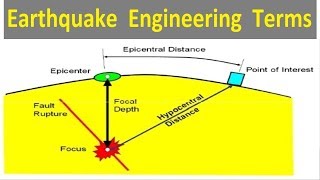
Depth of Focus
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Classification Based on Focal Depth
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today we're discussing the depth of focus for earthquakes, which significantly influences their destructiveness. Can anyone tell me what distinguishes shallow focus, intermediate focus, and deep focus earthquakes?

I think shallow focus earthquakes are the ones that happen very close to the Earth's surface, right?

Exactly! Shallow focus earthquakes occur at depths of less than 70 kilometers. They're usually the most destructive. Can you remember why they're more destructive?

Is it because they release energy closer to the surface?

Correct! Now, how about intermediate focus earthquakes? What depth range do they fall into?

They’re between 70 and 300 kilometers?

Right! And what about deep focus earthquakes?

Those are deeper than 300 kilometers, but they don't shake the surface as much, right?

Exactly, they disperse their energy and thus cause less surface shaking. Great job, everyone!
Impact of Depth on Seismic Activity
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's delve into how the depth impacts the intensity of an earthquake's shaking. Student_1, why do you think shallow focus earthquakes are generally more damaging?

Because they’re closer to us when they happen?

Exactly! The closer an earthquake is to the surface, the more severe the shaking experienced. Can someone explain what happens during an intermediate focus earthquake?

They can still shake a good amount, but not as much as shallow focus quakes?

Right. They cause noticeable shaking but are less destructive due to their depth. Now, how do deep focus earthquakes impact our world?

They don’t really affect us much on the surface, but they can tell us about activity deeper in the Earth?

Very insightful! They provide valuable information about the Earth’s interior but can be difficult to predict impact.
Practical Implications of Depth in Earthquake Engineering
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now that we understand depth, how do you think this knowledge affects civil engineering? Student_4, can you give a thought on this?

I guess engineers would design buildings differently depending on whether they’re in an area with shallow focus earthquakes?

Exactly! Structures in shallower areas would need to withstand more intense shaking. What could be a challenge with deeper earthquakes?

They might still affect structures because of their energy dispersal, right?

Good point! Engineers must consider potential risks even from deep focus earthquakes. How can this alter the way we build?

Maybe using materials that absorb more shock or designing flexible buildings?

Exactly! Flexibility and shock-absorbent materials are critical in earthquake-resistant design. Well done!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Earthquakes can be classified based on their focal depth, specifically into shallow, intermediate, and deep focus. Shallow focus earthquakes (<70 km) are typically more destructive, while deeper earthquakes result in less surface shaking due to energy dispersion. Understanding these classifications helps in assessing earthquake risk and engineering responses.
Detailed
Depth of Focus
Depth of focus plays a critical role in determining the impact and characteristics of earthquakes. This section classifies earthquakes based on their focal depth into three categories:
- Shallow Focus: Occurring at depths less than 70 km, shallow focus earthquakes are the most destructive and are often linked to tectonic boundaries, notably subduction zones and transform faults.
- Intermediate Focus: Ranging from 70 to 300 km, these earthquakes may still cause noticeable shaking but are generally less destructive than shallow focus earthquakes.
- Deep Focus: These earthquakes, occurring at depths greater than 300 km, are characterized by less intense surface shaking due to the dispersion of energy over a larger area.
Each category has distinct mechanisms and consequences, contributing to the assessment of seismic risk and enhancing infrastructure resilience.
Youtube Videos





Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Classification Based on Focal Depth
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Shallow Focus: < 70 km depth; most destructive.
Intermediate Focus: 70–300 km depth.
Deep Focus: > 300 km; less surface shaking due to energy dispersion.
Detailed Explanation
In this section, we categorize earthquakes based on their focal depth, which is the distance from the Earth's surface to the point where the earthquake begins. There are three main classifications:
- Shallow Focus: These earthquakes occur at depths of less than 70 kilometers. They are the most destructive because they are closer to the surface, allowing the released energy to cause significant shaking and damage.
- Intermediate Focus: Earthquakes in this category occur between 70 to 300 kilometers deep. They can still cause damage, but the effects are usually less severe than shallow focus earthquakes because the energy has to travel further to reach the surface.
- Deep Focus: These earthquakes occur at depths greater than 300 kilometers. They generally cause less surface shaking due to the energy being dispersed over a larger area as it travels to the surface. Even though they release a lot of energy, their depth means they are less likely to cause immediate damage.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a trampoline. If you jump close to the edge (shallow focus), the movement of the trampoline affects the surface a lot more than if you were to jump from the center (deep focus). We see this in earthquakes: the closer they are to the surface, the more movement and shaking we feel.
Origin of Shallow Earthquakes
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Shallow earthquakes are typically associated with subduction zones and transform faults.
Detailed Explanation
Shallow earthquakes often occur in specific geological settings. They are closely linked to:
- Subduction Zones: These are areas where one tectonic plate is being forced beneath another. The intense pressure and friction at these boundaries can lead to powerful shallow earthquakes.
- Transform Faults: These faults occur where two plates slide past each other. The stress caused by friction can also result in shallow earthquakes when the built-up tension is finally released.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine two cars on a road trying to pass each other but getting stuck due to friction. Eventually, one car might get a little push (like an earthquake) and move ahead. The friction at the edges (subduction zones and transform faults) creates the conditions for these 'pushes' (earthquakes) to happen.
Key Concepts
-
Shallow Focus: Causes severe damage and occurs < 70 km depth.
-
Intermediate Focus: Occurs between 70-300 km, less destructive.
-
Deep Focus: Greater than 300 km, minimal surface shaking.
Examples & Applications
The 2011 Tōhoku earthquake was a shallow focus earthquake that caused devastating effects in Japan.
Deep focus earthquakes like the 1970 Kola Peninsula quake usually do not cause much surface damage.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Shallow shakes cause the most fright, deep ones sleep out of sight.
Stories
Once in a town, the shallow quake brought panic; the deep one just made the ground a little frantic. The shallow was loud, while the deep was faint, each with a lesson, or so I'd feint.
Memory Tools
Remember 'Shallow shakes', 'Intermediate feels', and 'Deep silently heals' to distinguish between the depths.
Acronyms
S.I.D. - Shallow, Intermediate, Deep - a reminder of the earthquake depth classification system.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Shallow Focus
Earthquakes occurring at depths less than 70 km, typically causing the most destruction.
- Intermediate Focus
Earthquakes occurring between 70 - 300 km depth, causing noticeable shakes but generally less damage.
- Deep Focus
Earthquakes occurring at depths greater than 300 km, resulting in less intense surface shaking.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
