HBT (Heterojunction Bipolar Transistor)
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to HBTs
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're diving into Heterojunction Bipolar Transistors, or HBTs. They are semiconductor devices that utilize different materials joined together. Can anyone tell me what materials are commonly used for HBTs?

I think they use AlGaAs and GaAs.

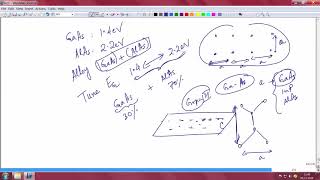
Exactly! AlGaAs/GaAs and InP/InGaAs are prevalent. The use of these materials contributes to a high gain-bandwidth product, which is fundamental to their performance in RF applications.

So, what does 'gain-bandwidth product' mean?

Great question! The gain-bandwidth product indicates how much amplification a device can provide at high frequencies. Think of it as how well a speaker can amplify sound without distortion as the frequency of sound increases.

Okay, that makes sense!

To review, HBTs utilize materials like AlGaAs and GaAs. Their high gain-bandwidth product enables efficient signal processing in devices like optical fiber drivers. Can you recall any specific applications of HBTs?

I remember you mentioned optical fiber drivers!

Correct! HBTs are crucial in optical communications, particularly for high-speed modulation.
Applications of HBTs
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's discuss the applications of HBTs. Where do you think we see them being used in technology today?

Are they used in high-speed internet connections?

Yes, exactly! HBTs play a pivotal role in GHz RF integrated circuits, which are essential for high-speed data transmission. Does anyone know how they function in these circuits?

I believe they help mix different frequencies?

That's right! They function in oscillator and mixer circuits, allowing for frequency modulation and signal amplification effectively. Can any of you name a specific example of where HBTs might be essential in real-world applications?

They might be used in satellite communications?

Correct! HBTs are crucial in satellite communication systems, contributing to reliable signal processing.
Comparative Advantages of HBTs
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

To wrap up, let’s compare HBTs with traditional silicon-based transistors. What do you think gives HBTs an edge?

I guess their ability to handle higher frequencies?

Absolutely! HBTs operate effectively in the GHz range due to their materials. Furthermore, their high gain capabilities outperform that of traditional silicon devices.

So, it’s mainly about high-frequency performance?

Yes, and they also have better efficiency in power handling. Their performance makes them indispensable for modern communication technologies.

Thanks, that really helps clarify how important HBTs are!

Glad to hear that! Remember, HBTs leverage compound semiconductors to achieve performance that silicon cannot match, especially at high frequencies. Any final thoughts?

It’s interesting how materials can change technology so much!

Definitely! Understanding these materials is key in the advances of electronic communications.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Heterojunction Bipolar Transistors (HBTs) are critical components in high-frequency devices, leveraging materials like AlGaAs/GaAs and InP/InGaAs to achieve a high gain-bandwidth product. They play vital roles in applications such as optical fiber drivers and GHz RF integrated circuits (ICs).
Detailed
HBT (Heterojunction Bipolar Transistor)
The Heterojunction Bipolar Transistor (HBT) is integral to high-frequency electronics, notably in RF integrated circuits (ICs) and optical fiber communications. Made from compound semiconductors like AlGaAs/GaAs and InP/InGaAs, HBTs boast a high gain-bandwidth product, which is crucial for maintaining integrity in signal transmission at high frequencies. Their unique configuration allows them to operate effectively in oscillator and mixer circuits used in a diverse array of modern applications, including optical fiber drivers that demand high-speed modulation and GHz RF ICs essential for advanced communication technologies. The discussion of HBTs illustrates the significant improvements that compound semiconductor materials offer over traditional silicon technologies, particularly in high-frequency operations.
Youtube Videos

Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Introduction to HBT
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● HBT (Heterojunction Bipolar Transistor)
● Material: AlGaAs/GaAs, InP/InGaAs
Detailed Explanation
The Heterojunction Bipolar Transistor (HBT) is a type of transistor that combines two different semiconductor materials, which are AlGaAs/GaAs or InP/InGaAs. The use of different materials with varying properties at the junction allows for better performance, especially in high-frequency applications.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a HBT as a sports team where each member has a unique skill. Just as a basketball team may include players specialized in shooting, passing, and defending, a HBT utilizes the strengths of each material to perform more effectively than one single material could do alone.
Features of HBT
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Features:
○ High gain-bandwidth product
○ Used in oscillator and mixer circuits
Detailed Explanation
HBTs are characterized by a high gain-bandwidth product, which means they can amplify signals effectively while maintaining high frequencies. This feature makes them suitable for use in oscillator and mixer circuits, which are crucial in applications that require signal processing, like radio frequencies. The gain-bandwidth product is a measure that indicates how much gain you can have without losing speed.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine you are in a classroom (the oscillator) trying to communicate (amplify) with a friend (the mixer) across the room. If you use a loud voice (high gain), you need to ensure you can still speak quickly (high bandwidth). The HBT does this exceptionally well, enabling clear communication even at high frequencies.
Applications of HBT
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Applications: Optical fiber drivers, GHz RF ICs
Detailed Explanation
HBTs find applications in various high-tech areas, especially in optical fiber drivers and GHz radio frequency integrated circuits (RF ICs). Optical fiber drivers are essential in telecommunications to convert electrical signals into optical signals, allowing for data transmission across fiber optic cables. GHz RF ICs utilize the capabilities of HBTs to operate effectively at gigahertz frequencies, which are vital for modern communication systems.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the HBT as a relay race team where each runner passes the baton quickly. Just as the runners work together to quickly transmit the baton across the finish line, HBTs efficiently convert and transmit signals in technologies like internet communications using optical fibers and advanced radio systems.
Key Concepts
-
HBT: A crucial technology in high-frequency devices, made of materials that enable superior performance over silicon.
-
Gain-Bandwidth Product: An important factor that determines the trade-offs between gain and frequency for transistors.
-
Applications: HBTs are widely used in optical fiber drivers and GHz RF ICs essential for modern communication.
Examples & Applications
HBTs are employed in optical communications to modulate signals for transmission over long distances via fiber optics.
In GHz RF ICs, HBTs facilitate mixing and amplification of signals in advanced communication systems, such as 5G networks.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
For signals bright and clear, an HBT is near, with a gain-bandwidth cheer!
Stories
In a bustling city of circuits, the HBTs worked tirelessly, ensuring signals travel quickly and efficiently, just like delivery bikes racing through red lights.
Memory Tools
Remember 'HBT' as 'High Bandwidth Transmitter' to recall its importance in RF applications.
Acronyms
HBT
High Gain
Better Transmission.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- HBT
Heterojunction Bipolar Transistor; a device using different semiconductor materials to enhance its performance in high-frequency applications.
- GainBandwidth Product
A parameter that reflects the trade-off between the gain and bandwidth of a transistor.
- Optical Fiber Drivers
Devices that modulate optical signals for transmission through optical fibers.
- GHz RF Integrated Circuits
RF circuits designed to operate at gigahertz frequencies, crucial for communication technologies.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
