Definition and Importance of Evaporation in Hydrology
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Evaporation
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're discussing evaporation, a crucial process in the hydrological cycle. Can anyone tell me what evaporation is?

Isn't it when water turns into vapor?

Exactly! Evaporation is defined as the process by which water changes from liquid to vapor. This happens due to factors like solar radiation, wind, and vapor pressure deficit.

Why is evaporation important in hydrology?

Great question! It's essential for managing water resources, like helping us design reservoirs and plan irrigation systems. Remember the acronym 'RIFW' for Reservoir, Irrigation, Flood routing, and Water availability—these are key areas dependent on evaporation data.

So it's not just about water disappearing?

That's right! It's about understanding how much water is lost and how we can manage that loss effectively. Evaporation affects everything from local weather patterns to global climate.

Can we measure evaporation directly?

Direct measurement is often challenging. That's why we use various methods and tools called evaporimeters for estimation. We'll dive deeper into those next time.

To summarize, evaporation is a significant process in hydrology impacting numerous water management practices. Remember its importance in reservoir operation, irrigation design, flood routing, and overall water availability.
Applications of Evaporation Data
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's explore how evaporation data is practically applied. Why do you think understanding evaporation is critical for reservoir operation?

To keep the water levels balanced?

Exactly! By knowing how much water evaporates, we can manage reservoir levels correctly. What about irrigation projects?

It helps farmers use the right amount of water?

Yes! Farmers can schedule irrigation based on evaporation rates to optimize water usage. This is crucial, especially in regions with limited water resources.

How does it relate to climate modeling?

Evaporation influences local climates, and accurate data contributes to understanding broader climate patterns. Think about the interconnectivity – water availability impacts agriculture, which in turn affects climate patterns.

So it's like a cycle?

Exactly! The hydrological cycle is deeply interwoven. To summarize, precise evaporation data supports effective reservoir management, irrigation design, flood routing, and aids in climate modeling.
Challenges in Measuring Evaporation
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, let's talk about measuring evaporation. Can anyone guess why measuring evaporation might be challenging?

Maybe it's hard to capture all the variables?

Exactly! Factors like wind, temperature, and solar radiation all affect evaporation rates. Precision depends on accurately measuring these parameters.

What if the area is too large?

Another great point! Direct measurements are not feasible over large areas, which is why we rely on indirect methods and tools like evaporimeters. There are many types of evaporimeters tailored to different settings.

But how accurate are these tools?

Their accuracy can vary! Typically, we apply a correction factor called the Pan Coefficient to account for differences between pan evaporation and actual evaporation. Each method has its strengths and limitations.

So we have to consider all these factors when planning?

Absolutely! It's critical to understand the context of evaporation measurement for practical applications. In summary, challenges in measuring evaporation stem from various environmental factors, requiring careful consideration and appropriate tools.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section defines evaporation as the conversion of liquid water to vapor; it is a critical aspect of the hydrological cycle. The accurate measurement of evaporation is crucial for effective water resource management, including reservoir operations and irrigation design.
Detailed
Definition and Importance of Evaporation in Hydrology
Evaporation is a key hydrological process wherein water transitions from its liquid state to vapor due to influences such as solar radiation, wind, and vapor pressure deficit. This phenomenon is a major loss component in the hydrologic budget of reservoirs, lakes, and ponds. Precise evaporation data is essential for various applications, including:
- Reservoir operation and planning: Understanding evaporation rates helps in managing water levels.
- Irrigation project design: Accurate evaporation estimates are vital for optimizing water use in agriculture.
- Flood routing: Knowing evaporation rates assists in predicting water flow and managing flood risk.
- Water availability studies: Evaporation data contributes to assessing how much water is available for consumption.
- Hydrological and climate modeling: For accurate modeling of water cycles and climate change effects, detailed evaporation data is required.
Thus, evaporation plays a fundamental role in hydrological studies and water management strategies.
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Definition of Evaporation
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
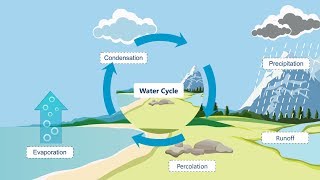
Evaporation is defined as the process by which water changes from liquid to vapor due to solar radiation, wind, and vapor pressure deficit.
Detailed Explanation
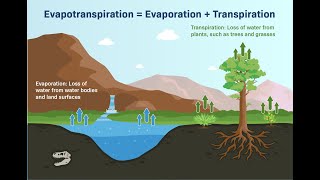
Evaporation is a natural process where water transforms from its liquid state into vapor, which is a gas. This transformation occurs primarily because of environmental factors such as solar radiation that heats the water, wind that helps to move the vapor away, and the vapor pressure deficit that drives the movement of water molecules into the air. Essentially, when energy is applied, usually from the sun, it gives water molecules enough energy to escape into the atmosphere.
Examples & Analogies
Think of evaporation like when you take a warm shower and the heat helps the water on your skin to turn into vapor. Just like the steam you see rising from your skin, evaporation occurs in larger water bodies as the sun heats the surface water, turning it into vapor.
Evaporation as a Major Loss Component
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
It is a major loss component in the hydrologic budget of reservoirs, lakes, and ponds.
Detailed Explanation
In hydrology, the hydrologic budget accounts for all the water entering and leaving a particular system. One significant aspect is evaporation, which accounts for the loss of water from reservoirs, lakes, and ponds. When water evaporates, it reduces the amount available for other uses—like irrigation or drinking water—thus influencing water supply and management strategies.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a cup of water left outside on a sunny day. Over time, you'll notice it becomes less full as water turns into vapor and leaves the cup. Similarly, lakes and reservoirs lose water to evaporation, influencing how much water is available for use.
Importance of Accurate Evaporation Data
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Precise evaporation data is essential for:
- Reservoir operation and planning
- Irrigation project design
- Flood routing
- Water availability studies
- Hydrological and climate modeling
Detailed Explanation
Understanding how much water is lost through evaporation is crucial for managing water resources effectively. For instance, if we plan to operate a reservoir, knowing the evaporation rates helps in deciding how much water to store and when to release it. Similarly, in agriculture, irrigation designs need to take evaporation into account to ensure crops receive adequate water. Additionally, in the context of floods and climate models, accurate evaporation data supports better predictions and planning to mitigate potential impacts.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a farmer planning their crops. If they know that evaporation is high during summer, they can schedule irrigation more effectively to ensure their crops don’t dry out. Just like you'd check the weather before planning a picnic, cities and engineers need to check evaporation rates to manage water resources wisely.
Key Concepts
-
Evaporation is a critical process in the hydrological cycle affecting water resource management.
-
Accurate evaporation data is essential for effective reservoir operation, irrigation, flood routing, and climate modeling.
Examples & Applications
Evaporation from a lake surface contributes to local humidity levels, potentially influencing regional weather patterns.
In agriculture, knowing the evaporation rate helps farmers schedule irrigation more efficiently to conserve water.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
From liquid to sky, evaporation is spry, a water cycle dance, watch it float and fly.
Stories
Once there was a lake named Luna, who loved to dance under the sun, evaporating into the sky, making clouds to deliver rain, nurturing fields and helping farmers run.
Memory Tools
Remember 'RIFW' for how evaporation helps: Reservoirs, Irrigation, Flood routing, Water availability.
Acronyms
E-Power
Evaporation
Planning
Operations
Water resources
Efficiency.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Evaporation
The process where water changes from liquid to vapor, influenced by solar radiation, wind, and vapor pressure deficit.
- Hydrological Cycle
The continuous movement of water on, above, and below the surface of the Earth.
- Reservoir
A large natural or artificial lake used for the storage of water.
- Evaporimeter
An instrument used to measure the rate of evaporation.
- Pan Coefficient
A correction factor used to adjust pan evaporation measurements to better reflect open water conditions.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
