Biogeographic regions of India
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Diversity in India
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we'll explore the incredible biodiversity of India, which is home to over 75,000 animal species and 45,000 plant species. Can anyone tell me why biodiversity is important?

Biodiversity is crucial because it helps maintain ecosystem balance and provides us with food, medicine, and clean air.

Exactly! Biodiversity supports ecosystems that are vital for our survival. Now, let's discuss the 10 distinct biogeographic regions of India. Can anyone name a few?

The Himalayan Zone and the Western Ghats!

Great! The Himalayan Zone features diverse climatic conditions that support various species, while the Western Ghats is known for its high rate of endemism, meaning many species are unique to that area.

What does endemic mean?

Endemic species are those found only in a specific geographic area. For instance, the Western Ghats hosts about 40% of India's total endemic plant species. Let's remember this with the acronym 'E for Endemic, Exclusive!'

That sounds helpful!

Fantastic! Remembering these key terms can really help in understanding our biodiversity. In summary, India's various biogeographic regions are essential to its identity.
Biogeographic Zones of India
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's dive into the specific biogeographic zones of India. Who remembers how many there are?

Ten distinct zones!

Correct! Each zone possesses unique characteristics and species. For instance, what can you tell me about the Desert Zone?

It's very dry and has adapted species like cacti and certain lizards.

Exactly! The Desert Zone is home to species that can withstand extreme conditions. And what about the NE Indian Zone?

It has a lot of varied ecosystems and many endemic species.

Spot on! The Northeastern region is a treasure trove of biodiversity. Remember, 'NE for Northeast, Nature's Enclave!' helps you recall its richness.

That's a great way to remember!

Let’s summarize: each region is vital for the unique biodiversity it harbors, which is essential for ecological balance.
Importance of Conservation
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now that we understand these biogeographic zones, why is conservation crucial?

To protect endangered species and maintain balanced ecosystems!

Yes! Conservation efforts are vital to prevent species extinction driven by habitat loss and climate change. What do we call areas rich in endemic species that require urgent protection?

Biodiversity hot spots!

Correct! For India, the Western Ghats and Eastern Himalayas are prime biodiversity hot spots. We can remember this as 'Hot Spots: Important for the Planet!'

What happens if we lose these species?

Losing species leads to weakened ecosystems and diminished resources for humans, which is why protecting biodiversity is essential. Let's keep that in mind! Conservation is key for our future.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
India's unique geographical and climatic conditions create diverse ecosystems, resulting in over 75000 animal species and 45000 plant species. The country is divided into 10 biogeographic zones, each showcasing a wealth of biodiversity and endemic species, especially in regions like the Himalayas and Western Ghats.
Detailed
Detailed Summary
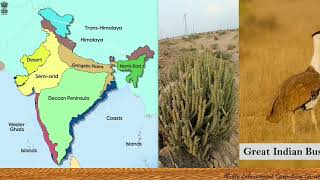
India, as a mega-diversity nation, is characterized by its diverse ecosystems and rich biological wealth. It houses approximately 75,000 species of animals and 45,000 species of plants, attributed to its varied geographical features which include mountains, forests, wetlands, and coastal areas. The Wildlife Institute of India classifies India into 10 biogeographical regions:
- Trans-Himalayan Zone: Arid and cold with unique flora.
- Himalayan Zone: Diverse ecosystem with different climatic conditions from north to south.
- Desert Zone: Characterized by limited flora and fauna adapted to extreme conditions.
- Semi-arid Zone: Transitional area with a mix of desert and agricultural land species.
- Western Ghats: One of the biodiversity hotspots with high endemism.
- Deccan Zone: Comprises the Deccan Plateau with distinct vegetation.
- Gangetic Plain Zone: Fertile area with significant agricultural biodiversity.
- NE Indian Zone: Rich in endemic species and varied ecosystems.
- Coastal Zone: Habitat for marine diversity.
- Islands: Unique ecosystems with high levels of endemism.
The Eastern Himalayas and Western Ghats are recognized as biodiversity hotspots due to their high species richness and endemism—about 62% of amphibians and 50% of lizards in India are endemic to these regions. Conservation of these biogeographical regions is essential for preserving India's ecological heritage.
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Biogeographic Zones of India
Chapter 1 of 1
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
According to the Wildlife Institute of India, the country has 10 distinct biogeographic zones or regions. They are:
- Trans-Himalayan Zone
- Himalayan Zone
- Desert Zone
- Semi-arid Zone
- Western Ghats
- Deccan Zone
- Gangetic Plain Zone
- NE Indian Zone
- Coastal Zone
- Islands around the country
Detailed Explanation
The Wildlife Institute of India outlines 10 distinct biogeographic zones, each representing unique ecosystems and diverse flora and fauna. These zones are:
- Trans-Himalayan Zone: Located beyond the main Himalayan range, it has unique species adapted to extreme conditions.
- Himalayan Zone: Rich in biodiversity, this area includes various climatic zones, leading to a wide variety of plants and animals.
- Desert Zone: Characterized by arid conditions, it supports specialized life forms that can survive with minimal moisture.
- Semi-arid Zone: This zone experiences more rainfall than deserts but is still quite dry, supporting different vegetation.
- Western Ghats: A significant area known for high endemism, home to numerous plant and animal species not found elsewhere.
- Deccan Zone: An area characterized by its plateau and various ecosystems, supporting several endemic species.
- Gangetic Plain Zone: Fertile and populated, this region has unique wetlands and agricultural biodiversity.
- NE Indian Zone: Rich in biodiversity due to its unique climate and geography, it is home to numerous endemic species.
- Coastal Zone: This area has diverse ecosystems, including mangroves and coral reefs.
- Islands around the country: Unique biodiversity due to their isolated nature and specific habitats.
Examples & Analogies
Think of India like a giant cake, where each slice represents a different biogeographic zone. Just like how each slice might have different flavors and textures, each zone has its unique environments and species that thrive there. For example, the Western Ghats are like the rich chocolate layer of the cake, full of unique and special ingredients (species) that can’t be found anywhere else. Each zone supports a different set of life forms, just like how different ingredients in cake contribute to its overall flavor.
Key Concepts
-
Biodiversity: The richness of living organisms in an ecosystem or geographic area.
-
Biogeographic Regions: Specific geographic areas defined by unique environmental conditions and species composition.
-
Endemic Species: Species uniquely found in a certain geographic area, showcasing the area's biodiversity.
-
Biodiversity Hot Spots: Regions critical for conservation due to high levels of species richness and endemism.
Examples & Applications
The Western Ghats hosts around 40% of India's total endemic plant species, highlighting the zone's significant biodiversity.
The Eastern Himalayas are crucial for many unique species, making them a biodiversity hot spot due to their rich flora and fauna.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In India's zones where nature hides, flora, fauna, endemism abides.
Stories
Imagine an explorer discovering the Western Ghats, where every turn brings a new endemic species, revealing nature's secrets.
Memory Tools
Remember E for Endemic, Exclusive to a zone!
Acronyms
BifE - Biodiversity in Forests and Ecosystems!
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Biodiversity
The variety of life in a particular habitat or ecosystem.
- Biogeographic Regions
Distinct geographical areas that support different species and ecosystems.
- Endemic Species
Species that are unique to a specific geographic area.
- Habitat Loss
The reduction or destruction of habitats, affecting the species that live there.
- Biodiversity Hot Spots
Regions with high levels of endemic species and significant habitat loss.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
