Integrated Water Resources Management (IWRM)
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to IWRM
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're discussing IWRM, which stands for Integrated Water Resources Management. Can anyone explain what they understand about this term?

Is it about managing water from different sources together?

Exactly! IWRM aims at the coordinated management of water, land, and related resources. It’s a holistic approach.

Why is it important?

Great question! It helps in maximizing economic and social welfare while ensuring sustainability. Think of it as a way to prevent water conflicts.
Key Principles of IWRM
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s dive deeper into the principles of IWRM. One key principle is a holistic view—why do you think it's crucial?

I think it helps to see the bigger picture and all of the interactions.

Exactly, it allows for more informed decision-making. Another important principle is stakeholder participation.

Does that mean everyone gets to have a say in water management?

Yes, involving everyone ensures that the needs of different groups are met. This helps prevent conflicts and leads to more sustainable solutions.
Challenges and Benefits of IWRM
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s discuss some challenges of IWRM. One challenge is climate change—how might that impact water management?

It could make water sources less reliable, right?

Exactly! Climate change can lead to droughts or floods, complicating management efforts. But what are some benefits of using IWRM?

It probably helps to use water more efficiently!

Yes! It enhances economic efficiency and helps in achieving the Sustainable Development Goals.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Integrated Water Resources Management (IWRM) is emphasized as a holistic approach that seeks to optimize the use of water resources, improve economic and social welfare, and ensure environmental sustainability. It calls for collaboration among various sectors and stakeholders.
Detailed
Detailed Summary of Integrated Water Resources Management (IWRM)
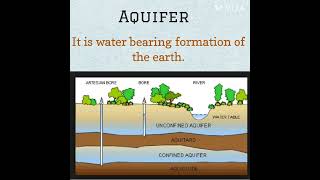
Integrated Water Resources Management (IWRM) is a comprehensive approach that aims to manage water resources in a way that balances economic, social, and environmental needs. It promotes the coordinated development and management of water, land, and related resources to maximize economic and social welfare in an equitable manner, all while safeguarding vital ecosystems. According to UNEP, successful IWRM requires collaboration among various stakeholders, ensuring that the interests of different sectors, such as agriculture, industry, and urban development, are taken into account.
Key principles of IWRM include:
- Holistic View: Recognizing the connections between water resources and other sectors, as well as among different user groups.
- Stakeholder Participation: Involving stakeholders at all levels—from government to local communities—in decision-making processes.
- Sustainability: Ensuring that water management practices contribute to environmental sustainability and resilience against climate change.
- Equitable Access: Striving to provide equitable access to water resources for all users, particularly marginalized communities.
The significance of IWRM is particularly evident as regions grapple with increasing water scarcity, pollution, and the impacts of climate change. By pursuing integrated strategies, regions can enhance resilience, improve economic efficiency, and contribute to sustainable development goals.
Youtube Videos
![Definition, Need, and 3E's/ 3 pillars of Integrated Water Resources Management[IWRM].](https://img.youtube.com/vi/8vLd0Ezgl8o/mqdefault.jpg)







Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Definition of IWRM
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Integrated Water Resources Management (IWRM) is a process that promotes the “coordinated development and management of water, land and related resources in order to maximise economic and social welfare in an equitable manner without compromising the sustainability of vital ecosystems” (UNEP).
Detailed Explanation
Integrated Water Resources Management (IWRM) is a strategy that encourages the effective management of water resources by coordinating the various elements involved, such as water, land, and related resources. The goal is to ensure that water is used in a way that promotes general economic and social benefits while also protecting the environment and supporting ecosystems. This means that the needs of people for water must be balanced with the need to maintain healthy ecosystems.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a community that relies on a river for drinking water, irrigation, and recreation. If the river is polluted, it affects not only drinking water but also fish habitats and the local economy that depends on fishing and tourism. By using IWRM, this community can develop rules for water use that protect the river's health, ensuring everyone benefits without depleting the resource.
Benefits of IWRM
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
IWRM aims to maximize economic and social welfare in an equitable manner while ensuring the sustainability of important ecosystems.
Detailed Explanation
The benefits of implementing IWRM are significant. By coordinating the management of water resources, different sectors can work together, leading to more efficient use of resources. This approach ensures that water allocation is fair and that all stakeholders, including marginalized communities, have access. It also helps in preserving ecosystems, making sure that habitats for wildlife are maintained while meeting human demands for water.
Examples & Analogies
Think of IWRM as a communal garden where all neighbors share the responsibility of watering, weeding, and caring for the plants. If everyone contributes equally, the garden thrives, producing enough fruits and vegetables for all without depleting resources or harming the environment. In contrast, if one person takes more than their fair share, it could lead to wilting plants and less food for everyone.
Challenges in Implementing IWRM
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Implementing IWRM faces challenges such as institutional barriers, lack of stakeholder participation, and financial constraints.
Detailed Explanation
Despite its benefits, implementing IWRM can be difficult. One major challenge is the presence of institutional barriers, where different governmental bodies may not communicate or cooperate effectively. Additionally, often stakeholders, such as local communities or businesses, may not be involved in decision-making processes, which can lead to conflicts or misuse of resources. Financial constraints can also limit the capacity to develop and maintain IWRM systems, resulting in ineffective management of water resources.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a restaurant where the kitchen staff (cooks) and the wait staff (servers) do not communicate. If the cooks are making too much food (water demand) but the servers aren’t aware, they can’t deliver it effectively to customers (resources/users), leading to wasted food and unsatisfied customers. Similarly, in IWRM, a lack of communication among different water management entities can lead to ineffective resource allocation and environmental degradation.
Key Concepts
-
Holistic View: Importance of considering interconnectedness in water management.
-
Stakeholder Participation: Engaging all relevant parties in the water management process.
-
Ecosystem Sustainability: Ensuring that water resources are managed in a way that maintains ecological health.
Examples & Applications
IWRM has been successfully implemented in countries like Australia and South Africa, where water resources are limited and collaboration across sectors is essential.
Urban areas have adopted IWRM approaches to manage stormwater effectively, integrating green infrastructure solutions.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In water we trust, manage with care, for a future that's bright, let's be aware.
Stories
Once upon a time, water was everywhere but poorly managed. People would often fight for it until they realized the need to collaborate—a lesson that turned their communities into thriving cities through IWRM.
Memory Tools
The acronym 'SHE'—Sustainability, Holistic view, Engagement—helps to remember the key principles of IWRM.
Acronyms
IWRM
Integrating Water
Resources
and Management effectively.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Integrated Water Resources Management (IWRM)
A process promoting coordinated development and management of water, land, and related resources to maximize welfare without compromising ecosystem sustainability.
- Stakeholder Participation
Involvement of all relevant parties in the decision-making process regarding water management.
- Ecosystem Sustainability
Maintaining the health and capacity of ecosystem processes over time.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
