MESFET (Metal-Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor)
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to MESFETs
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we are diving into the Metal-Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor, or MESFET. Can anyone tell me what a FET is?

Isn’t it a type of transistor that uses an electric field to control the flow of current?

Exactly! FETs control current with an electric field, and MESFETs are specifically designed for high-frequency applications, typically utilizing materials like GaAs and InP.

Why do we need to use GaAs or InP instead of silicon?

Great question! GaAs has higher electron mobility, which means faster signal transmission. This is crucial for applications operating in the GHz to THz range.

What are some applications of MESFETs?

They are widely used in radar systems and as low-noise amplifiers, which are essential for clear signal transmission.

So, they help in communication systems and detection systems, right?

Correct! In summary, MESFETs are vital for achieving high-performance in high-frequency applications like radar and telecommunications.
Materials Used in MESFETs
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s talk about the materials. Why do we choose GaAs and InP for MESFETs?

Because they have high electron mobility?

Exactly! High electron mobility enables faster signal transmission. In addition, these materials have a direct bandgap, making them effective in high-frequency operation.

What does direct bandgap mean?

A direct bandgap allows efficient light emission and absorption, which is beneficial in optoelectronic applications as well.

Can we use silicon then in these applications?

While silicon is great for many applications, it doesn’t compare in terms of high-frequency performance due to lower electron mobility.

So, using GaAs and InP really enhances performance for devices like MESFETs?

Exactly! In summary, using these materials is crucial for the performance enhancement of MESFETs in high-frequency applications.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section discusses the MESFET (Metal-Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor), its operational capabilities up to 30-40 GHz, materials used like GaAs and InP, its features, and key applications in low-noise and driver amplifiers for radar and base stations.
Detailed
MESFET - Detailed Overview
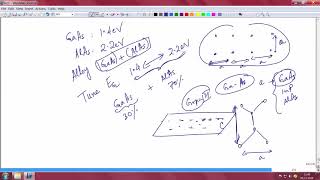
The Metal-Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor (MESFET) is a significant player in high-frequency electronics, particularly in applications demanding operation in the microwave range. MESFETs predominantly utilize compound semiconductors such as Gallium Arsenide (GaAs) and Indium Phosphide (InP), which provide superior material properties essential for high-performance transistors.
Features and Advantages
- Operational Range: MESFETs operate effectively at frequencies of approximately 30-40 GHz.
- Applications: They are extensively used in low-noise amplifiers (LNAs) and driver amplifiers, which are crucial for radar systems and base station communications.
- Advantages of Compound Semiconductors: The choice of materials like GaAs leads to enhanced performance due to higher electron mobility, which translates to faster signal transmission and lower power consumption.
Key Applications
- Radar Systems: MESFETs are integral to modern radar technology, providing the necessary amplification to detect objects at various distances.
- Base Stations: In telecommunications, they serve in base stations, enabling effective communication through various frequency bands.
In summary, the MESFET stands out in high-frequency device applications due to its ability to leverage the exceptional properties of compound semiconductors, making it essential in sectors such as aerospace, defense, and telecommunications.
Youtube Videos

Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Overview of MESFET
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Material: GaAs, InP
● Features:
○ Operates up to ~30–40 GHz
○ Used in low-noise amplifiers (LNAs) and driver amplifiers
Detailed Explanation
The MESFET, or Metal-Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor, is a type of transistor made from materials like Gallium Arsenide (GaAs) and Indium Phosphide (InP). It is designed to operate at high frequencies, specifically up to approximately 30 to 40 gigahertz (GHz). This high frequency makes it suitable for applications that require minimal noise, particularly in low-noise amplifiers (LNAs) which are crucial in communication systems.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the MESFET as a highly skilled librarian in a quiet library. Just like the librarian ensures that no distractions disturb the reading experience, the MESFET minimizes interference and noise in amplifying signals for clear communication.
Applications of MESFET
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Applications: Radar, base stations, satellite transceivers
Detailed Explanation
MESFETs are widely used in various critical applications including radar systems, base stations for mobile communication, and satellite transceivers. Their ability to operate at high frequencies and low noise makes them essential for transmitting and receiving signals in these technologies.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine you are in a crowded room trying to have a conversation. A person with a good microphone can speak clearly and be heard over the noise. Similarly, MESFETs use their technology to ensure that signals in radar and communications are amplified and sent without much disturbance, allowing for effective information transfer.
Key Concepts
-
MESFET: A field effect transistor utilizing metal-semiconductor structures for high-frequency operation.
-
GaAs: A semiconductor material favored for high-frequency applications.
-
InP: An alternative semiconductor material used in MESFETs known for its properties.
Examples & Applications
MESFETs are used in radar signal processing where low-noise amplification is critical.
In communications, MESFETs serve in base stations for reliable data transmission.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In radar, MESFETs play, fast signals are their way!
Stories
Imagine a team of superheroes, each representing GaAs and InP, racing to transmit signals faster than any other material, ensuring our communications stay clear amid interference. That's the speed of MESFETs!
Memory Tools
Remember 'Gainsly' for GaAs, where 'G' stands for Gallium and 'A' for Arsenic, key materials in the efficiency of MESFET.
Acronyms
MEMS = Metal-Electron-Mobility-Super-Fast – which captures the essence of what MESFETs achieve.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- MESFET
Metal-Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor, a device that operates at high frequencies using compound semiconductors.
- GaAs
Gallium Arsenide, a compound semiconductor known for its high electron mobility.
- InP
Indium Phosphide, another compound semiconductor material ideal for high-frequency applications.
- LowNoise Amplifier (LNA)
An amplifier designed to amplify weak signals without adding significant noise.
- Cutoff Frequency
The frequency at which the gain of a device starts to roll off.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
