Introduction to the Course
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
The Importance of Disaster Recovery
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Welcome everyone! Today we discuss the critical importance of disaster recovery in architecture. Can anyone share why you think this is relevant?

I believe it helps us prepare for natural disasters and protects communities.

Exactly, Student_1! Disaster recovery not only safeguards lives but also informs how we design resilient structures. Remember the acronym B.E.S.T. — Build, Engage, Sustain, Transform — which encapsulates this process.

What does 'Engage' mean in this context?

Great question! 'Engage' refers to involving the community in the planning and design processes. Can anyone think of an example where community involvement made a difference?

Laurie Baker's work with local masons is a good example. He involved them in the construction process to make it cost-effective.

Perfect, Student_3! Collaboration enriches the architectural process. To wrap this up, what are the key takeaways about disaster recovery?

It protects communities and involves them in the design process for better outcomes.

Absolutely! Involve, protect, and learn—key steps for us as future architects.
Global Context of Disaster Recovery
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's consider the global context of disaster recovery in architecture education. How do you think various cultural setups influence our understanding of DRR?

Different countries face different types of disasters, so their approaches might vary.

Exactly! And this diversity enriches our lessons. Can anyone think of how climates affect DRR practices?

Tropical climates may need more emphasis on flood resistance, while arctic areas might focus on snow loads.

Right! That's why exposed curricula in places like India or Sweden show different strategies for resilience. Can anyone summarize how this influences our educational strategies?

We should adapt our learning methods based on the specific challenges of each region.

Excellent! Adaptation is key in making sure our education remains relevant and impactful.
The Evolution of Architectural Education
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s talk about how architectural education has evolved. Historically, we focused on monumental architecture. Student_4, can you share why that was the case?

It was about great achievements and the influence of strong architects.

Correct! But now we see the need for integration and community. Why do you think this shift is necessary?

Because buildings are part of a community, and we need to understand their social impact.

Excellent insight! Building a better future is about empowering communities. Let’s not forget the importance of flexibility in our designs as well. What might that look like in practice?

Using local materials and involving local builders can make designs more adaptable.

Absolutely! By integrating local knowledge, we not only respect cultural significance but also ensure longevity in our designs.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section outlines the relevance of incorporating disaster recovery and resilience into built environment education. The author, Prof. Ram Sateesh Pasupuleti, shares insights from his extensive experience across different climates and cultures, elaborating on the educational frameworks and teaching methodologies that effectively integrate these essential concepts into architecture and planning curricula.
Detailed
Introduction to the Course
This lecture from Prof. Ram Sateesh Pasupuleti of the Indian Institute of Technology, Roorkee, introduces the theme of disaster recovery (DRR) and the principle of building back better in built environment education. Drawing from two decades of personal experience, the author highlights how diverse cultural and environmental contexts shape the teaching of DRR to architecture and planning students.
The core discussion begins with the historical context of architecture and planning education, traditionally focused on monumental examples of architecture, often taught in isolated segments like design, construction, and historical significance. Prof. Pasupuleti emphasizes the need for integrating these components holistically to better understand architectural practice today.
The section argues for a transition from a singular educational vision to a shared one, recognizing the importance of involving stakeholders in the design and planning processes. This shift is crucial in addressing issues related to climate, culture, and socio-economic disparities, particularly as societies face increasing challenges influenced by globalization, poverty, and conflict.
Reinforcing the significance of community engagement, the lecture cites examples of modern architects like Laurie Baker, illustrating how education that promotes collaboration with local populations enhances the learning process. Overall, the introduction sets the stage for a course focused on training professionals who can navigate the complexities of disaster risk reduction in the built environment.
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Welcome and Introduction
Chapter 1 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Welcome to the course; disaster recovery and build back better, my name is Ram Sateesh, I am an Assistant Professor in Department of Architecture and Planning IIT, Roorkee.
Detailed Explanation
In this introductory statement, Professor Ram Sateesh welcomes the students to the course on disaster recovery and building back better. He introduces himself, highlighting his role as an Assistant Professor in the Department of Architecture and Planning at IIT Roorkee. This sets the tone for the course, establishing who the students will be learning from and the focus of the course.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine entering a new class for the first time. The teacher introduces themselves and shares their background, creating an atmosphere that makes you feel welcome and excited about the journey ahead. This introduction acts similarly, laying the foundation for a new learning experience.
Purpose of the Course
Chapter 2 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Today, we are going to discuss about how to teach disaster recovery and build back better in built environment education.
Detailed Explanation
The professor outlines that the main focus of this lecture will be on strategies for teaching disaster recovery (DRR) and the concept of building back better in the context of education related to the built environment. This indicates that the course will combine theoretical concepts with practical teaching methods suited for architecture and planning students.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a cooking class where the instructor's goal is not just to teach recipes but to explain the techniques behind them. In the same way, this course aims to provide deeper insights into teaching DRR, equipping future architects and planners with essential skills.
Experiences in Disaster Recovery Education
Chapter 3 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
This lecture is being prepared based on my own experiences for about 2 decades how I have been involved both as a student and as a faculty in different cultural and environmental setups.
Detailed Explanation
Here, the professor shares that the course content is informed by two decades of personal experience in disaster recovery and education, emphasizing the importance of real-world experiences in academic settings. His diverse background spans various cultural and environmental contexts, which will enrich the learning experience for students.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a seasoned traveler who shares stories from their journeys across different countries. Their firsthand experiences provide valuable lessons and insights that can only come from having lived through various scenarios, much like the professor's valuable experiences in disaster recovery.
Integration of Disaster Recovery in Education
Chapter 4 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
So, how disaster has been integrated in the curriculum, in the education and the methods which were adopted and in fact, some of the courses which were actually executed by me and where I keep testing different methods of how to teach the disaster risk reduction and build back better for the built environment professionals...
Detailed Explanation
The professor intends to detail how disaster recovery is woven into academic curricula, touching upon the teaching methodologies he has developed and utilized in various courses he has executed. This section suggests a practical approach to learning, where students not only understand disaster theory but also observe and practice teaching methods based on real-life examples.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a sports coach who not only talks about strategies and techniques but also demonstrates them during practice sessions. Similarly, the professor plans to showcase methods for teaching disaster recovery through examples from his own curriculum.
Acknowledgment of Diverse Climatic Contexts
Chapter 5 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
This has given me a good exposure of working in temperate climates and the tropical climates, Mediterranean climates and the arctic climates so, I keep testing various tools and methods in teaching this DRR...
Detailed Explanation
The professor reflects on his experience working in diverse climatic settings, which allows him to test various teaching tools and methods effectively. This exposure is significant because the understanding of disaster recovery can vary widely depending on regional climates and their specific challenges.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a chef who specializes in cooking for different cuisines—they must adapt their techniques based on local ingredients and flavors. Similarly, the professor tailors his teaching based on the unique challenges faced in different climates.
The Importance of Historical Context in Architecture Education
Chapter 6 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
When we start about architecture or planning or urban design any of these studies which are related to the built environment orientation, in the past, we mostly have talked about the monumentality of the architecture...
Detailed Explanation
The professor emphasizes the historical approach to architectural education, noting that traditional studies often focused on monumental architecture and landmark structures. Recognizing this can help students see the broader implications of architecture beyond just structures, including societal and cultural contexts.
Examples & Analogies
Think of how history classes often focus on important events or figures. Just as this approach builds understanding of a nation's journey, acknowledging monumental architecture helps students appreciate how historical contexts shape current practices in architecture.
Key Concepts
-
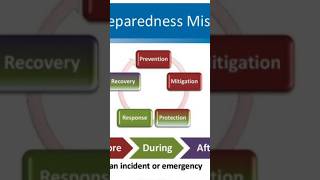
Disaster Recovery (DRR): A proactive approach to minimizing disaster impacts.
-
Build Back Better (BBB): Reconstructing with resilience in mind.
-
Community Engagement: Involving local people in the design and planning processes.
Examples & Applications
Laurie Baker’s approach to using local materials and techniques in architecture, emphasizing community involvement.
Urban planning in post-independent India, incorporating Western philosophies into local contexts for inclusive development.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Build it strong, build it right, For disaster's coming to take flight.
Stories
Imagine a village recovering from a flood, with builders and locals working together, transforming rubble into homes that withstand future storms.
Memory Tools
R.E.S.T. - Resilience, Engagement, Sustainability, Transformation — the keys to disaster recovery.
Acronyms
D.R.E.A.M. - Disaster Recovery, Resilience Enhancement, Architectural Methodologies.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Disaster Recovery (DRR)
The process of planning, preparing for, and recovering from disasters to minimize their impacts.
- Build Back Better (BBB)
A strategy to rebuild infrastructure and communities in a way that is more resilient to future disasters.
- Stakeholder
An individual or group that has an interest or investment in a project and its outcomes.
- Resilience
The ability to recover from or adjust easily to misfortune or change.
- Community Engagement
The process of involving the community in decision-making and planning activities.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
