Moist Unit Weight Calculation
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Moist Unit Weight
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we’re going to discuss the significance of measuring moist unit weight. Why do you think this measurement is crucial when we first get the soil in the lab?

Because the properties might change during transportation?

Exactly! Changes in moisture content can affect soil behavior. Remember, moisture affects soil strength. That's why we calculate the moist unit weight right away.

How do we actually calculate the moist unit weight?

Great question! We’ll actually dive deep into that with some examples. First, let’s discuss the formula for dry unit weight.
Calculating Dry Unit Weight
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

To calculate the dry unit weight, we can use the formula: \( γ_d = \frac{γ}{1 + w} \). Can anyone recall what each symbol represents?

γ is the moist unit weight, and w is the moisture content, right?

Correct! Now, if our moist unit weight is 17.38 kN/m³ and moisture content is 0.12, what would our dry unit weight be?

Using the formula, it should be around 15.51 kN/m³.

Well done! This reinforces the importance of learning how to manipulate the formulas to find the right values.
Moist Unit Weight Calculation and Saturation
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's examine how to determine the amount of water needed for saturation. If we know the dry unit weight and we want to make the soil saturated, what should we do?

We find the saturated unit weight and subtract the moist unit weight.

Exactly! For example, if our saturated unit weight is 19.62 kN/m³, how much water do we need to add if our moist unit weight is 17.38 kN/m³?

That would be 2.24 kN of water for per cubic meter of soil.

Very good! Remember, this is crucial for achieving desired soil conditions for construction.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The section emphasizes the need to quantify soil characteristics like moisture content and unit weight upon arrival at the laboratory. It provides methods for calculating dry unit weight, moist unit weight, and the amount of water required for saturation through examples.
Detailed
Moist Unit Weight Calculation
Understanding the moisture content and unit weight of soil is vital for soil mechanics and geotechnical engineering. These properties can change during transport and storage, making their accurate measurement essential upon acquisition in the lab. Once the water content and bulk unit weight are known, the dry unit weight can be calculated using relationships between them.
Key Relationships:
- Dry Unit Weight (γ_d) can be calculated from the moist unit weight (γ) and moisture content (w) using the formula:
\[ γ_d = \frac{γ}{1 + w} \]
- Moist Unit Weight (γ) can be calculated from bulk density and moisture content.
- Calculating the amount of water to saturate soil involves determining the desired saturated unit weight (γ_sat) using the specific gravity of soil solids (G) and void ratio (e) through:
\[ γ_sat = \frac{G(γ_w)}{1 - e} \]
Once saturated, the difference between saturated unit weight and moist unit weight gives the amount of water needed per cubic meter of soil.
Importance:
These calculations are crucial for various engineering applications, including foundation design, excavation work, and soil stabilization. Accurate initial measurements help in predicting behavior under load and environmental conditions.
Youtube Videos

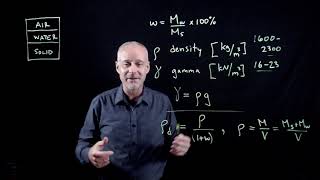

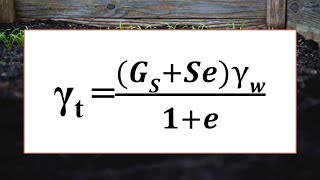





Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Understanding Moist Unit Weight
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The moist unit weight is a measure of the weight of soil per unit volume when the soil contains water. It is important for understanding the overall weight of the soil when it is saturated or in a wet condition.
Detailed Explanation
Moist unit weight combines both the solids of the soil and the water present in the voids. To calculate it accurately, we need to consider the weight of the dry soil and add the weight of the water it contains. This provides a clearer picture of how much the soil weighs in real-world conditions, especially when constructing foundations or other structures.
Examples & Analogies
Think of moist unit weight like measuring the weight of a sponge. When the sponge is dry, it weighs much less than when it is soaked in water. Just like the sponge, soil can change weight based on how much water it contains, which is why moist unit weight is crucial in civil engineering.
Calculating Moist Unit Weight
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
To calculate the moist unit weight, the formula is typically given as follows:
Moist Unit Weight (γ) = Dry Unit Weight (γ_d) + Water Content (w)
where water content is expressed as a mass fraction.
Detailed Explanation
The formula for moist unit weight helps you to add the contributions of the dry soil weight and the water weight together to get the total weight per cubic meter. Essentially, you need to first find out how much the dry soil weighs, then figure out how much the additional water contributes to that weight. The resulting moist unit weight is then used for various engineering applications.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine you are making a fruit salad. You first weigh the bananas (dry unit weight), and then you add a cup of yogurt (water content). The total weight of your fruit salad reflects both the bananas and yogurt combined, just like how moist unit weight reflects the dry soil weight plus water content.
Importance of Accurate Measurements
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Accurate measurement of water content and unit weight is critical because they can change during transportation and storage.
Detailed Explanation
When soil is transported or stored, it can gain or lose moisture, directly impacting its weight and properties. For civil engineering projects, knowing the precise moist unit weight helps in calculating loads that structures will bear. For example, if the soil's weight is overestimated, it may lead to the risk of structural failure.
Examples & Analogies
Think about carrying groceries. If you keep adding water bottles to your shopping bag, the total weight increases significantly, making it harder to carry. Similarly, if the weight of the soil isn't accurately known due to fluctuating water content, it becomes challenging for engineers to ensure the integrity of buildings or roads.
Key Concepts
-
Moist Unit Weight: Weight including water content.
-
Dry Unit Weight: Weight excluding water.
-
Saturation: All voids filled with water.
-
Porosity: Volume ratio of voids.
-
Specific Gravity: Soil solids’ density compared to water.
Examples & Applications
Example 1: Calculating dry and moist unit weight using given void ratio and moisture content.
Example 2: Determining void ratio and specific gravity from known dry density and porosity.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
To find the dry weight, just divide with fate; moist by one plus those who wait.
Stories
Imagine a soil scientist measuring weights. They find moist soil heavy. To lighten it, they decide to calculate just the dry weight before adding any water.
Memory Tools
Remember: Wet leads to Dry via Division (γ_d = γ / (1 + w)).
Acronyms
The acronym 'DWMC' (Dry Weight Moist Content) can help you recall the relationship between dry unit weight and moisture content.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Moist Unit Weight
The weight of the soil per unit volume including the water content.
- Dry Unit Weight
The weight of the soil per unit volume excluding water.
- Saturation
The condition when all voids in the soil are filled with water.
- Porosity
The ratio of the volume of voids to the total volume of soil.
- Specific Gravity
The ratio of the density of soil solids to the density of water.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
