Environmental Quality: Monitoring and Analysis
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Vapor Phase Analysis
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today's focus is on vapor phase analysis in environmental quality monitoring. Who can remind us why we need to separate vapor from particulate matter?

To measure the concentration of specific vapors without interference from particulate matter.

Exactly! We utilize filters to achieve this separation. Can anyone describe what a filter does in this context?

A filter captures particles while allowing vapor to pass through.

Great! This sets the stage for our sampling methods. One of the simplest methods is grab sampling. Can anyone tell me what it involves?

It's where you take a direct sample of the vapor at a single point in time.

Correct! Just like grabbing a scoop of water. We need to ensure high concentrations for grab sampling to be effective.

What if the concentration is low?

Good question! We would use an accumulation method instead. Let's summarize: Vapor phase analysis is essential for accurate environmental monitoring, and we use techniques like grab sampling when concentrations are high.
Grab Sampling vs. Accumulation Method
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's dive deeper. What's one advantage of grab sampling?

It's quick and doesn’t require processing if the concentration is high enough.

Exactly! And what circumstances would make grab sampling less effective?

When the concentration levels are low or if the vapor is dispersed.

Right! Can anyone think of locations where grab sampling is ideal?

Close to emission sources, like chimneys or exhausts of cars.

Correct! Now let's contrast this with the accumulation method. What does it involve?

We let an absorbent collect vapor samples over time to increase the volume available for analysis.

Very well! Let's summarize this session: Grab sampling is ideal for high concentrations, while accumulation methods work for lower concentrations, emphasizing the importance of choosing the right technique.
Assuring Sample Integrity
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

As we collect vapor samples, what’s an important factor to keep in mind regarding sample integrity?

Preventing loss of volatile compounds during collection and analysis.

Excellent! Can anyone suggest methods to maintain this integrity during the sampling process?

Using suitable absorbents that are stable and minimizing exposure to the atmosphere.

Exactly! Loss of compounds can significantly distort readings. What do you think is a common problem we face with volatile organic compounds during extraction?

They may evaporate or degrade quickly.

Absolutely! Vigilant handling and choice of materials are crucial to avoid sample loss. Let’s recap: Maintaining integrity when analyzing vapors, particularly volatile compounds, is vital for accurate results.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The section discusses the importance of vapor phase analysis in the context of environmental quality, elaborating on sampling methods like grab sampling and the use of different containers. It also examines the challenges posed by varying concentration levels and the necessary adjustments in analytical techniques.
Detailed
Environmental Quality: Monitoring and Analysis
In this section, we focus on the methods used for vapor phase analysis in environmental monitoring, particularly the need to differentiate between particulate matter (PM) and vapor. The initial consideration involves the use of filters to separate particles from vapor in air samples. The process commences with preparing a filter that helps to collect necessary vapor samples. Key techniques include:
- Grab Sampling: This method allows for direct sampling of high-concentration vapor phases, particularly near emission sources like industrial stacks or automobile exhausts. Using a specific gas volume, it’s possible to take a sample and analyze it without further processing. However, grab sampling is limited when concentrations are low or dispersed in the ambient environment, risking inaccurate inferences.
-
Accumulation Method: When the concentration of contaminants is low, an absorbent is used to collect vapor over extended periods, thereby increasing the samples’ mass for analysis. The collected absorbent is then analyzed to extract specific organic compounds. Considerations during this process include possible losses of volatile components during extraction, emphasizing the importance of choosing appropriate absorbents and methods.
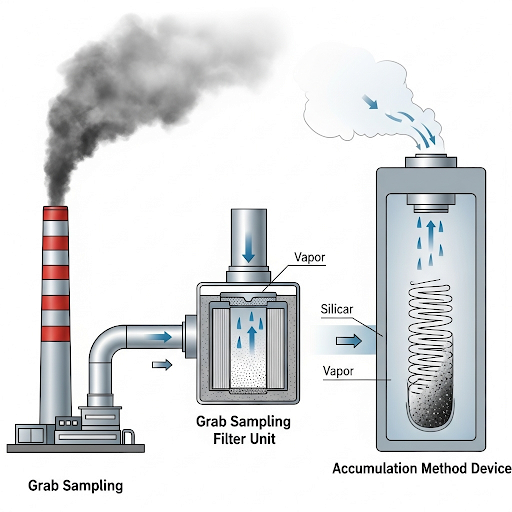
Overall, the section outlines both fundamental and advanced techniques for vapor phase analysis and the constraints that researchers face in accurately capturing and quantifying environmental pollutants.
Youtube Videos










Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Introduction to Vapor Phase Analysis
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
This is for PM. What about vapor? So there is a bunch of things we talked about for sampling of PM using impactors and all that. How do we do vapor phase analysis? Vapor phase, but in the atmosphere we have everything vapor phase and PM, we only want vapor phase, the first thing we need to do is cut off the particles. So, you need a filter so, vapor phase at the downside of the filter paper usually. And so, we use an air stream we have a pre filter here we take out all the particulate matter here and then we use an absorbent.
Detailed Explanation
In this chunk, we learn about vapor phase analysis, which is the process of studying gases in the atmosphere while excluding particulate matter (PM). Vapor refers to substances in their gaseous state, while PM consists of tiny solid or liquid particles suspended in the air. To conduct vapor phase analysis effectively, it is essential to filter out these particles. This is done using a filter paper along with a pre-filter to capture the particulate matter. Following this step, an absorbent material is used to collect the vapor phase for analysis.
Examples & Analogies
Think of this process like trying to see a clear view of the sky through a dirty window. The dirt on the window represents particulate matter that obstructs our view of the clear sky (vapor phase). Just as we would clean the window to get a better view, we must filter out the particulate matter from the air to analyze the gases present.
Using Containers for Sampling
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
One possible container for a grab sample? Need a container wait what containers will you use. You can use a cylinder for all gas storage everything we use a cylinder so we use a small cylinder, a small cylinder which has a valve.
Detailed Explanation
When performing grab sampling, a cylindrical container with a valve is often used to hold the air sample. These containers can be evacuated (air removed) to create a vacuum, ensuring that the air sample remains uncontaminated. After air fills the container by opening the valve and equilibrating, the valve is closed to secure the sample. This method allows for safe transport and subsequent analysis of the vapor.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a balloon that you fill with air; once you tie the balloon, the air inside it is securely contained. Similarly, using a cylinder with a valve allows you to trap the air sample like sealing the balloon, ensuring no outside air enters and contaminates your sample.
Key Concepts
-
Vapor Phase Analysis: The assessment of gaseous compounds in the air for monitoring environmental quality.
-
Grab Sampling: A straightforward sampling technique for analyzing high-concentration vapors.
-
Accumulation Method: A technique for collecting air samples over time to analyze low-concentration vapors.
-
Absorption: The mechanism by which absorbents capture vapors for analysis.
Examples & Applications
Grab sampling can be conducted near industrial smokestacks to measure pollutant concentrations directly.
The accumulation method might be used to collect data on VOCs in an urban area over several hours.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In the air, vapors hide, near the source they'll abide. Grab a sample if it’s strong, or let it flow all day long.
Stories
Imagine a scientist standing next to a factory smokestack. They're equipped with a grab sampler that they quickly use to capture the strong emissions before they dissipate into the air. This direct action represents the essence of grab sampling.
Memory Tools
GAS - Grab (for high), Accumulate (for low), Study (analyse).
Acronyms
VAPOR - Volatile Analysis using Proper Optimized Resources.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Vapor Phase Analysis
The study of gaseous phases in the environment for the purpose of monitoring and assessing air quality.
- Grab Sampling
A sampling method where a single sample of air is taken for immediate analysis.
- Accumulation Method
A long-term sampling method that collects air samples over time using an absorbent.
- Absorbent
A material used to capture and hold gaseous compounds from air samples for analysis.
- Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs)
Organic chemicals that have a significant vapor pressure and can readily evaporate into the atmosphere.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
