Case Studies and Practical Implementations
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Indira Sagar Reservoir Overview
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's explore the Indira Sagar Reservoir as an effective case study in managing evaporation. This reservoir experiences significant evaporation rates, estimating around 2.3 meters annually. What method do you think they used for estimating this evaporation?

Maybe they used a common method? Like the pan evaporation method?

Good guess! They actually used the Penman method which accounts for different atmospheric conditions. Additionally, meteorological stations were set up for accurate data collection. Why do you think it's important to measure evaporation accurately?

To make better decisions about water usage and resource management?

Exactly! This data helps improve the strategies for reducing evaporation losses, such as suggesting windbreaks and floating PV strategies. Let's remember the key acronym 'PEM' for Penman, Estimation, Management.

PEM - That's easy to remember!

Great! So, to summarize, the Indira Sagar Reservoir uses Penman method estimations along with effective strategies like windbreaks to manage evaporation.
Pilot Study on Floating Covers
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Next, we have a fascinating pilot study on floating covers in Maharashtra. What do you think is the purpose of using monomolecular films in reservoirs?

To prevent evaporation losses!

Absolutely! These films can reduce evaporation by about 35%. However, every innovation faces challenges. What challenges do you think might arise from using these films?

Wind drift could be a problem, right?

Yes! Wind drift can cause operational issues. Developing creative solutions to minimize these challenges is crucial. Remember the phrase 'Cover and Conserve' for both the method and its purpose!

That sounds like a great way to remember it!

To sum it up, the pilot study showed promising results with monomolecular films but needs to address the challenges like wind drift.
NTPC Simhadri Floating Solar Project
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let's dive into the NTPC Simhadri Floating Solar Project. Why might this project be significant in the context of reservoir evaporation?

It's producing renewable energy and also reducing evaporation at the same time.

Exactly! The dual benefits of reducing evaporation while generating power make it a stellar example of innovation. What strategy do you think led to effective evaporation management here?

Using floating solar panels helps shade the water and reduce evaporation?

Yes! Floating solar panels are a modern approach that helps keep water cool and reduces evaporation. Remember the mnemonic 'E-G-S': Energy Generation, Sustainability, to link the purpose and benefits.

'E-G-S,' got it!

In conclusion, the NTPC Simhadri project exemplifies how innovative technology can be integrated into traditional water resource management.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
In this section, notable case studies illustrate practical implementations aimed at reducing reservoir evaporation. The examples highlight various strategies, including meteorological assessments and innovative solutions like floating solar projects and monomolecular film applications.
Detailed
Case Studies and Practical Implementations
This section provides real-world examples to illustrate the effective management of reservoir evaporation due to its significant implications for water resource management. The following case studies highlight different strategies implemented to mitigate evaporation losses:
1. Indira Sagar Reservoir (Madhya Pradesh)
- Estimated Annual Evaporation: Approximately 2.3 m.
- Methods Used: Utilized meteorological stations and the Penman method for accurate evaporation estimation.
- Suggested Strategies: Implementation of windbreaks and floating solar PV strategies to reduce evaporation percentages.
2. Pilot Study on Floating Covers in Maharashtra
- Focus: Trials of monomolecular films to cover reservoir surfaces.
- Results: Achieved about a 35% reduction in evaporation losses.
- Challenges Faced: Operational issues due to the influence of wind drift.
3. NTPC Simhadri Floating Solar Project
- Project Overview: A 25 MW floating solar power project covering a reservoir.
- Benefits: Demonstrated significant reduction in evaporation while simultaneously producing renewable energy.
These case studies underline the potential of integrating engineering and innovative technologies into sustainable water resource management strategies.
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Indira Sagar Reservoir Overview
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Indira Sagar Reservoir (Madhya Pradesh)
• Estimated annual evaporation: ~2.3 m
• Used meteorological stations and Penman method for estimation
• Suggested windbreak and floating PV strategies
Detailed Explanation
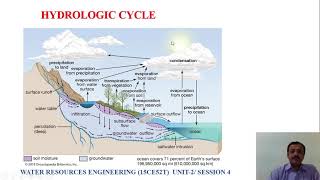
The Indira Sagar Reservoir, located in Madhya Pradesh, has an estimated annual evaporation rate of approximately 2.3 meters. To measure this evaporation accurately, meteorological stations were set up around the reservoir, employing the Penman method for estimation. This method calculates evaporation based on factors like temperature, humidity, and wind speed. Additionally, strategies such as constructing windbreaks and integrating floating photovoltaic panels (solar panels that float on the water) were proposed to reduce evaporation losses.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the Indira Sagar Reservoir as a large swimming pool under the sun. If it's windy or hot, the water level decreases faster, similar to how the evaporation makes the pool lose water. So, engineers installed windbreaks, like tall fences, around the pool to reduce the breeze and added floating solar panels, akin to covers that also produce energy while shielding the water from the sun.
Pilot Study on Floating Covers in Maharashtra
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Pilot Study on Floating Covers – Maharashtra
• Monomolecular film trials showed ~35% evaporation reduction
• Faced operational issues due to wind drift
Detailed Explanation
A pilot study conducted in Maharashtra tested floating covers made of monomolecular films on the surface of water bodies. These films effectively reduced evaporation by about 35%, demonstrating a significant improvement in water conservation. However, the study also encountered challenges, particularly with wind drift, which caused the films to move unpredictably and diminish their effectiveness as a barrier against evaporation.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine trying to keep a bowl of soup warm by placing a thin film on top. If there's a breeze, the film might fly away, and the soup cools down faster. Similar issues were observed in Maharashtra where the wind caused the floating films to drift away, highlighting the importance of stability in protecting water bodies from evaporation.
NTPC Simhadri Floating Solar Project
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- NTPC Simhadri Floating Solar Project
• 25 MW floating solar project over reservoir
• Significantly reduced evaporation while generating renewable energy
Detailed Explanation
The NTPC Simhadri Floating Solar Project is a 25 MW solar energy initiative that operates atop a reservoir. This project serves a dual purpose: it generates renewable energy while also significantly decreasing water evaporation from the reservoir’s surface. By covering the water body with solar panels, it reduces the sunlight exposure, thereby lowering the evaporation rate and, at the same time, contributes to clean energy production.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a greenhouse where plants are shaded from direct sunlight, reducing their need for water. Similarly, the solar panels act as a shade for the reservoir, protecting the water underneath from evaporating too quickly, while also producing energy, akin to how crops in a greenhouse thrive with less water stress.
Key Concepts
-
Reservoir Evaporation: The phenomenon of water loss from a reservoir's surface to the atmosphere.
-
Penman Method: A scientific approach integrating various factors for accurate evaporation estimation.
-
Floating Solar Projects: Initiatives combining renewable energy generation with evaporation control.
-
Windbreaks: Barriers used to minimize evaporation from reservoirs by influencing wind patterns.
Examples & Applications
The Indira Sagar Reservoir uses the Penman method for evaporation estimation and implements floating PV strategies.
In Maharashtra, a pilot study demonstrated a 35% reduction in reservoir evaporation using monomolecular films.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
To save the water by the hour, cover it with films, it's our power.
Stories
Imagine a large sunlit reservoir losing its water fast - until floating solar panels arrived, shading the surface and generating renewable energy, saving both water and the environment.
Memory Tools
Remember 'C.E.W.' - Covers, Energy, Water for floating solar projects.
Acronyms
P.E.M. for Penman, Estimation, Management highlights its focus.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Evaporation
The process by which water is converted from a liquid into vapor.
- Penman Method
A method used to estimate evaporation combining radiation and aerodynamic factors.
- Floating Covers
Covers placed on water surfaces to reduce evaporation and may include various materials.
- Windbreaks
Physical barriers that reduce wind speed and thereby decrease evaporation rates.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
