Types of mining
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Mining
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today we will discuss mining. Can anyone tell me what mining is?

Isn't it just digging in the ground for minerals?

Exactly! Mining is the process of extracting valuable minerals from the Earth. The two main types are surface mining and underground mining. Can anyone guess what the difference might be?

Surface mining sounds like it’s closer to the surface, while underground mining goes deeper in, right?

Correct! Surface mining removes the soil and rock above mineral deposits, making it more visible, while underground mining digs shafts and tunnels to access minerals deep beneath the surface. Let's remember this with the acronym 'SUD' - Surface, Underground, Different!

What kinds of minerals can be extracted?

Great question! We can extract metals like gold, copper, and coal. They’re essential for various industries.

So, what's the main takeaway here? Mining is crucial for resource extraction, but the methods differ based on the depth and location of the minerals.
Types of Surface Mining
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's dive deeper into surface mining. Can anyone name some methods of surface mining?

I think there's open-pit mining and maybe strip mining?

Correct! Open-pit mining creates a giant pit, while strip mining involves removing layers of the earth to access the minerals. Can anyone explain how these processes might impact the environment?

I guess they can damage the land and habitats?

That's right! They can lead to deforestation, soil erosion, and even water pollution. Remember the acronym 'PES' for 'Pit, Erosion, Stripping' to keep these impacts in mind.

But what about the economic benefits?

Excellent point! While surface mining can be harmful environmentally, it also provides jobs and resources essential for industries. Balancing these factors is key.
Underground Mining Methods
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s move on to underground mining. What do you think makes it different from surface mining?

It probably needs more complex mining techniques since it’s deeper?

Exactly! Underground mining is more dangerous and requires tunnels or shafts. Can anyone name a risk involved with this type of mining?

Cave-ins could be really dangerous, right?

Very true! In addition, poor air quality can lead to health issues. One way to remember these risks is by using the mnemonic 'DUST's' - Dangerous, Underground, Safety, Threats! So, what’s our takeaway about underground mining?

It’s riskier and more complicated than surface mining!

Well done! Always weigh the risks against the benefits.
Environmental Effects of Mining
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's tackle the environmental effects of mining. Why do you think mining can be harmful to the environment?

It can destroy habitats and pollute air and water, right?

Exactly! Mining activities cause deforestation, soil erosion, and pollution. Let’s remember that with the acronym 'HAP' - Habitat, Air, Pollution!

But what about the resources it provides?

That's a crucial point! Although mining offers vital resources, we must consider sustainable practices to mitigate these environmental impacts. What are some sustainable alternatives we could explore?

Maybe recycling materials instead of mining new ones?

Spot on! Recycling is a fantastic method to reduce mining pressure.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The section outlines the different methods of mining, such as surface and underground mining, detailing their procedures and environmental consequences. Key terms related to mining processes and their effects are also highlighted.
Detailed
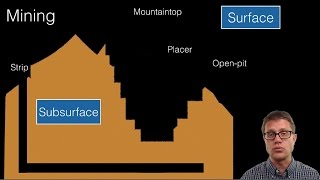
Types of Mining
Mining is a crucial activity for extracting valuable minerals and fossil fuels from the Earth. The two main types of mining are surface mining and underground mining, which vary based on the depth and location of the mineral deposits.
Surface Mining
Surface mining involves removing soil and rock overlying the ore. It includes methods like open-pit mining, strip mining, and quarrying. Each method has specific applications and impacts, such as land degradation and ecosystem disruption.
- Open-Pit Mining - A large pit is created for extracting ores close to the surface.
- Strip Mining - Long strips of material are removed; effective for horizontally-located minerals.
- Quarrying - This is used for extracting building materials like stone and sand.
Underground Mining
In contrast, underground mining involves digging tunnels or shafts to reach deep-seated minerals, making it more costly and dangerous due to risks like cave-ins and exposure to hazardous conditions.
Environmental Impacts
Both mining types profoundly affect landscapes, increase deforestation, and lead to soil erosion. Moreover, the mining process often results in significant air and water pollution, which can harm both the environment and human health. Understanding these mining methods is essential for evaluating their long-term sustainability and economic impact.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Overview of Mining Methods
Chapter 1 of 7
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The method of mining has to be determined depending on whether the ore or mineral deposit is nearer the surface or deep within the earth. Mines are of two types: a) Surface (open cut or strip mines) b) Deep or shaft mines.
Detailed Explanation
Mining methods are chosen based on the location of the mineral deposits. If the minerals are close to the Earth's surface, surface mining methods are used; if they are located deeper underground, deep or shaft mining techniques are employed. This determination is essential because it affects how efficiently and safely the minerals can be extracted.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine you’re trying to gather apples from a tree. If the apples are hanging low, you can easily pick them (surface mining), but if they are high up, you might need to climb the tree or use a ladder (deep mining) to reach them.
Surface Mining Techniques
Chapter 2 of 7
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
a) Surface Mining: Surface mining is used to obtain mineral ores that are close to Earth’s Surface. The soil and rocks over the ore are removed by blasting. Typically, the remaining ore is drilled or blasted so that large machines can fill trucks with the broken rocks. Surface mining includes open-pit mining, quarrying, and strip mining.
Detailed Explanation
Surface mining involves removing the layers of soil and rock above the ore deposits through blasting. This technique is efficient for extracting minerals that are relatively shallow. After the top layers are removed, heavy machinery is used to crush and transport the ore to processing facilities. The main types of surface mining include open-pit mining, strip mining, and quarrying. Each method has specific applications based on the type of mineral and geography.
Examples & Analogies
Think of it like digging a hole in your backyard. If you want to plant a garden, you first remove the grass and topsoil (just like removing rock and soil in surface mining) before digging deeper to plant your seeds.
Open-Pit Mining
Chapter 3 of 7
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
1) Open-pit mining creates a big pit from which the ore is mined. The size of the pit grows until it is no longer profitable to mine the remaining ore.
Detailed Explanation
Open-pit mining is a method where a large excavation is made to extract minerals. The process begins by digging a large hole, or pit, into the ground. As ore is extracted, the pit gets larger until it no longer holds enough economically viable ore for continued mining. This method is particularly effective for minerals that are near the surface, like copper or gold.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a giant bowl that you keep scooping ice cream from. Eventually, as you eat more and more ice cream, the bowl gets deeper, and you’ll reach a point where it's not worth digging for the last few scoops.
Strip Mining
Chapter 4 of 7
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
2) Strip mines are similar to pit mines, but the ore is removed in large strips.
Detailed Explanation
Strip mining involves removing minerals in long strips rather than a deep pit. This process is particularly efficient for coal and other minerals that are located near the surface. The method starts by stripping away the topsoil and then removing the ore in sections. Once one strip is mined, the process moves to the next strip.
Examples & Analogies
Think of strip mining like peeling a long ribbon of tape off a roll, where you take off one piece at a time instead of taking off the whole roll at once.
Quarrying
Chapter 5 of 7
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
3) A quarry is a type of open-pit mine that produces rocks and minerals that are used to make buildings.
Detailed Explanation
Quarrying is a specific type of open-pit mining aimed at extracting building materials like stone, gravel, and sand. It serves the construction industry by providing essential materials to build roads, homes, and other structures. Quarries are typically located where there are large deposits of rocks that can be economically extracted.
Examples & Analogies
You can think of quarrying like gathering pieces of large stones from a rocky beach to build a sandcastle. Instead of pulling at the sand (which serves a different purpose), you focus on collecting the bigger stones that can help create your structure.
Underground Mining Techniques
Chapter 6 of 7
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
b) Underground Mining: Underground mining is used for ores that are deep in Earth's surface. For deep ore deposits, it can be too expensive to remove all of the rocks above the ore.
Detailed Explanation
Underground mining is applied when the ore deposits are too deep to extract economically using surface methods. This process involves creating tunnels and shafts in the earth to access the minerals. Although underground mining is generally more complex and dangerous than surface mining, it is essential for accessing certain mineral deposits that would otherwise remain untapped.
Examples & Analogies
You can compare underground mining to exploring a cave. Instead of just visiting the entrance (surface mining), you have to navigate through narrow and deep paths to reach interesting formations deep within.
Challenges of Underground Mining
Chapter 7 of 7
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
For deep ore deposits, it can be too expensive to remove all of the rocks above the ore. Underground mines can be very deep. The deepest gold mine in South Africa is more than 3,700 meters deep (that is more than 2 miles)! There are various methods of underground mining. These methods are more expensive than surface mining because tunnels are made in the rock so that miners and equipment can get to the ore.
Detailed Explanation
Accessing deep ore deposits involves significant costs and engineering challenges. The construction of tunnels must ensure miner safety and environmental stability. For example, the deepest gold mine in South Africa extends over 3,700 meters, highlighting the extent of investment and effort required for successful extraction. Furthermore, various techniques, such as room and pillar or longwall mining, are used, each suited to different mineral types and geological settings.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine needing to build a staircase to reach a treehouse that’s very high up. It requires careful planning to ensure the steps are safe and can hold weight. Similarly, underground mining requires secure tunnels to ensure miners can safely dig for minerals without risking collapse.
Key Concepts
-
Mining: The extraction of minerals from the Earth.
-
Surface Mining: Involves removing the overlying material to reach minerals.
-
Underground Mining: Tunnels or shafts are created to reach deep minerals.
-
Open-Pit Mining: A large pit is created to extract minerals.
-
Environmental Impact: Refers to the adverse effects mining has on the ecosystem.
Examples & Applications
Open-pit mining is commonly used for gold and copper extraction.
Underground mining is often applied in coal mining operations.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Mining for gold and precious stone, in pits and shafts where ore is grown.
Stories
Once in a forest, miners worked hard, digging into the earth with great regard. They sought precious minerals, but the land they marred, learning later the cost was quite regard.
Memory Tools
Remember 'MICE' for managing impacts from mining: Minimize waste, Improve technology, Conserve water, and Emphasize restoration.
Acronyms
Use 'SUN' to remember
Surface mining
Underground mining
and their environmental needs.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Mining
The process of extracting valuable minerals and fossil fuels from the earth.
- Surface Mining
Mining that involves removing soil and rock covering the ore.
- Underground Mining
Mining that uses tunnels or shafts to reach deep-seated minerals.
- OpenPit Mining
A method of surface mining that creates a large pit to extract minerals.
- Environmental Impact
The effect that mining activities have on the ecosystem, including air and water quality.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
