Function of Heat Exchangers
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Heat Exchangers
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we'll explore the function of heat exchangers. Who can tell me what a heat exchanger does?

Isn’t it a device that transfers heat between fluids without them mixing?

Exactly! They transfer heat between two or more fluids at different temperatures without mixing. Why do you think this might be important?

I guess it helps in conserving energy and controlling temperatures?

Great observation! Heat exchangers improve energy efficiency and maintain temperature controls in various systems. Let's remember this with the acronym **HEAT**: Heat Exchange Application Technology.

Sounds easy to remember!

Good! Always think of heat exchangers as essential tools in power generation, HVAC, and radiators in our cars. They keep systems running smoothly.
Applications of Heat Exchangers
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Can anyone list some industries where we find heat exchangers?

They are used in power plants and refrigeration!

Also in HVAC systems!

Yes! Heat exchangers are widely used in power plants, refrigeration systems, HVAC units, and even in automobile radiators. Can you think of why it’s important to prevent fluids from mixing?

It keeps the processes safe and protects sensitive materials.

Exactly! This separation is vital for operational safety and efficiency.
Efficiency and Importance
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s dive into why heat exchangers are vital in terms of efficiency. How do you think they contribute to energy savings?

By recovering waste heat from processes?

Right! They recover waste heat which boosts overall system efficiency. Think of it like recycling energy. What’s a common effect of increased efficiency?

Lower operational costs!

Correct! Less energy consumption leads to lower operational costs, making heat exchangers indispensable in modern engineering.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
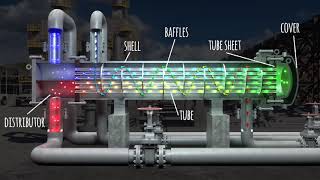
Heat exchangers are devices designed to transfer heat between two or more fluids at differing temperatures without any mixing occurring. They are essential in many applications including power plants, HVAC systems, refrigeration, and automobile radiators.
Detailed
Function of Heat Exchangers
Heat exchangers are critical engineering devices used for transferring heat between two or more fluids that are at different temperatures while preventing them from mixing. This functionality makes them crucial in numerous industrial fields, such as power generation, refrigeration, heating, ventilation, air conditioning (HVAC), and automotive applications.
Heat exchangers serve several key functions including:
1. Energy Efficiency: By recovering waste heat, they improve the overall efficiency of heating and cooling systems.
2. Temperature Control: They regulate temperatures in various industrial processes and systems.
3. Safety: By isolating chemicals or fluids, they enhance operational safety.
Overall, the application and design of heat exchangers directly impact energy consumption and system performance, highlighting their importance in engineering.
Youtube Videos






Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Definition of Heat Exchangers
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Devices that transfer heat between two or more fluids at different temperatures without mixing them
Detailed Explanation
Heat exchangers are specialized devices designed to facilitate the transfer of thermal energy from one fluid to another. Importantly, these fluids are at different temperatures and do not mix. This is a key function as it allows for efficient heating or cooling processes in various applications.
Examples & Analogies
Think of heat exchangers like the radiators in your car. The hot coolant from the engine flows through the radiator, transferring heat to the air outside, but the air and coolant never mix. This helps to cool the engine down while keeping the two fluids separate.
Applications of Heat Exchangers
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Widely used in power plants, refrigeration, HVAC, chemical processing, and automobile radiators
Detailed Explanation
Heat exchangers are versatile tools employed across multiple industries. In power plants, they help in recovering waste heat to improve efficiency. In refrigeration systems, they assist in transferring heat to maintain low temperatures. HVAC (heating, ventilation, and air conditioning) systems utilize them to manage indoor climate effectively. Additionally, they play a crucial role in chemical processing and automobile radiators, where they aid in temperature control and efficiency.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine your refrigerator during a hot summer. It's the heat exchanger that keeps the inside cool while allowing heat from the warm air inside to escape outside. Similarly, in power plants, heat exchangers help convert heat from burning fuel into electricity, much like how your flashlight turns the energy from batteries into light.
Key Concepts
-
Heat Transfer: The process of thermal energy moving from a hotter object to a cooler one.
-
Fluid Separation: Keeping different fluids from mixing to ensure safety and efficiency in processes.
Examples & Applications
Heat exchangers in refrigeration allow refrigerants to absorb heat from inside a fridge while releasing it outside.
In car radiators, heat exchangers cool the engine coolant by transferring heat to air while preventing the coolant from mixing with other fluids.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Heat exchangers flow with ease, transferring warmth as a breeze.
Stories
Imagine a busy kitchen, where hot soup and cold salad need to stay separate; the heat exchanger does just that while letting the heat flow, keeping the meals just right.
Memory Tools
Remember HEAT: Heat Exchange Always Transfers.
Acronyms
C.E.S. - Conservation of Energy Systems refers to how heat exchangers contribute to energy efficiency.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Heat Exchanger
A device that transfers heat between two or more fluids at different temperatures without mixing them.
- Energy Efficiency
The ability of a system to utilize less energy to perform the same task or function.
- HVAC
Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning; a system used for regulating air quality and temperature.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
