OECD’s Strategic Policies for Sustainable Infrastructure
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
The Importance of Sustainable Infrastructure
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're discussing sustainable infrastructure. Why do you think it's important for our society?

I think it's important because it can help reduce pollution.

Exactly! Sustainable infrastructure aims to minimize environmental harm, which leads us to the OECD's goal of a low-carbon future. Can anyone explain what a low-carbon transition means?

Maybe switching to renewable energy sources?

Correct! Transitioning away from fossil fuels to renewables is key for reducing our carbon footprint. Remember the acronym 'REDUCE' - it stands for: Renewable energy, Efficient processes, and Durable materials.

How do we implement these ideas?

Great question! This leads us to the OECD's strategic policies. The emphasis is on integrating innovation and technology in these projects. We will delve deeper into that next.

What’s one example of technology in infrastructure?

An example would be Building Information Modeling, or BIM, which helps optimize resources. To summarize, sustainable infrastructure focuses on reducing environmental impact while ensuring that we can meet our needs without compromising future generations.
OECD Principles for Quality Infrastructure Investment
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let's explore the G20 Principles for Quality Infrastructure Investment. Who can tell me what that means?

Are they the guidelines for building infrastructure?

Yes! They aim to maximize the socio-economic impact of infrastructure investments. One principle is resilience. What might that encompass?

Making sure structures can withstand disasters?

Exactly! Resilience is crucial for sustainable infrastructure. One memory aid to remember the principles is the acronym ‘STRIVE’: Sustainability, Technology, Resilience, Inclusiveness, Value for money, and Efficiency. Can you think of an example of one of these principles in action?

Maybe solar panels on public buildings?

Exactly, that's a fantastic example of using technology to create sustainable infrastructure. As we conclude, remember the key principles of STRIVE. They're vital for ensuring our infrastructure meets the needs of today and the future.
Innovations and Methodologies for Sustainability
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let’s discuss the innovations and methodologies promoting sustainability. Can anyone name one innovation we've talked about?

Green infrastructure!

Correct! Green infrastructure uses natural processes for urban solutions, such as rain gardens. Another example is Integrated Water Resources Management, or IWRM—what does that involve?

Managing both water and land resources together?

Exactly! This coordination helps maximize social welfare. Let's reinforce this with the mnemonic ‘WATER’ which stands for: WaSte reduction, Access, Technology, Efficiency, and Resilience. Any other methodologies that come to mind?

Circular economy sounds important, right?

Absolutely! The circular economy promotes reducing waste through recycling. In summary, embracing innovations like green infrastructure and methodologies like IWRM are critical for achieving sustainable development.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The OECD emphasizes the need for strategic policies in sustainable infrastructure, focusing on themes like low-carbon transitions, inclusivity, and innovative technology to achieve a sustainable future. The section also discusses various methodologies and innovations essential for infrastructure development.
Detailed
OECD’s Strategic Policies for Sustainable Infrastructure
This section provides an overview of the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD)’s strategies to enhance sustainable infrastructure development globally. The OECD estimates a staggering annual investment of USD 6.9 trillion needed by 2050 to achieve development goals aligned with a low-carbon and climate-resilient world.
Key themes addressed by OECD policies include:
- Low-Carbon Transition: This involves transitioning existing infrastructure to more sustainable alternatives, minimizing carbon emissions.
- Technology and Innovation: The integration of advanced technologies aids in improving the efficiency and sustainability of infrastructure projects.
- Inclusiveness and Accessibility: Ensuring that infrastructure development is inclusive and accessible to all segments of the population.
Additionally, the OECD is developing tools based on G20 Principles for Quality Infrastructure Investment, which advocates for maximizing infrastructure's positive impact while fostering resilience against natural disasters. The UN Environment Assembly’s recent resolution promotes investment in sustainable and resilient infrastructure. This resolution is tied to several guiding principles that advocate for strategic planning, comprehensive sustainability assessments, and participatory decision-making processes.
Innovative methodologies supporting sustainable infrastructure include:
- Green Infrastructure: Utilizing natural systems for urban development, such as green roofs and permeable surfaces.
- Integrated Water Resources Management (IWRM): Coordination of management strategies for water and land resources.
- Circular Economy: Focus on resource efficiency and waste elimination through recycling initiatives.
- Environmental Impact Assessments (EIA): A systematic process for evaluating potential environmental impacts of projects.
The section emphasizes the critical role that civil engineers play in ensuring that infrastructure design and development are aligned with sustainability principles, fostering both societal benefits and global environmental protection.
Youtube Videos
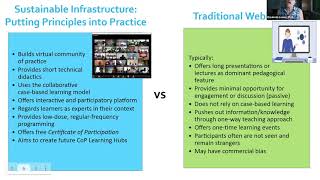








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Importance of Sustainable Infrastructure
Chapter 1 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Sustainable Infrastructure, be it built, natural or hybrid, are systems that are “planned, designed, constructed, operated and decommissioned in a manner that ensures economic and financial, social, environmental, including climate resilience, and institutional sustainability over the entire infrastructure life cycle” (UNEP).
Detailed Explanation
Sustainable infrastructure refers to any type of infrastructure—whether it's buildings, roads, or natural resources—that is designed with sustainability in mind. This includes several stages such as planning, designing, constructing, and eventually decommissioning (taking apart or recycling the infrastructure). The goal is to make sure that the infrastructure is good for the economy and society, protects the environment, and remains strong and reliable in the face of changes, such as climate issues, throughout its entire life span.
Examples & Analogies
Think of sustainable infrastructure like planting a tree. Just like a tree grows, provides shade, and produces oxygen throughout its life, sustainable infrastructure is designed to continuously benefit people and the planet, not just in the moment but for years and decades to come.
OECD Investment Requirements
Chapter 2 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) estimates that an annual investment of USD 6.9 trillion is needed for infrastructure to meet development goals and create a low carbon, climate resilient future by 2050.
Detailed Explanation
The OECD has calculated that for countries to develop their infrastructure effectively and address climate change, they need to invest a massive amount of USD 6.9 trillion each year up until 2050. This investment is crucial to ensure that infrastructure can help communities adapt to climate-related challenges while also promoting economic growth and sustainability.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine trying to upgrade a city’s transportation system to use electric buses instead of diesel ones. This kind of transition may require a hefty investment at first, but down the road, it can save money on fuel and maintenance while also reducing pollution and benefiting the environment.
OECD’s Toolkit Development
Chapter 3 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Presently the OECD is developing a toolkit on quality infrastructure investment for policymakers and practitioners, based on the G20 Principles for Quality Infrastructure Investment (QII), developed under the Japanese G20 Presidency.
Detailed Explanation
The OECD is working on creating a set of resources (a toolkit) designed to help decision-makers and planners in the field of infrastructure investments. This toolkit will be based on principles set during a G20 meeting in Japan, which emphasizes the importance of quality in infrastructure to maximize its benefits for sustainable development.
Examples & Analogies
Think of this toolkit like a recipe book for baking. Just as a recipe guides you through the ingredients, measurements, and steps needed to bake a perfect cake, the OECD's toolkit will guide policymakers in creating high-quality infrastructure that benefits everyone.
International Cooperation on Infrastructure
Chapter 4 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The UN Environment Assembly (UNEA) Members States in March 2023 adopted a resolution on ‘Sustainable and Resilient Infrastructure’ encouraging them to provide opportunities for engaging relevant stakeholders, promote investment in sustainable and resilient infrastructure, natural infrastructure and nature-based solutions.
Detailed Explanation
In 2023, member states of the UN Environment Assembly agreed on a resolution focused on promoting infrastructure that is both sustainable and resilient. This means they want to create systems for engaging different groups and stakeholders in the planning process and encourage investments in projects that not only have modern infrastructure but also integrate nature and sustainability into their designs.
Examples & Analogies
Consider how a community garden project engages local residents to determine what plants to grow; similarly, this resolution encourages various groups to work together to create infrastructure that meets shared goals while respecting the environment.
Guiding Principles for Sustainable Infrastructure
Chapter 5 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The ‘International Good Practice Principles for Sustainable Infrastructure’ includes principles such as Strategic Planning, Responsive, Resilient, And Flexible Service Provision, and Comprehensive Life Cycle Assessment of Sustainability.
Detailed Explanation
The principles under the International Good Practice for Sustainable Infrastructure provide guidelines on how infrastructure should be planned and implemented. For instance, Strategic Planning refers to the need for careful forecasting and design, while Responsive and Resilient service provision means that infrastructure should adapt to changing circumstances without being overwhelmed. A Comprehensive Life Cycle Assessment evaluates the sustainability of a project from start to finish, ensuring it truly benefits the environment and society.
Examples & Analogies
Think of these principles as a checklist for building a new playground. You want to plan the layout (Strategic Planning), ensure it's safe and fun for children even as their needs change (Responsive and Resilient), and make sure the materials used will last and are eco-friendly (Comprehensive Life Cycle Assessment) before building it.
Key Concepts
-
Sustainable Infrastructure: Designed to support environmental and societal sustainability throughout its lifecycle.
-
Low-Carbon Transition: The process of reducing carbon emissions through renewable energy sources.
-
Quality Infrastructure Investment: Guidelines ensuring that infrastructure investments yield maximum socio-economic benefits.
-
Green Infrastructure: Utilization of natural systems for urban development.
Examples & Applications
The use of green roofs in urban planning to manage stormwater and improve air quality.
BIM is used in construction projects to enhance collaboration and data sharing among stakeholders.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Use green planning as a key plan, for a cleaner world, it’s in our hands.
Stories
Imagine a city where every building has a green roof, where rainwater is captured, and the air is clean. This dream city follows sustainability principles championed by the OECD.
Memory Tools
Remember ‘SCORE’ for sustainable infrastructure: Sustainability, Coordination, Optimization, Resilience, and Engagement.
Acronyms
Use ‘GROW’ to remember the principles
Green initiatives
Resilience
Opportunity for all
and Waste reduction.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Sustainable Infrastructure
Systems planned and operated to ensure economic, environmental, and societal sustainability.
- LowCarbon Transition
The shift towards infrastructure that minimizes carbon emissions, typically by utilizing renewable energy sources.
- OECD
Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development, which promotes policies that improve the economic and social well-being worldwide.
- G20 Principles for Quality Infrastructure Investment
A set of guidelines aimed at maximizing the socio-economic benefits of infrastructure development.
- Green Infrastructure
Infrastructure that uses natural processes and systems to improve environmental outcomes.
- Circular Economy
An economic model that minimizes waste and promotes the continual use of resources.
- Building Information Modeling (BIM)
A digital technology facilitating the design and management of building projects throughout their lifecycle.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
