Effect of Water Content - 1.1
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Effect of Water Content
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we will examine how water content affects compact density. Can anyone tell me what happens to density as we increase water content?

I think it increases up to a point, but then it decreases.

Exactly! This point where the density is highest is called Maximum Dry Density (MDD). Remember that as the water content grows beyond the Optimum Moisture Content (OMC), air voids can actually increase, which pulls down the dry density.

So, what happens at lower water contents?

Good question! At lower than OMC, the attractive forces among soil particles dominate, and there's low inter-particle repulsion. This means a denser arrangement of particles.

Can you explain the role of the diffused double layer?

Certainly! An increase in water content expands this double layer around particles, reducing the attractive forces. It’s essential to visualize this when thinking about particle behavior in wet soils.

In summary, if we think of MDD as the peak of our density hill, going either way on water content creates different challenges.
Effect of Amount of Compaction
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s dive into the impact of compaction amount. How does increasing compactive effort affect MDD and OMC?

It seems that more compaction increases MDD.

Correct! However, it also reduces OMC. It's worth noting that this isn’t a straightforward linear relationship.

Why isn’t it linear? What factors play a role?

Several factors can influence soil behavior under compaction, including particle size and moisture interaction. Each soil responds uniquely, complicating predictions.

So, different soil types can yield different results even with the same amount of compaction?

Exactly. A takeaway here is to always consider the soil type when planning compaction strategy.

Remember, more effort does not always equal proportionally better results.
Effect of Method of Compaction
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Next, let’s discuss the methods of compaction. What are some characteristics that affect the achieved dry density?

I suppose it depends on the weight of the equipment used?

Yes! The weight of compacting equipment plays a significant role. Can anyone think of others?

The type of compaction and contact area must matter too, right?

Spot on! Time of exposure during compaction also contributes. Each of these aspects can optimize densification in different soil types.

How do we know which method is best for our soil?

Research and test! Identify soil types and then match the method accordingly. Understanding soil characteristics is key.

To summarize, choosing the right compaction method is critical based on soil type and environmental conditions.
Effect of Type of Soil
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Finally, let’s evaluate the soil type. How does it influence MDD?

I know coarse-grained soils can achieve higher densities at lower water content.

Exactly! And fine-grained soils often require more water to achieve satisfactory densities. Why do you think this difference matters?

Because it affects how we approach compaction in various contexts, like building foundations.

Right! Every soil type presents unique challenges and opportunities for compaction, critical for effective engineering.

As we wrap up, always consider soil type when planning for compaction—it significantly affects outcomes.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The section defines how the compact density of soils is influenced by multiple factors including water content, compaction method, and soil type. It elaborates on the maximum density achieved, the role of moisture, and the implications of different compaction methods.
Detailed
Detailed Summary
This section delves into the various factors influencing the compact density of soils, elucidating key concepts critical for understanding soil compaction._
Factors Affecting Compact Density
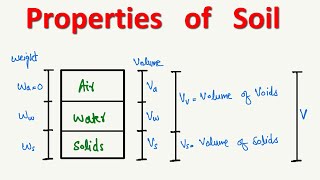
- Water Content: The interaction of moisture with soil impacts compact density significantly. As water content increases, compacted density can rise to a peak, known as Maximum Dry Density (MDD), beyond which it declines. This phenomenon occurs because, at lower moisture levels than the Optimum Moisture Content (OMC), the attractive forces among soil particles are stronger, leading to denser packing. Conversely, surpassing OMC introduces excess water, which increases air voids and reduces dry density due to particle lubrication.
- Amount of Compaction: Increasing the compactive force generally raises the MDD while reducing the OMC; however, this relationship is not linear, highlighting the complexity of soil behavior under varying conditions.
- Method of Compaction: The specific technique employed (e.g., dynamic, static) affects the resulting dry density due to factors such as the weight of equipment, type of compaction, contact area, and exposure time.
- Type of Soil: Soil types significantly affect achieved densities; coarse-grained soils typically reach higher densities at lower water contents, whereas fine-grained soils may require higher water contents to achieve maximum density.
Understanding these factors is essential for effective soil compaction in engineering applications.
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Effect of Water Content
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- With increase in water content, compacted density increases up to a stage, beyond which compacted density decreases.
- The maximum density achieved is called MDD and the corresponding water content is called OMC.
- At lower water contents than OMC, soil particles are held by the force that prevents the development of diffused double layer leading to low inter-particle repulsion.
- Increase in water results in expansion of double layer and reduction in net attractive force between particles. Water replaces air in void space.
- Particles slide over each other easily increasing lubrication, helping in dense packing.
- After OMC is reached, air voids remain constant. Further increase in water, increases the void space, thereby decreasing dry density.
Detailed Explanation
The effect of water content on compacted density refers to how the amount of water present in the soil changes its density during compaction. Initially, as water content increases, the density increases due to the moisture helping in particle arrangement and packing. This increase continues until a certain point known as the Optimum Moisture Content (OMC), where the density reaches its maximum value called the Maximum Dry Density (MDD). Beyond OMC, adding more water results in the soil becoming less dense because the additional water creates more voids, leaving less space for the soil particles themselves.
Examples & Analogies
Think of making a snowball. When you first gather some snow, if you add a little water, it helps the snow particles pack together tightly, making a solid snowball. However, if you keep adding water beyond a certain point, the snowball becomes slushy and messy, with more air pockets and less overall substance. The right amount of water makes for the perfect snowball—like how soil needs the right moisture level for maximum density.
Effect of Amount of Compaction
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- As discussed earlier, effect of increasing compactive effort is to increase MDD and reduce OMC (Evident from Standard & Modified Proctor’s Tests).
- However, there is no linear relationship between compactive effort and MDD.
Detailed Explanation
The amount of compaction refers to how forcefully the soil is compacted. Increasing the compactive effort generally leads to a higher Maximum Dry Density (MDD) of the soil. This means that with more force, the soil particles can be packed tighter. However, it is important to note that this effect is not linear; that is, doubling the compactive effort does not necessarily result in double the density. Therefore, understanding how much effort is required for optimal compaction is crucial for effective soil management.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine trying to compress a sponge. If you press down just a little, the sponge compresses a bit. If you exert more force, it compresses more—but if you press too hard, the sponge will just squish out the sides without becoming denser in the center. Similarly, with soil, there’s a sweet spot for how much force to apply to achieve the best compaction without losing efficiency.
Effect of Method of Compaction
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The dry density achieved by the soil depends on the following characteristics of compacting method:
1. Weight of compacting equipment
2. Type of compaction
3. Area of contact
4. Time of exposure
5. Each of these approaches will yield different compactive effort. Further, suitability of a particular method depends on type of soil.
Detailed Explanation
The method used for compaction significantly impacts the density of the soil. Factors such as the weight of the compaction equipment, the type of compaction (like vibration or static pressure), the area of contact (how much surface area is being compacted at one time), and the time spent compacting all play crucial roles. Different methods can yield varying results in terms of compacted density, and choosing the right method is vital, as not all soils respond the same way to different compaction techniques.
Examples & Analogies
Consider baking a cake. The density of the cake batter can change depending on how you mix it, what tools you use (like a whisk or a mixer), and the cooking time. If you whisk lightly, you might have a fluffy cake, but if you mix it vigorously, you'd end up packing it down tightly. Likewise, how you compact soil influences its final properties.
Effect of Type of Soil
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Maximum density achieved depends on type of soil.
- Coarse grained soil achieves higher density at lower water content and fine grained soil achieves lesser density, but at higher water content.
Detailed Explanation
The type of soil has a major influence on how dense it can become when compacted. Coarse-grained soils, such as gravel, can achieve greater densities when there is less water present. On the other hand, fine-grained soils, like clay, can become denser but require more water to facilitate the compaction process. Understanding these differences is critical to applying the right techniques for achieving the desired density in soil engineering.
Examples & Analogies
Think of two types of fruits: apples and blueberries. When you pack apples in a basket, they need some space due to their shape, and you can pack them tightly without much effort. With blueberries, you can get more in the basket if you add a bit of syrup or juice (representing water) to help them fit together. In soil, different types react differently to moisture and compaction, just like how different fruits fill a basket.
Key Concepts
-
Water Content: Affects compact density significantly, with MDD being the peak density at specific moisture levels.
-
Amount of Compaction: Increased compaction raises MDD and reduces OMC, but not in a linear fashion.
-
Method of Compaction: Different methods yield varying results based on equipment and technique used.
-
Type of Soil: Soil composition impacts maximum density, with coarse soils performing better at lower water contents.
Examples & Applications
Coarse-grained soils, like gravels, achieve higher density at lower moisture content than fine-grained soils like clays.
In a construction project, using dynamic compaction might yield better results for sandy soils, compared to static methods.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Water makes soil tighter, just up to the right height, then it starts to spread and loses its might.
Stories
Imagine packing a suitcase. You add clothes (water) until it’s full (MDD), but overstuffing leads to gaps (decreased density).
Memory Tools
WAMOST: Water content, Amount, Method, OMC, Soil Type—key factors in compact density.
Acronyms
CAMP
Compaction Amount Matters for density—never forget this!
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Maximum Dry Density (MDD)
The highest density a soil can achieve under optimum conditions.
- Optimum Moisture Content (OMC)
The moisture content at which a soil reaches its maximum dry density.
- Diffused Double Layer
The layer of water surrounding soil particles that influences soil properties.
- Compactive Effort
The amount of force applied during the compaction process.
- Soil Type
The classification of soil, including coarse-grained and fine-grained.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
