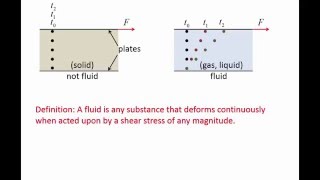
Definition of a Fluid
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Fluids
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we are going to explore the definition of a fluid. What do we mean when we say a fluid continuously deforms under shear stress?

Does that mean fluids can flow?

Exactly! Fluids can flow and change shape. They include liquids, gases, and even plasmas. Can anyone tell me how fluids differ from solids?

Solids don't change shape or flow under stress.

That's right! While solids resist deformation, fluids adjust easily to applied forces. Let's remember this with the acronym 'FLUID': Flowing, Liquids, Unrestricted, Indefinite shape, and Deformable.

So, all liquids are fluids, but not all fluids are liquids?

Absolutely! Gases also qualify as fluids. Great observation, Student_3. To recap: fluids deform and flow, unlike solids.
Applications and Importance of Fluids
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Why do you think studying fluids is crucial in engineering and science?

Fluids are everywhere! They affect things like weather and how we move.

Exactly! The behavior of fluids impacts a variety of fields, from meteorology to mechanical systems. Can anyone think of a specific application?

How about hydraulics?

Great example! Hydraulics relies on liquid fluids for force transmission. This leads us to our next point: understanding the properties of fluids enhances our ability to design efficient systems.

So, if we can predict fluid behavior, we can create better machines?

Exactly! And that's why fluid mechanics is such a fundamental part of engineering.
Distinguishing Fluids from Solids
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's compare fluids and solids further. What's a characteristic unique to fluids?

Fluids have no fixed shape.

Correct! Fluids can adapt to the shape of their container. What else?

They flow under stress.

Exactly! Solids resist shear stress, while fluids yield and flow. This is described in Newton's law of viscosity, which we will cover next. But for now, remember: fluids flow, solids stay.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Fluids are substances that flow easily and do not resist deformation when subjected to shear stress. This category includes not only liquids and gases but also plasmas, distinguishing them from solids, which maintain their shape.
Detailed
Definition of a Fluid
A fluid is a material that can undergo continuous deformation when subjected to shear stress, regardless of its magnitude. Fluids encompass a wide range of substances, including liquids, gases, and plasmas. Unlike solids, which resist deformation, fluids have the ability to flow and take the shape of their container, making them essential in various applications such as hydraulics and aerodynamics. Understanding the properties of fluids is fundamental in the study of fluid mechanics, which analyzes the behavior of fluids in motion and at rest.
Youtube Videos


![[Fluid Mechanics: Fundamentals] What are fluids?](https://img.youtube.com/vi/L8Cm8CF2vlY/mqdefault.jpg)
Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
What is a Fluid?
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
A fluid is a substance that continuously deforms (flows) under the action of a shear stress, no matter how small the stress may be.
Detailed Explanation
A fluid is defined as a material that can flow and change shape when a force is applied. The key concept here is 'shear stress', which is a type of force that acts parallel to a surface. Even a small application of shear stress can cause a fluid to change shape. Unlike solids, which maintain their shape when a force is applied, fluids react by flowing.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine honey on a plate. If you tilt the plate, the honey slowly flows to one side. This behavior illustrates how fluids respond to shear stress, while a solid object like a rock would just stay in its place.
Different Types of Fluids
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Includes liquids, gases, and plasmas
Detailed Explanation
Fluids can be categorized into three main types: liquids, gases, and plasmas. Liquids have a definite volume but take the shape of their container. Gases, on the other hand, do not have a fixed shape or volume and will expand to fill any container. Plasma is a state of matter where gases become ionized and conduct electricity, typically found in stars, including the sun.
Examples & Analogies
Think of different fluids as different types of drinks in various containers. Water (liquid) can fill a glass but remains at a certain level. Air (gas) can fill a balloon and will expand to fit it. Plasma is like the energy release when a fluorescent bulb lights up.
Fluids and Deformation
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Fluids do not resist deformation, unlike solids
Detailed Explanation
Fluids are unique because they do not resist deformation. This means when a fluid is subjected to forces, it easily changes shape to adapt to the forces acting on it. In contrast, solids are rigid and maintain their shape under similar conditions.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a water balloon. When you squeeze it, the shape changes instantly, and it adapts to the pressure applied. However, if you squeezed a rubber ball, while it might deform a little, it quickly returns to its original round shape because it is a solid.
Key Concepts
-
Continuous Deformation: Fluid's ability to change shape when subjected to shear stress.
-
Types of Fluids: Includes liquids, gases, and plasmas, all of which flow.
Examples & Applications
Water flowing from a tap which illustrates how it takes the shape of its container.
Air pressure affecting the shape of a balloon as it expands when filled with air.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Fluids can flow, they change and bend, solids hold firm, on that we depend.
Stories
Imagine a river that flows around rocks. Just like the river takes the shape of the ground, fluids adapt to their surroundings, while stones remain in place.
Memory Tools
Remember 'FLUID' for Flowing, Liquids, Unrestricted, Indefinite shape, and Deformable.
Acronyms
Listen to the acronym 'GAP' for Gases, Air, and Plasmas as types of fluids.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Fluid
A substance that continuously deforms under shear stress.
- Shear Stress
A force that causes deformation by sliding layers of material past one another.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
