Integration of Infiltration and Consumptive Use in Hydrologic Planning
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Importance of Infiltration and Consumptive Use
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we are going to explore the importance of integrating infiltration and consumptive use in hydrology. Can anyone explain what infiltration is?

It's the process of water entering the soil from the surface!

Exactly! And what about consumptive use? Who can define that?

It's the amount of water used by plants and not returned to the original source, right?

Right on! Together, these concepts are crucial for managing our water resources effectively.
Applications of Infiltration and Consumptive Use
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's dive into the applications of these concepts. How does understanding infiltration and consumptive use help in irrigation?

It helps design systems that use the right amount of water based on crop needs!

Great insight! It also aids in scheduling irrigation. How does that factor into drought management?

If we know how much water is used, we can manage it better during dry periods.

Exactly! Accurately assessing groundwater recharge through these processes can mitigate drought impacts.
Hydrologic Models and Water Budgeting
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

In hydrologic models, why is it important to address infiltration losses and consumptive use simultaneously?

So we can create accurate water budgets?

Correct! Accurate water budgeting ensures that we properly allocate water resources based on needs and availability. Can someone share how this can prevent erosion?

By managing runoff, we can reduce soil erosion caused by excessive water flow.

Exactly! Integrating these components allows for better overall resource management.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Effective hydrologic planning requires an understanding of both infiltration and consumptive use, as they play critical roles in irrigation design, drought management, and groundwater assessments.
Detailed
Integration of Infiltration and Consumptive Use in Hydrologic Planning
Both infiltration and consumptive use are essential components in hydrology that influence water resource management. Understanding how water infiltrates into the soil determines how efficiently it can recharge groundwater and affect surface runoff. Meanwhile, consumptive use quantifies how much water is utilized by plants and lost through evaporation. This integration is vital for designing efficient irrigation systems, managing water scarcity, and preventing runoff-related erosion. Properly addressing both aspects leads to comprehensive water budgeting and effective resource planning by allowing for scheduling irrigation according to crop needs and soil moisture levels.
Youtube Videos

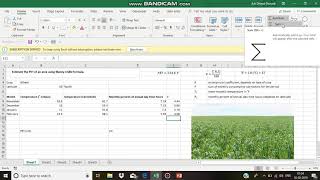







Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Importance of Infiltration and Consumptive Use
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Both infiltration and consumptive use are key for:
- Designing efficient irrigation systems
- Managing drought and water scarcity
- Assessing groundwater recharge
- Preventing runoff-related erosion
- Scheduling irrigation based on crop water needs and soil moisture replenishment
Detailed Explanation
This chunk outlines the significance of understanding infiltration and consumptive use in water management. Infiltration refers to how water enters the soil, while consumptive use is how water is used or lost through evaporation and transpiration. By combining knowledge of both, water resource managers can effectively design irrigation systems that minimize water waste and support crops effectively, especially in regions facing drought. For instance, when irrigation is scheduled based on actual soil moisture and plant needs rather than generic schedules, water use becomes more efficient.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a gardener trying to keep a flower bed healthy. If they water every day without checking the soil's moisture levels, they may overwater, leading to water waste and drowning the plants. Conversely, if they check the soil first and only water when necessary, the plants thrive, using the right amount of water. This analogy highlights the importance of understanding both infiltration (how much water the soil can take) and consumptive use (how much water the plants actually need).
Hydrologic Models and Water Budgeting
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Hydrologic models must simultaneously address infiltration losses and consumptive use to provide accurate water budgeting and resource planning.
Detailed Explanation
This chunk emphasizes the role of hydrologic models in integrating both infiltration and consumptive use data. To create accurate water budgets—which track the input and output of water within a system—hydrologists need to consider how much water infiltrates into the soil and how much is consumed by plants. This integration is vital for making informed decisions in managing water resources, especially in planning for future water needs and potential shortages.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a hydrologist as a chef preparing a recipe. The recipe must balance all ingredient components (water input from various sources) to achieve the desired dish (healthy ecosystems, sufficient water supply). Just as a chef can't ignore the importance of both spices (infiltration) and cooking time (consumptive use) to create a delicious meal, hydrologists can't neglect either factor in order to ensure a sustainable water supply.
Key Concepts
-
Integration of Infiltration and Consumptive Use: Necessary for efficient water resource management.
-
Groundwater Recharge: Critical for maintaining sustainable water supplies.
-
Water Budgeting: Essential for effective water resource planning.
Examples & Applications
Using infiltration data to develop a drought management plan.
Designing an irrigation system that considers both consumptive use and rainfall.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Infiltration is water's cute migration, sinking down with hydration.
Stories
Imagine a thirsty plant that drinks water through its roots, using it up, not sending it back!
Memory Tools
I-C-E: Infiltration Creates Efficient water management.
Acronyms
RUG
Remember Underground groundwater from rain.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Infiltration
The process by which water enters the soil from the ground surface.
- Consumptive Use
The portion of water used by plants and lost through evaporation that is not returned to the water source.
- Groundwater Recharge
The process of water moving downward into underground aquifers.
- Water Budgeting
The calculation and management of water availability and usage in a specific area.
- Irrigation Management
The practice of efficiently delivering water to crops to ensure optimal growth.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
