Roof top rain water harvesting (RTRWH)
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Rainwater Harvesting
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we'll discuss rainwater harvesting, particularly focusing on roof top rainwater harvesting, or RTRWH. Can anyone tell me why rainwater harvesting might be important?

It can help supply water during dry seasons.

Exactly! It helps reduce dependency on traditional water sources. So, why else should we care?

It can recharge groundwater levels, right?

Yes! By capturing rainwater, we can help refill aquifers and minimize soil erosion. Great responses!
Components of RTRWH
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's delve into the key components of an RTRWH system. Who can name one component?

The catchment area! That's where the rainwater lands.

Exactly! The catchment is crucial. What about the mechanism to move the water?

We use gutters and conduits to transport it, right?

Right again! And we also need filters and storage tanks to complete the system. Remember the acronym 'CGFST' for Catchment, Gutters, Filters, Storage, to help recall these components.
Benefits of RTRWH
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Why do you think implementing RTRWH is beneficial for the environment and community?

It saves water and can lower our water bills!

And it helps reduce stormwater runoff, which can cause flooding.

Great points! Additionally, it fosters a community culture of conservation. Let's summarize: RTRWH supports water conservation, protects groundwater, and can also provide an additional water resource during dry periods.
Real-life Applications of RTRWH
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Can anyone think of real-life places or examples where RTRWH is implemented?

I’ve seen installations in schools where they use rooftop systems to collect water for toilets.

Yeah! Certain communities use it for gardens too, right?

Exactly! It’s versatile and can provide for irrigation and domestic use. Remember, implementing RTRWH can turn rainwater into a valuable asset for communities.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
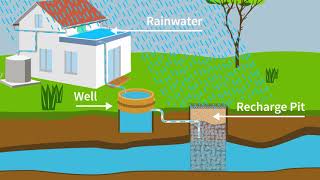
RTRWH involves the collection of rainwater falling on rooftops and its storage or recharge into the ground. This technique helps augment groundwater supply, reduce surface runoff, and minimize soil erosion while fostering a culture of water conservation.
Detailed
Detailed Summary
Roof top rainwater harvesting (RTRWH) is a sustainable practice that allows individuals and communities to collect and utilize rainwater directly from the rooftops of buildings. By capturing rainwater, RTRWH aids in mitigating the decline of groundwater levels, enhances the quality of aquifers, conserves surface water runoff during rains, reduces soil erosion, and promotes a water conservation ethic among the general populace. Since rainwater harvesting techniques are not new, especially in regions like India where various methods have been practiced for centuries, the approach leverages modern methods to increase efficiency and effectiveness.
The rainwater can be collected from various surfaces such as rooftops, paved areas, open fields, water bodies, and stormwater drains. This practice is bifurcated mainly into two categories: collecting rainwater directly from roofs (RTRWH) and charging it into soil for further usage.
Components of RTRWH System
The system comprises several components, including:
- Catchment: The surface that receives rainfall, typically rooftops made of materials like RCC or metal sheets.
- Gutters and Conveyance: Channels that transport the collected water to storage or recharge areas.
- First Flush Device: Mechanisms to divert initial runoff that may contain contaminants.
- Filters: Systems in place to ensure collected water is free from debris and contaminants.
- Storage Tanks: Containers that hold the harvested water for future use.
In operation, well-implemented RTRWH can significantly improve local groundwater levels while providing a valuable resource for irrigation, domestic use, or even drinking water, depending on the purification measures taken.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Introduction to Roof Top Rain Water Harvesting
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
It is a system of catching rainwater where it falls. In rooftop harvesting, the roof becomes the catchments, and the rainwater is collected from the roof of the house/building. It can either be stored in a tank or diverted to an artificial recharge system. This method is less expensive and very effective and if implemented properly helps in augmenting the groundwater level of the area.
Detailed Explanation
Roof Top Rain Water Harvesting (RTRWH) refers to the practice of collecting rainwater that falls on rooftops. When rain falls, it collects on the roofs of buildings, which are considered catchments. The harvested rainwater can be stored for later use or directed to recharge groundwater. This method is affordable and highly efficient, especially when properly implemented, as it contributes to increasing the groundwater levels in the surrounding area.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a sponge soaking up water from a spilled drink. Just like a sponge absorbs water, rooftops can capture rainwater. If you have a bucket under the sponge, you collect all that water to use later. Similarly, RTRWH helps communities catch rainwater from roofs, allowing them to use it for watering plants or even for drinking after it’s purified.
Components of Roof Top Rain Water Harvesting System
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The system mainly constitutes the following sub components: Catchment, Coarse mesh, Gutters, Conduits or Conveyance, Transportation, First flush, Filter, Storage, Supply unit.
Detailed Explanation
The RTRWH system is made up of several key components. These include:
- Catchment: The surface collecting the rainwater (like rooftops).
- Coarse Mesh: A filter preventing large debris from entering the system.
- Gutters: Channels that carry the collected rainwater from the catchment.
- Conduits or Conveyance: Pipes that transport rainwater to storage.
- Transportation: The methods used to move rainwater from gutters to storage.
- First Flush: A system that diverts the initial dirty water runoff from the first rainfall before clean water can be collected.
- Filter: A device to clean the water further before it's stored.
- Storage: Tanks or containers where the collected rainwater is stored for future use.
- Supply Unit: The mechanism that allows the use of the stored water.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the RTRWH system like a well-organized kitchen for cooking. The rooftop acts as the pot where ingredients (rainwater) are collected. A fine mesh strainer is used to remove large lumps (debris) before pouring it into a pot (the storage tank). Just as you would separate the ingredients before cooking, the first flush system cleans out dirty rainwater first, ensuring clean 'ingredients' are cooked (used) later.
Catchments in Rain Water Harvesting
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The catchment of a water harvesting system is the surface which directly receives the rainfall and provides water to the system. It can be a paved area like a terrace or courtyard of a building, or an unpaved area like a lawn or open ground. A roof made of reinforced cement concrete (RCC), galvanized iron or corrugated sheets can also be used for water harvesting.
Detailed Explanation
The catchment area is where the rainwater first falls and is collected. This could be various surfaces such as:
- A flat rooftop, being ideal when made from materials that allow efficient collection.
- Courtyards or paved areas, which can also channel rainwater towards collection systems.
- Open ground or lawns, though less efficient, they can still collect rainwater in certain conditions.
Materials like reinforced cement concrete or corrugated sheets are preferred for rooftops because they are durable and effective at directing water into the harvesting system.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the catchment like a big, wide sponge placed outside during a rainstorm. The materials you choose to make your rooftop (like RCC or galvanized iron) determine how quickly and efficiently the sponge collects water. If it’s a clean, flat surface, it will soak up and direct that water easily into your system, just like a sponge would soak up all the surrounding water.
Key Concepts
-
Rooftop Rainwater Harvesting: A method of collecting and storing rainwater from rooftops for reuse and groundwater recharge.
-
Components of RTRWH: Key parts include catchment, gutters, storage tanks, filters, and first flush mechanisms.
-
Importance of Conservation: RTRWH contributes to water conservation, sustainable practices, and local groundwater recharge.
Examples & Applications
A school utilizing RTRWH for flushing toilets and irrigation.
A community garden that employs harvested rainwater to sustain plants.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Rain on the roof, catch it fast, helps our water last and last!
Stories
Imagine a dry town that began collecting rainwater from rooftops. They built storage tanks, and soon their gardens flourished, proving nature’s gift can sustain life when captured properly.
Memory Tools
Remember 'CGFST' for Catchment, Gutters, Filters, Storage Tanks to easily recall the RTRWH components.
Acronyms
RTRWH - Rainwater Treatment, Recharging Water to help understand the initiative.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Catchment
The surface area that collects rainwater for harvesting.
- First Flush Device
A system that diverts initial runoff to prevent contaminants from entering the storage.
- Storage Tanks
Containers used to store harvested rainwater for future use.
- Recharge
The process of replenishing groundwater supplies.
- Surface Runoff
Water that flows over land when it rains and does not infiltrate into the ground.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
