Relationship Between Duty and Delta
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Duty and Delta
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, let's discuss how Duty and Delta relate to each other in irrigation planning. Can anyone tell me what Delta represents?

Delta is the depth of water required by a crop over its growth period, right?

Exactly! Now, what about Duty? Who can explain that?

Duty is the area that can be irrigated by a certain amount of water discharge!

Well done! Remember, both parameters are crucial for efficient irrigation management. A helpful way to remember this is that Duty tells us what area we can cover, while Delta tells us how much water crops need. Let's look more deeply into the relationship between the two.
Mathematical Relationship
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

The relationship is mathematically expressed as Δ = (8.64 × B) / D. What do you think the significance of the number 8.64 is?

Isn't it a constant that helps convert discharge into depth over area?

Correct! It allows us to maintain consistency in our calculations. Can any of you summarize what the formula tells us?

As Delta increases, Duty must decrease if the base period remains constant.

Exactly! This shows how water must be allocated efficiently in irrigation systems. Let’s move on to practical applications of this formula.
Real-World Applications
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Understanding the Duty-Delta relationship is critical for designing irrigation canals. How might we apply this in a real-world scenario?

If we know the base period for a crop and its Delta, we can determine the amount of land that can be irrigated with a specific discharge.

Exactly! This relationship helps farmers plan their crop acreage smartly. What if the duty is less than anticipated?

They would need to adjust their irrigation methods or find a way to increase water efficiency.

Great insight! Efficient water management is essential for sustainability in agriculture. Let’s do a quick recap of what we learned today.
Importance of Duty and Delta
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Why do you think understanding Duty and Delta is crucial for civil engineers?

To optimize the use of available water resources in agriculture!

Yes, and it also helps in designing effective canal systems! Remember the acronym D.E.S.I.G.N: Duty ensures sustainability, Efficiency, and management of water resources in irrigation systems. Can anyone think of another reason?

It definitely helps in maximizing crop yields while minimizing water wastage!

Exactly! These concepts are essential not just for engineering but also for farmers and the ecosystem. Excellent discussions today!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The relationship between Duty and Delta is expressed mathematically and is vital for irrigation planning. Understanding how to balance the area irrigated with water supplied helps maximize agricultural efficiency and minimizes water loss.
Detailed
In irrigation engineering, the relationship between Duty (D) and Delta (Δ) is paramount for effective water management. It is mathematically represented as Δ = (8.64 × B) / D, where Δ is the depth of water required, B is the base period in days, and D is the area that can be irrigated per unit discharge. This relationship guides engineers in designing irrigation systems to ensure that crops receive the necessary water without wastage. This understanding aids in balancing the economic viability of agricultural operations with ecological sustainability.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Basic Formula for Duty and Delta
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
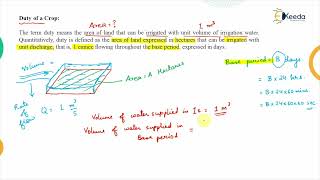
The relationship between Duty (D) and Delta (Δ) is essential in irrigation planning and is expressed as:
Δ = 8.64 × B / D
Where:
- Δ = Delta in metres
- B = Base period in days
- D = Duty in hectares/cumec
- 8.64 = Constant (derived from converting discharge to depth over area)
Detailed Explanation
This formula connects Delta (the depth of water needed) with Duty (the area that can be irrigated with a given water discharge). Here, the Delta is calculated using the base period (B) in days and Duty (D) in hectares per cumec. The constant 8.64 is used to convert the water flow rate into a usable depth measurement over an area, indicating that the relationship isn't random but mathematically defined.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine measuring how much water your garden needs. The more days you water (base period), the more water is needed overall. If you have a hose (duty) that can water a certain section of your garden, the Delta helps you understand how deep the water is needed based on how long you water the plants.
Derivation of the Formula
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Derivation:
Let 1 cumec of water run for B days. Volume = 1 × 86400 × B cubic metres. If this irrigates D hectares, the depth of water = (86400 × B) / (D × 104)
Detailed Explanation
To derive the relationship, consider that if 1 cumec of water is supplied for B days, we calculate the total volume of water supplied. This volume is used to irrigate D hectares of land. The depth of water supplied to each hectare is then derived by dividing the total volume by the area irrigated and converting the units to get depth in meters.
Examples & Analogies
Think of running a tap for a day in your backyard. The total volume of water that flows can be calculated, and if you spread that water over your garden, the formula helps you find out how deep the water would create a puddle across the entire area. It quantifies the relationship of time (how long the tap runs) to the depth of water on your land.
Key Concepts
-
Duty and Delta are critical for irrigation efficiency.
-
Delta indicates water need; Duty indicates irrigated area.
-
The formula Δ = (8.64 × B) / D is key to planning.
Examples & Applications
An irrigation canal has a discharge of 10 cumecs and irrigates 20,000 hectares. The Duty can be calculated as D = A / Q = 20,000/10 = 2000 hectares/cumec. If the base period is 120 days, Δ is found using Δ = (8.64 × 120) / 2000 = 0.5184 meters or 51.84 cm.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In irrigation plots, Duty's the area sought, Delta's the depth that the crop has brought.
Stories
Imagine a farmer named Delta who wanted to irrigate his field (Duty). He noticed that the amount of water he had could cover a particular area, and he figured out how deep each crop needed that water.
Memory Tools
Remember 'D&D': Duty shows the Area; Delta shows the Depth.
Acronyms
D.E.S.I.G.N
Duty Ensures Sustainability In Good Nature.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Duty (D)
The area of land that can be irrigated with a unit discharge of water flowing continuously during the entire base period of a crop.
- Delta (Δ)
The total depth of water required by a crop during the entire base period, from sowing to harvesting.
- Base Period (B)
The duration in days over which a crop requires water.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
