Tectonic Forces and Crustal Deformation
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Tectonic Plates
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we are going to explore tectonic forces and crustal deformation. Can anyone tell me what tectonic plates are?

I think they are large pieces of the Earth's crust that float on the mantle.

Exactly! These tectonic plates float on the semi-fluid asthenosphere. They can move in various directions and interact at their boundaries—can anyone name the three types of plate boundaries?

Convergent, divergent, and transform boundaries!

Great job! Can you summarize what happens at each type?

At convergent boundaries, plates push together; divergent boundaries pull apart; and transform boundaries slide past each other!

Perfect! Remember the acronym 'C-D-T' for Convergent, Divergent, and Transform to help you recall them. Let's move to stress accumulation next.
Types of Plate Boundaries
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now that we know about plate boundaries, let's dive deeper. Can anyone explain what happens at convergent boundaries?

Yes! At convergent boundaries, plates collide, leading to compression and often creating mountains or causing earthquakes.

Exactly! And what about divergent boundaries?

At divergent boundaries, the plates move apart and it leads to the formation of new crust, like mid-ocean ridges!

Amazing! Now think about transform boundaries. Can someone describe the stress involved?

They slide past each other, causing shear stress, which can lead to earthquakes as well!

Right! Remember, the acronym 'C-D-T' not only helps with types but also with their actions—compress, diverge, slide! Now, let’s talk about stress accumulation at these boundaries.
Stress Accumulation
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

We've discussed boundaries; now, let’s focus on stress accumulation. What prevents movement at these boundaries?

Friction prevents continuous movement!

Correct! So, what happens when strain energy builds up in rocks?

The rocks deform elastically until the stress surpasses their yield strength, which can cause a rupture.

Exactly! This release of energy results in seismic events. Can anyone tell me why this is significant for understanding earthquakes?

It helps predict seismic activity and assess earthquakes' potential impact!

Yes! Understanding this cycle of stress and rupture is essential for earthquake preparedness.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The section explores how the Earth's lithosphere consists of tectonic plates that interact at convergent, divergent, and transform boundaries. These interactions lead to stress accumulation, which deforms the crust and can result in significant geological events.
Detailed
Tectonic Forces and Crustal Deformation
The Earth's lithosphere is comprised of tectonic plates, which float on the semi-fluid asthenosphere beneath them. These plates are in constant motion and interact at their boundaries, classified into three primary types:
- Convergent Boundaries - Where plates move towards each other, leading to compression.
- Divergent Boundaries - Where plates move apart, resulting in tension.
- Transform Boundaries - Where plates slide past one another, inducing shear stress.
At these boundaries, continuous movement is inhibited by friction, which leads to the accumulation of strain energy in the rock masses. As this energy builds up, the rock deforms elastically until its yield strength is exceeded, leading to sudden rupture and the release of energy, producing seismic events. This foundational understanding of tectonic forces is crucial for recognizing the mechanics behind earthquakes and crustal deformation.
Youtube Videos


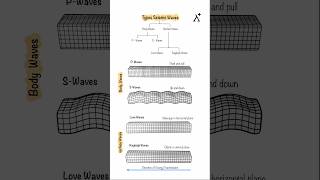






Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Overview of the Earth's Lithosphere
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The Earth's lithosphere is divided into several tectonic plates that float over the semi-fluid asthenosphere.
Detailed Explanation
The lithosphere is the rigid outer layer of the Earth, consisting of the crust and the upper mantle. It is divided into tectonic plates, which are large pieces that move over a softer layer called the asthenosphere. This movement is crucial for the Earth's geological processes.
Examples & Analogies
Think of tectonic plates like icebergs floating on the ocean. Just as icebergs drift and collide with each other, causing changes in the water, tectonic plates move and interact, leading to geological events like earthquakes and volcanic activity.
Interaction of Tectonic Plates
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
These plates constantly interact at their boundaries—converging, diverging, or sliding past each other—causing stress accumulation within the crust.
Detailed Explanation
At the boundaries of tectonic plates, various interactions occur. Plates can push against each other (converging), pull apart (diverging), or slide against one another (transform). These interactions create stress within the Earth's crust, much like how stretching a rubber band produces tension.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a group of friends playing tug-of-war. When one side pulls hard, the rope (representing the Earth's crust) becomes tense. If the tension is released suddenly, it can snap or jerk. This is similar to how stress builds up at plate boundaries and can lead to earthquakes.
Types of Tectonic Plate Boundaries
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Convergent Boundaries: Plates move towards each other causing compression.
• Divergent Boundaries: Plates move apart, leading to tension.
• Transform Boundaries: Plates slide past each other, inducing shear stress.
Detailed Explanation
There are three main types of tectonic plate boundaries:
1. Convergent Boundaries: Where plates push against each other, causing compression. This can lead to mountain formation or subduction zones, where one plate moves under another.
2. Divergent Boundaries: Where plates move apart, creating tension and often resulting in mid-ocean ridges.
3. Transform Boundaries: Where plates slide past each other, this lateral movement causes shear stress, which can lead to earthquakes.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a crowded subway train. At a convergent boundary (like two people pushing toward each other), the resulting compression can create discomfort. At a divergent boundary (like when people move away from each other), space opens up. At transform boundaries, imagine people sliding past each other in an aisle, occasionally bumping into one another, which can represent the friction and stress that lead to earthquakes.
Stress and Strain in the Earth's Crust
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
At these plate boundaries, friction prevents continuous movement. As a result, strain energy builds up over time in the rock masses. The rock deforms, storing elastic energy, until the stress exceeds the rock's yield strength.
Detailed Explanation
As tectonic plates engage at their boundaries, friction keeps them from moving continuously. Over time, this causes energy to accumulate, deforming the rocks in the crust. When enough stress builds up and exceeds the strength of the rock, it leads to a sudden shift, or faulting, releasing that stored energy.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a spring being compressed. As you push it, it stores potential energy. Once you push too hard, it snaps back to its original shape, releasing the energy all at once. In the Earth, similarly, accumulated strain can lead to an earthquake when the rocks finally shift.
Key Concepts
-
Tectonic Movement: The movement of large sections of the Earth's surface impacts seismic activity.
-
Boundary Types: Convergent, Divergent, and Transform boundaries each handle stress differently.
-
Stress Accumulation: The friction at boundaries prevents movement and leads to energy build-up.
Examples & Applications
The Himalayas formed at convergent boundaries where two plates collide and create mountain ranges.
Mid-ocean ridges are created at divergent boundaries, where new oceanic crust is formed.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
When plates converge they push and shove, Mountain peaks grow with earth’s love!
Stories
Imagine two friends meeting for a hug. They lean into each other (converging), but when they step back (diverging), they create space again—like tectonic plates at a divergent boundary!
Memory Tools
C-D-T: Converging to hug, Diverging to part, Transforming to slide, that’s how they start!
Acronyms
Remember C-D-T for Convergent, Divergent, and Transform boundaries.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Tectonic Plates
Large pieces of the Earth's lithosphere that move and interact at their boundaries.
- Convergent Boundaries
Plate boundaries where two plates move towards each other, causing compression.
- Divergent Boundaries
Plate boundaries where two plates move apart, leading to tension.
- Transform Boundaries
Plate boundaries where two plates slide past each other, inducing shear stress.
- Stress Accumulation
The build-up of strain energy in rock masses due to tectonic forces and friction.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
