Summary
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Importance of Data Structures
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're diving into why data structures are so important. Can anyone tell me why we should care about them?

I think they make programs run faster?

Exactly! Efficient algorithms rely on the right data structures. Remember the acronym 'FAST': Fast Access, Storage, and Traversal.

What do you mean by storage?

Great question! Storage refers to how we organize and keep our data. Using the right structure can make retrieval quicker.
Choosing Data Structures
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

You've learned about various data structures. How do we decide which one to use?

Maybe it depends on what we need to do with the data?

Correct! Factors like size, operations needed, and performance all play a role. Think of 'SCOPE' for Size, Complexity, Operations, Performance, and Ease of use.

So, if I have a lot of data, should I always go for a complex structure?

Not necessarily! Sometimes simpler structures work better, depending on your use case.
Applications of Data Structures
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s discuss where we use data structures in real-life applications. Who can give me an example?

I know databases use them for storing information!

Absolutely! Think of how trees and graphs are utilized in databases and networks. Use the mnemonic 'DANGERS' - Databases, AI, Networks, Graphic representation, Efficient Sorting.

What about in AI?

Great point! Graphs, in particular, are essential in modeling connections and pathways.
Key Operations on Data Structures
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's focus on the key operations we commonly perform: insertion, deletion, traversal, searching, and sorting. Who can describe one of these operations?

Insertion is when we add a new item, right?

Yes! It's all about using the right structure to handle these actions efficiently. Remember 'TESS': Traverse, Efficient storage, Search, Sort.

How does maintaining efficiency impact these operations?

Excellent inquiry! Efficient implementations can drastically impact the performance of these operations in large-scale applications.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The summary highlights the foundational role of data structures in algorithmic problem-solving. It emphasizes the importance of selecting appropriate data structures to enhance program efficiency and readability, which is critical for software development, system design, and technical interviews.
Detailed
Summary of Section 1.8
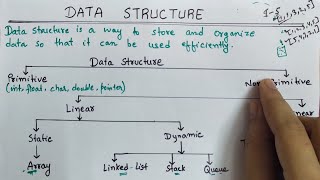
Data structures are pivotal in the domain of algorithmic problem-solving. They provide the essential framework for how data is organized, accessed, and manipulated in computer programs. Choosing the correct data structure not only improves the performance of algorithms but also enhances the readability and maintainability of code. This foundational knowledge of both linear and non-linear data structures is vital for individuals pursuing careers in software development, system design, and for those preparing for technical interviews, as it significantly impacts the ability to design efficient and effective solutions.
Youtube Videos


Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Foundation of Algorithmic Problem-Solving
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Data structures form the foundation of algorithmic problem-solving.
Detailed Explanation
This statement underscores the vital role that data structures play in the field of computer science and programming. It means that without a solid understanding and application of data structures, it is challenging to effectively tackle computational problems. When you're trying to find a solution, recognizing how to structure and manage data is the first step to finding an efficient algorithm.
Examples & Analogies
Think of data structures as the building blocks or tools in a toolkit. Just like a carpenter needs the right tools (like hammers, screws, and saws) to build a strong house, programmers need appropriate data structures (like arrays, lists, and trees) to create efficient algorithms and software.
Organization of Data
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● They define how data is organized, accessed, and modified.
Detailed Explanation
Data structures are essential for specifying how data is stored in memory and how it can be manipulated. For instance, certain structures allow quick access to elements (like arrays), while others provide more complex ways to organize data (like graphs). This organizational aspect directly affects how quickly and effectively a program can retrieve or change information.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a library, where books are organized on shelves. If the books are sorted by genre or author (like a well-structured data organization), it's easier and faster to find a specific book, just as well-structured data structures make it easier for programs to find and modify data.
Efficiency and Readability
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● The correct choice of data structure enhances program efficiency and readability.
Detailed Explanation
This statement highlights the importance of selecting the right data structure for a given problem. A well-chosen data structure can make the code not only faster but also more understandable for others who may read or maintain the code later. For example, choosing a stack for function calls can lead to clearer logic in programs.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine choosing between a backpack (for carrying many books) and a briefcase (for carrying only a few documents). If you select the backpack for a few documents, it might be cumbersome and less organized. Similarly, using the wrong data structure can lead to bloated and unclear code, hindering future work on the project.
Importance of Linear and Non-linear Data Structures
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Fundamental knowledge of linear and non-linear data structures is critical for software development, system design, and technical interviews.
Detailed Explanation
Understanding both linear (like arrays and linked lists) and non-linear (like trees and graphs) data structures is crucial for aspiring software developers and engineers. This knowledge is not only applicable in constructing systems and applications but also vital for problem-solving in technical interviews, where you might be asked to choose or implement specific data structures to solve problems efficiently.
Examples & Analogies
Think of linear and non-linear data structures as two different approaches to organizing a team. In a linear approach, everyone might be in a straight line, where they follow each other directly. In a non-linear approach, they might be grouped in a circle or in clusters based on project needs. Each structure allows for different dynamics in teamwork, just as linear and non-linear data structures offer unique strategies for handling data.
Key Concepts
-
Data Structures: Foundation for organizing and managing data efficiently.
-
Algorithmic Problem-Solving: The role of data structures in enhancing program performance.
-
Linear vs. Non-linear Structures: The difference between how data can be organized.
-
Importance of Selection: Choosing the right data structure affects efficiency and readability.
Examples & Applications
An array is a linear data structure that allows quick access to elements via an index.
A binary tree is a non-linear data structure used for quick searching and data representation in hierarchical relationships.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In data's land of stack and queue, to choose the right one is up to you.
Stories
Imagine organizing a library. The books on the shelf represent linear structures, while the connections between genres showcase non-linear structures.
Memory Tools
For operations, just remember 'TESS' - Traverse, Efficient storage, Search, Sort.
Acronyms
SCOPE
Size
Complexity
Operations
Performance
Ease - consider these factors in choice.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Data Structure
A method of organizing, storing, and managing data that allows for efficient access and modification.
- Algorithm
A step-by-step procedure or formula for solving a problem, often reliant on data structures.
- Linear Data Structure
Data structures that organize data in a sequential manner, such as arrays and linked lists.
- Nonlinear Data Structure
Data structures that organize data in a hierarchical or web-like manner, such as trees and graphs.
- Abstract Data Type (ADT)
A model for data types that focuses on operations rather than implementation details.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
