Groundwater in the Global Budget
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Groundwater
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we'll discuss groundwater and its vital role in the global water budget. Who can tell me what percentage of freshwater is accounted for by groundwater?

Is it around 30%?

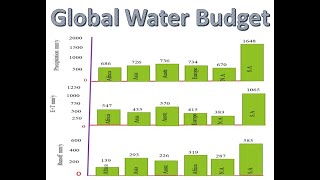
That's correct! Groundwater actually represents about 30% of all global freshwater. Can anyone tell me how much that contributes to the total water volume on Earth?

I think it's about 0.7% of total water.

Exactly! Groundwater makes up around 0.7% of total water resources. Groundwater is often referred to as a long-term reservoir because it has slow recharge and discharge rates. Why do you think that is important?

It means that we can't just use it up quickly; we need to manage it wisely!

Right! Sustainable management is key because over-extraction can lead to depletion. Let's summarize: groundwater accounts for about 30% of freshwater and has slow recharge rates, making its usage critical.
Aquifer Types
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let's talk about aquifer types. There are two main types: confined and unconfined aquifers. Can anyone define the difference?

A confined aquifer is surrounded by impermeable layers, while an unconfined aquifer is only partially covered, allowing direct recharge from above.

Well explained! Confined aquifers can be under pressure, which affects how groundwater is accessed. Why is this distinction important when considering groundwater depletion?

Because the recharge process is different, unconfined aquifers can be more vulnerable to contamination and quicker to deplete.

Exactly! So when discussing groundwater management, we need to understand both types of aquifers. Remember: confined equals pressure, and unconfined equals more vulnerability.
Groundwater Depletion
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's dive into the implications of groundwater depletion. Can anyone give an example of how over-extraction might impact local water budgets?

If a community relies on groundwater for irrigation and keeps extracting it without allowing it to recharge, they could face water shortages.

Exactly! Over-extraction can create imbalances in the local water supply, leading to issues like land subsidence and reduced stream flows. What do you think can be done to mitigate this?

Maybe implementing regulations on water withdrawal or promoting conservation practices.

Those are excellent strategies! Remember: sustainable management and protecting our groundwater is crucial for maintaining a healthy water budget.
Recharge Mechanisms
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

It’s also essential to understand recharge mechanisms for groundwater. How do you think groundwater is replenished?

I think it’s through processes like precipitation infiltrating the ground.

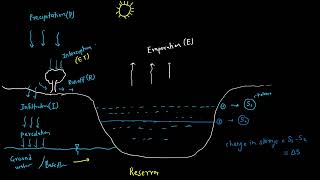
Correct! Precipitation, as well as surface water, can recharge aquifers. Why is this cycle important to maintain?

If we disrupt this cycle, we may not have enough groundwater available when we need it!

Right again! The dynamic between recharge and extraction must be in balance, or we risk serious depletion.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section discusses the importance of groundwater within the global water budget, highlighting its role as a long-term reservoir that supplies approximately 30% of freshwater resources. It also addresses issues surrounding aquifer types and the impacts of groundwater depletion.
Detailed
Groundwater in the Global Budget
Groundwater is a crucial component of the global water budget, representing about 30% of the world’s freshwater and approximately 0.7% of the total water volume. It functions as a long-term reservoir, characterized by slow recharge and discharge rates compared to other water sources. Key aspects of groundwater include its types, such as confined and unconfined aquifers, and the mechanisms that facilitate its recharge.
However, groundwater is facing significant challenges due to over-extraction, which can lead to depletion and create imbalances in local and regional water budgets. Such depletion highlights the importance of sustainable management practices to ensure long-term availability and protect this vital resource. Understanding these dynamics is essential for hydrologic modeling and water resource management.
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Overview of Groundwater
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Groundwater represents:
• ~30% of global freshwater
• ~0.7% of total water
Detailed Explanation
Groundwater makes up approximately 30% of the world's freshwater resources. This means that if you were to gather all the freshwater in the world, a significant portion, almost a third, comes from groundwater. However, groundwater accounts for only about 0.7% of all the water available on Earth, including oceans, ice, and other reservoirs. This highlights its importance as a resource for human activities.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a large pool of water where only a small section at the bottom is available for us to use. This small section represents groundwater. Even though it's a small part of the entire pool, it plays a crucial role in providing water for drinking, agriculture, and industries.
Characteristics of Groundwater
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
It's a long-term reservoir with slow recharge and discharge rates. Key aspects include:
• Aquifer types (confined/unconfined)
• Recharge mechanisms
• Over-extraction and its impact
Detailed Explanation
Groundwater is often referred to as a long-term reservoir because it is stored in aquifers, which can take a long time to recharge after water has been extracted. There are two types of aquifers: confined aquifers, which are trapped between layers of rock and cannot easily release water, and unconfined aquifers, which are open to the surface and can be recharged more quickly. The methods through which aquifers are replenished with water are called recharge mechanisms. One significant issue with groundwater is over-extraction; when too much water is withdrawn, it can lead to depletion and imbalance in local water budgets, making it harder for ecosystems and communities relying on this resource.
Examples & Analogies
Think of groundwater like a large sponge soaked with water, sitting in a tray. If you press down on it (over-extraction), it releases water quickly, but if you continue to press it without allowing it to soak back up (recharge), it becomes less effective at holding water in the long term. This can leave surrounding areas dry and uninhabitable.
Impact of Groundwater Depletion
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Groundwater depletion contributes to long-term imbalance in local and regional water budgets.
Detailed Explanation
When groundwater is depleted, it can create significant imbalances in the local and regional water budget. This depletion results in less water available for families, farms, and industries, which can lead to severe water shortages. It’s important to understand that groundwater isn't just a backup resource; it plays a critical role in maintaining the overall balance of water available in that area. Without proper management, depletion can lead to long-term sustainability issues.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a bank account that you keep withdrawing money from but aren't adding any funds to it. Eventually, your account will run dry. Groundwater works in a similar way. If we keep using it faster than we can refill it, soon there may be none left for us, just like the bank account scenario.
Key Concepts
-
Groundwater: A vital source of freshwater, accounting for 30% of global freshwater reserves.
-
Aquifer: Underground layers that store water, with confined and unconfined types.
-
Recharge mechanisms: Processes like precipitation that replenish groundwater supplies.
-
Over-extraction: Excessive use of groundwater leading to depletion.
Examples & Applications
In many regions, farmers rely on groundwater for irrigation, and if they fail to implement sustainable practices, they may experience severe water shortages during dry seasons.
In urban areas, groundwater extraction can lead to land subsidence, where the ground sinks due to the depletion of aquifers.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Groundwater, down below, slow to flow, keep it high, let it grow.
Stories
Imagine a garden that depends on deep roots for water. If you keep watering the top, the roots dry out and the garden wilts. Groundwater is like those roots—it needs time to replenish!
Memory Tools
Acronym W.A.R. (Water, Aquifer, Recharge) to remember key terms linked to groundwater management.
Acronyms
G.R.O.W. (Groundwater, Recharge, Over-extraction, Wise management) to recall the essentials of groundwater sustainability.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Groundwater
Water that is stored in underground aquifers, constituting about 30% of the world's freshwater.
- Aquifer
An underground layer of water-bearing rock that can yield water to wells and springs.
- Confined Aquifer
An aquifer that is trapped between impermeable layers of rock or sediment, often under pressure.
- Unconfined Aquifer
An aquifer that is open to the surface, allowing direct recharge from precipitation and surface water.
- Recharge
The process through which groundwater is replenished, mainly by precipitation infiltrating into the soil.
- Overextraction
The excessive withdrawal of groundwater beyond its natural replenishment rate.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
