Regional Planning and Multi-Stakeholder Perspectives
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Methodologies of Assessments
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're going to explore the methodologies used in disaster recovery assessments. Can anyone tell me why we need these assessments?

To understand the risks we face and how to address them!

Exactly! Now, one key methodology focuses on location approaches in land-use planning. Can someone explain what that involves?

It involves identifying areas at risk from hazards, right?

Correct! And what do we do after identifying these areas?

We categorize them into zones for risk management.

That's right! Remember the acronym ZAP for Zoning, Assessing, and Planning. It captures the essence of this step. Finally, what role does strategic planning play in this?

It helps in developing infrastructure for emergencies!

Great job! So, to summarize, we must identify risks, zone areas, and then strategically plan to manage those risks.
Challenges of Implementation
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s discuss some challenges we face in implementing disaster risk assessments. Can anyone name a few?

Economic constraints are a big issue!

Absolutely! Poverty can hinder the implementation of effective strategies. What about education?

Yes! Lack of education can limit understanding of risks and effective responses.

Right! Additionally, cultural compliance is critical. Can someone elaborate on that?

It's about whether local communities accept the regulations and guidelines.

Good point! So everyone, remember the acronym PEC - Poverty, Education, and Compliance, for these key challenges. Summarizing, these socioeconomic factors greatly impact DRR implementation.
The Importance of Multi-Stakeholder Perspectives
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s talk about multi-stakeholder perspectives in disaster planning. Why is it necessary to have multiple stakeholders involved?

They can provide different insights and resources!

Exactly! Collaboration leads to a more comprehensive approach. Can anyone think of a disadvantage of not engaging multiple stakeholders?

We might miss critical perspectives or solutions.

Right! The lack of input from various sectors could lead to ineffective planning. Remember the term CCF - Comprehensive Collaboration Framework. This is crucial for effective disaster management. Summarizing, engaging various stakeholders enriches the planning process.
Regional Planning in Disaster Recovery
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Moving on to regional planning! Why do you think it's necessary in disaster management?

Because disasters don't always follow local boundaries!

Exactly! Disasters affect broader areas than just the local community. Can someone describe an example of this?

A flood affecting multiple towns would need cooperation across regions to effectively plan responses.

Perfect example! Therefore, we need a Regional Approach, which must involve cross-border collaborative planning. In summary, regional planning enhances disaster response on a larger scale.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The section details different assessment methodologies in disaster recovery focusing on global and local perspectives. It highlights challenges in implementing disaster risk reduction (DRR) strategies and underscores the need for comprehensive planning and engagement from various stakeholders to enhance resilience and efficiency in disaster response.
Detailed
Regional Planning and Multi-Stakeholder Perspectives
In this section, the importance of assessments in disaster recovery is explored, particularly through the lens of the Global Assessment Report (GAR) on disaster risk reduction (DRR). The GAR focuses on enabling environments for risk reduction, especially in low and middle-income countries, where vulnerabilities to disasters are significant.
Key Points Covered:
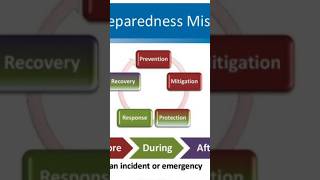
- Methodologies of Assessments: Various assessment methodologies are highlighted, with a focus on their objectives and strategies. Two main approaches in disaster risk reduction are addressed: location and design approaches.
- Location Approach: This approach emphasizes land-use planning, risk identification, and strategic spatial planning that considers vulnerabilities to hazards and integrates preparedness into urban design.
- Design Approach: This concerns building design and regulatory compliance. It highlights the challenges faced in adherence to building codes in developing countries due to socio-economic factors.
- Multi-Stakeholder Engagement: The section stresses the importance of having a multi-faceted perspective in planning for disaster risk reduction, ensuring that different actors contribute to and play roles in enhancing community resilience. Traditional separation of planning and disaster management hinders effective integration.
- Regional Planning Significance: There’s a call for regional planning that transcends local governance boundaries to address the interconnectedness of risks and vulnerabilities in the face of disasters. Effective DRR requires comprehensive analysis and collaboration between civil society, governmental agencies, and the private sector.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Importance of Regional Planning
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The importance of regional level planning, I just said to you now, the Mahabaleshwar case, being a part of the eco-sensitive zone, the approach has to not go only that a city level or a town level or urban level. It has to relate with the larger ecosystem that’s where the regional level understanding has to come. Similarly, in Uttarkashi to Gangotri, where the eco-sensitive zone has been declared.
Detailed Explanation
Regional planning is essential because it considers the bigger picture beyond just city or town boundaries. For instance, if a region is marked as eco-sensitive, such as Mahabaleshwar, planning must account for environmental protection and the ecosystem as a whole. This ensures that developments in one area do not negatively impact other areas, like constructing buildings on a fault line that could trigger landslides or affect water flow in surrounding areas.
Examples & Analogies
Think of regional planning like a family managing a household together. If one person decides to renovate their room without considering how it affects shared spaces like the living room or kitchen, it might create conflicts or chaos in the house. Similarly, decisions made in one area of a region can affect others, so everyone must collaborate and think about the whole ecosystem.
Reducing Disaster Risk in Informal Settlements
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Reducing disaster risk in informal settlements through planning, land management, and upgrading.
Detailed Explanation
Informal settlements often occupy vulnerable locations and lack proper infrastructure, putting their residents at higher risk during disasters. To mitigate this risk, integrated planning and upgrading programs can strengthen their resilience. This involves not only physical improvements, such as better drainage or access roads, but also involving residents in the planning process to ensure their needs and vulnerabilities are addressed.
Examples & Analogies
Think of informal settlements like a makeshift tent village—if it rains, water gathers around these tents, making them prone to flooding and damage. By creating drainage systems and offering more stable structures, the risk can be minimized. Involving the residents in these decisions ensures that the solutions are practical for their day-to-day reality.
Key Concepts
-
Assessment Methodologies: Approaches and their significance in disaster risk reduction.
-
Challenges in Implementation: Socioeconomic factors affecting disaster management.
-
Multi-Stakeholder Engagement: Importance of collaborative planning across different sectors.
-
Regional Planning: Need for broader community integration in disaster recovery planning.
Examples & Applications
The Global Assessment Report as a framework for understanding disaster risk management on a global scale.
Zoning practices that categorize areas based on risk levels, which can guide urban planning.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In disaster zones, we must plan, / With zoning, assessment, and a careful hand.
Stories
Imagine a city preparing for a flood. Town planners gather, mapping out high-risk areas, zoning them for better safety, ensuring the community knows where to shelter. Their combined efforts save lives, highlighting teamwork's power.
Memory Tools
Remember CCF - Comprehensive Collaboration Framework for effective disaster planning!
Acronyms
PEC - Poverty, Education, Compliance
Key challenges in DRR.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Disaster Risk Reduction (DRR)
Strategies aimed at minimizing vulnerabilities and disaster impacts to safeguard communities.
- Land Use Planning
The process of managing land resources to support sustainable development priorities.
- MultiStakeholder Perspective
Involving various stakeholders in decision-making processes to achieve collective goals.
- Strategic Spatial Planning
A method of planning that integrates land use with the community's needs and resources.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
