Strategic Environmental Assessment (SEA) - 4.3.3
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Importance of Initiation and Scoping
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're diving into the Initiation and Scoping phase of the SEA process. Can anyone tell me why this phase is crucial?

Is it because it sets the groundwork for the entire assessment?

Exactly! This phase helps ensure that all relevant factors are considered. It allows us to identify the objectives we want to achieve with the assessment.

What does a typical scoping process look like?

Good question! Scoping typically involves identifying stakeholders, determining relevant legal frameworks, and outlining the key issues to be assessed.

So, what happens if critical issues are missed in the scoping process?

If key issues are overlooked, it can lead to a less effective assessment and potentially negative environmental impacts down the line.

To sum it up, proper initiation and scoping help streamline the SEA process and ensure meaningful stakeholder engagement. It’s the foundation of all subsequent steps.
Identifying Stakeholders
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Next, let’s discuss stakeholder engagement. Why is it important to identify key stakeholders early in the SEA process?

I think it’s to ensure that all voices are heard, especially those affected by the project.

Exactly! Engaging stakeholders can provide valuable insights and help to build trust among the community.

How do we go about identifying these stakeholders?

Typically, you’d look at individuals or groups that will be directly affected, government agencies, NGOs, and possibly industry experts.

So, it’s about gathering a diverse range of perspectives?

Absolutely! A comprehensive list minimizes gaps in the assessment.

Remember, effective stakeholder engagement can significantly impact the success of the assessment and future project implementation.
Legal and Institutional Frameworks
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s talk about the legal and institutional frameworks. Why are they important for conducting an SEA?

They probably guide what we need to consider during the assessment.

Exactly! These frameworks provide guidelines that ensure compliance with national and international regulations.

How do these frameworks affect the scope of our assessment?

Good question! They dictate the boundaries of what must be assessed with respect to environmental impacts. Violating them can lead to legal ramifications.

So, it’s best to be thorough in understanding our legal responsibilities!

Absolutely! Summarizing, knowing the legal context enhances our assessment's credibility and compliance.
Defining Boundaries and Impacts
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s focus on how we define the boundaries of an SEA. Why is this step important?

It helps limit our assessment to what’s manageable, right?

Correct! Setting boundaries allows us to focus on the most critical impacts without overextending our resources.

What type of impacts do we need to consider?

You should consider a range of impacts, such as social, economic, and environmental factors. Identifying these early on is crucial.

So, would thorough scoping prevent us from missing anything significant?

Precisely! A thorough scoping phase leads to a comprehensive assessment, facilitating better environmental protection.

To conclude, defining boundaries while identifying potential impacts is key for effective decision-making during the SEA.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
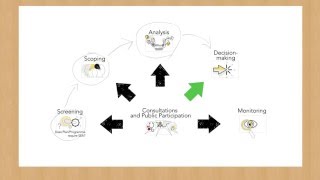
The Initiation and Scoping phase of the Strategic Environmental Assessment (SEA) is critical as it sets the framework for assessing environmental impacts within strategic planning. This phase identifies stakeholders, objectives, and relevant regulatory frameworks while establishing the boundaries for the assessment.
Detailed
The Initiation and Scoping phase is a vital first step in the Strategic Environmental Assessment (SEA) process. In this phase, the necessity for conducting an SEA is assessed, alongside establishing clear objectives and anticipating the scope of the evaluation. It involves identifying key stakeholders including decision-makers and affected communities, ensuring comprehensive participation throughout the process. Legal and institutional frameworks governing the SEA are delineated, helping to guide the assessment in alignment with established regulations. By defining the boundaries and potential impacts to be examined, this scoping can lead to a more focused and effective assessment overall, allowing for the identification of significant environmental issues which will be considered in subsequent stages.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Need for SEA
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Determine the need for SEA and establish the objectives and scope of the assessment.
Detailed Explanation
The first step in the Strategic Environmental Assessment (SEA) process is to determine whether an SEA is necessary for a given project or policy. This involves defining the specific goals of the assessment, which guides its focus and ensures that it effectively addresses environmental concerns related to the project. Establishing the scope helps clarify what will be included in the assessment, such as what environmental aspects will be evaluated and how detailed the analysis will be.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine you are planning a road trip. Before you leave, you decide where you want to go and what route you’ll take. This planning step is like determining the need for an SEA – you decide if your journey (the project) needs an assessment (planning) to ensure you have everything in order.
Stakeholder Involvement
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Identify the key decision-makers and stakeholders who should be involved in the SEA process.
Detailed Explanation
Identifying the key decision-makers and stakeholders is crucial for the SEA process. Stakeholders include individuals or groups who may be affected by the project, such as local communities, government officials, NGOs, and industry representatives. Involving them ensures that diverse perspectives are considered, and their insights can lead to a more comprehensive understanding of potential environmental impacts, contributing to more informed decision-making.
Examples & Analogies
Think of it like organizing a community event. You wouldn't just decide everything on your own; you'd talk to various community members to hear their opinions and suggestions. Similarly, the SEA process benefits from the input of all involved parties.
Legal and Institutional Framework
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Define the legal and institutional framework for conducting the SEA.
Detailed Explanation
The third step involves setting up the legal and institutional framework necessary to conduct the SEA. This framework comprises the laws, regulations, and guidelines that govern environmental assessments in a specific jurisdiction. It ensures that the assessment process adheres to required standards and protocols, thus lending credibility and legitimacy to the assessment outcomes.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine every game has rules – it makes the game fair and organized. Similarly, the legal framework provides a set of rules for the SEA, ensuring that everyone follows the correct procedures for assessing environmental impacts.
Key Concepts
-
Initiation Phase: The first step in the SEA process, where the need for assessment is established.
-
Scoping: The determination of objectives, key impacts, and stakeholder engagement necessary for the SEA.
-
Stakeholder Engagement: Identifying and involving those affected by or interested in the project to solicit input and feedback.
-
Legal Framework: Understanding the regulations and laws that guide the SEA process.
Examples & Applications
For instance, during a scoping phase for a new transportation project, relevant stakeholders may include local communities, state transportation agencies, environmental NGOs, and local business owners.
An example of defining boundaries could be focusing solely on the regional environmental impacts rather than wider geographical areas which could complicate the assessment.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In initiation and scoping, we seek to know, who’s involved and what impacts will show.
Stories
Once upon a time, in a town planning for development, officials made sure to talk to the local farmers, environmentalists, and government agents to gather input and create a successful plan, illustrating how scoping ensures everyone’s voice is heard.
Memory Tools
IAST – Initiation, Assessment, Stakeholders, Target – a reminder of steps in setting up an SEA.
Acronyms
SCOPE – Stakeholders, Context, Objectives, Potential impacts, Evaluation – key elements in scoping.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Strategic Environmental Assessment (SEA)
A systematic process for evaluating the environmental impacts of proposed policy, plan, or program initiatives.
- Stakeholders
Individuals or groups that have an interest in or are affected by a project, policy, or initiative.
- Legal and Institutional Frameworks
The set of laws, regulations, and institutions that govern the conduct of environmental assessments.
- Scoping
The process of determining the boundaries, objectives, and key issues to be assessed in an SEA.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
