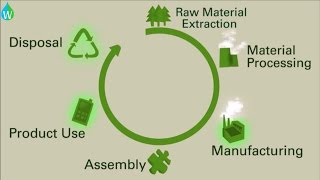
Life Cycle Inventory (LCI) is a vital methodology that aggregates all relevant data related to the inputs and outputs at each stage of a product’s life cycle. This includes the materials consumed, energy utilized, and the emissions and wastes produced. Conducting an LCI entails rigorous data collection from both primary and secondary sources, creating a detailed model that reflects the entirety of a product's life - from raw material extraction to end-of-life disposal.
Key Aspects of LCI:
- Data Compilation: Collecting data on resource inputs (energy, materials, water) and outputs (emissions, wastes) for various life cycle stages.
- Importance: Provides the groundwork for assessing environmental impacts through Life Cycle Assessment (LCA), enabling stakeholders to make informed choices towards sustainability.
- Critical Role: LCI helps in identifying resource-intensive processes and potential areas for improvement, allowing for more sustainable practices within industries.
Understanding LCI is instrumental for sectors aiming to enhance their sustainability measures, as this inventory plays a crucial role in shaping effective environmental strategies.
Youtube Videos









Key Concepts
-
Life Cycle Inventory (LCI): The method of collecting data on inputs and outputs in a product's life.
-
Inputs: Resources used during production stages, including materials, energy, and water.
-
Outputs: Waste and emissions produced in the life cycle of a product.
-
Data Collection: The process of gathering relevant data to feed into the LCI.
-
Sustainability: The overarching goal of utilizing LCI—promoting environmentally responsible practices.
Examples & Applications
An example of LCI is a manufacturer collecting data on the amount of plastic, energy, and water used in producing a plastic bottle.
Another example is measuring the emissions produced during the transportation and disposal of a product at the end of its life.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
For every input you count, there's an output to amount. Track them both, don't dismount, sustainability's what we scout.
Stories
Imagine a plastic bottle living its life: born from raw materials, powered by energy, but at the end, it wonders about the waste it caused. Its journey teaches us how our choices affect the environment.
Memory Tools
I.O. for LCI: Inputs, Outputs for Life Cycle Inventory, track them right for sustainability!
Acronyms
LCI = Life Cycle Inputs + Outputs.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Life Cycle Assessment (LCA)
A methodology for assessing the environmental impacts associated with all stages of a product's life.
- Inputs
Resources consumed (materials, energy, water) during a product's life cycle.
- Outputs
Waste products and emissions produced during a product's life cycle.
- Data Collection
The process of gathering information on inputs and outputs for LCI.
- Sustainability
Meeting our own needs without compromising the ability of future generations to meet theirs.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
