Swelling Index(C )
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to the Swelling Index
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we are going to explore the concept of the Swelling Index, C. Can anyone tell me what they think this index measures?

Maybe it has to do with how much soil expands?

Correct! The Swelling Index measures the volumetric change in soil, especially clay, when subjected to changes in effective stress. It’s crucial for predicting how soils behave under load.

What’s an effective stress?

Effective stress is the stress that contributes to soil strength. Think of it as the pressure transmitted through the soil skeleton. Remember, effective stress equals total stress minus pore water pressure. So, when we discuss swelling, we’re interested in how the change in this stress affects the void ratio in clay.

So if the effective stress decreases, will the soil swell more?

Exactly! When effective stress decreases, the soil can take in more water and expand, which is why we must be careful in construction practices involving clayey soils. Let’s summarize: The Swelling Index is a key parameter that reflects changes in soil volume with effective stress. Remember the acronym 'SCE' for Swelling, Compressibility, and Effective stress!
The Role of the e-log σ’ plot
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let’s talk about the e-log σ' plot. This graphical representation helps us visualize the compressibility of soil. How do you think this could relate to the Swelling Index?

It might show how the void ratio changes with stress?

Yes! The e-log σ' plot allows us to see the relationship between the void ratio (e) and the effective stress (σ'). By interpreting this plot, we can quantify the Swelling Index and better understand the settlement or heave of the soil.

How do we actually calculate the Swelling Index from this plot?

Great question! To calculate the Swelling Index, you look at the slope of the curve on the e-log σ' plot. The slope indicates how much the void ratio changes with varying effective stresses. This helps engineers assess soil behavior under different loading conditions.

So, the steeper the slope, the more compressible it is?

Exactly! And now to recap: the e-log σ' plot is essential for determining both compressibility and the Swelling Index in clays. Use the acronym 'CEK' for Compressibility, e-log σ', and Knowledge about soil!
Application of the Swelling Index
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Finally, let's discuss how the Swelling Index is applied in engineering projects. Why do you think it's important?

If we don’t know it, structures could fail?

Exactly, Student_3! If a structure is built on expansive soils without accounting for the Swelling Index, it can lead to serious problems like cracking or settling.

What types of structures are most affected?

Good question! Structures like buildings, roads, and bridges are particularly sensitive to soil movements caused by swelling and shrinkage. The Swelling Index helps us create designs that can accommodate these changes. To remember, think 'COS' for Construction, Observations, and Swelling!

So, it’s all about risk management?

Precisely! By understanding the Swelling Index, engineers can mitigate risks associated with soil behavior during and after construction. Let’s conclude by reinforcing: the Swelling Index is vital in predicting soil behavior related to construction. Use the end acronym 'CRS' for Construction, Risk management, and Swelling!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section outlines the importance of the Swelling Index (C) in relation to soil compressibility. It examines how the index affects the behavior of sedimentary soils under load and its implications for engineering applications.
Detailed
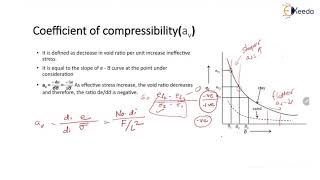
Swelling Index (C)
The Swelling Index (C) is a significant measure of soil's compressibility characteristics, specifically in cohesive soils like clay. It represents the ratio of the change in void ratio to the change in effective stress within the soil structure. This parameter is crucial for predicting the volumetric changes that occur when soils undergo loading and unloading cycles. Understanding the Swelling Index is vital for geotechnical engineers as it aids in evaluating the stability and settlement behavior of structures built on or within such soils.
Through a thorough examination of the e-log σ' plot, one can derive insights into the compressibility and swelling potential of the soil, which is critical in the design of foundations, embankments, and earth structures.
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Understanding the Swelling Index
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The Swelling Index (C) is a measure of volume increase of a material when it absorbs water.
Detailed Explanation
The Swelling Index is an important property of materials, particularly soils, that indicates how much a material will expand when it comes in contact with water. This expansion is due to the absorption of water molecules into the material's structure, which causes it to occupy more space. Understanding this concept is crucial for applications in construction, agriculture, and environmental science, where material behavior in wet conditions can significantly impact performance.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a sponge. When you place a dry sponge in water, it absorbs the water and swells, becoming larger in size. This is similar to how certain soils swell when they take in water, impacting their stability and strength.
Importance of the Swelling Index
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The Swelling Index helps in predicting the behavior of soil and materials in varying moisture conditions.
Detailed Explanation
Knowing the Swelling Index allows engineers and scientists to predict how soil will behave when it gets wet. This is particularly vital for the design of foundations, embankments, and other structures where soil stability is a concern. If soil swells too much, it can cause cracks in roads and buildings, leading to significant structural issues. Therefore, the Swelling Index is a key parameter in geotechnical engineering.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine building a house on a soil that swells significantly when it rains. Without understanding the Swelling Index, builders might not know to use deeper foundations or special construction techniques to prevent the house from tilting or cracking, much like how a poorly built structure on a spongey surface would shift and become unstable.
Applications of the Swelling Index
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The Swelling Index is used in various fields like construction, agriculture, and environmental studies.
Detailed Explanation
In construction, the Swelling Index is used to determine the suitability of soil for supporting structures. In agriculture, it helps in understanding how crops grow in different soil types. Environmental scientists use it to assess how land will respond to water levels, especially in areas prone to flooding. By using the Swelling Index, professionals can make informed decisions about land usage and resource management.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a farmer who wants to plant crops. By understanding the Swelling Index of the soil, they can choose crops that thrive in that specific type of soil or decide to amend the soil conditions through irrigation, similar to how having the right ingredients is essential for a successful recipe.
Key Concepts
-
Swelling Index (C): A measure that indicates how soil volume changes in relation to effective stress.
-
Effective Stress: The stress available for soil strength after accounting for pore water pressures.
-
e-log σ' Plot: A critical graph for analyzing soil compressibility and swelling potential.
Examples & Applications
When designing a building on clayey soil, engineers must consider the Swelling Index to avoid structural failure.
In a road construction project, the e-log σ' plot guides engineers in assessing the suitable materials and methods to mitigate swelling issues.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
When soil swells, the structure might fail, keep it checked, or it will derail.
Stories
Imagine a curious builder deep in clay soil, unaware of swelling. When rains come, the soil expands, the foundation shifts, and cracks emerge, teaching him to always check the Swelling Index before beginning his project.
Memory Tools
To remember the impacts of the Swelling Index, think 'SCE': Swelling, Compressibility, and Effective stress.
Acronyms
The acronym 'COS' stands for Construction, Observations, and Swelling, helping engineers to remember the importance of calculating the Swelling Index.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Swelling Index (C)
A measure of the volume change in soil, specifically clay, with changes in effective stress.
- Effective Stress
The stress that contributes to soil strength, calculated as total stress minus pore water pressure.
- Void Ratio
The ratio of the volume of voids to the volume of solids in a soil sample.
- elog σ' Plot
A graph representing the relationship between the void ratio and effective stress in soils.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
