Duty and Delta Relationship
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding Duty (D)
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we are going to dive into the concept of Duty in irrigation. Can anyone tell me what Duty means?

Isn't Duty the area irrigated by a specific amount of water?

Exactly! Duty is the area that can be irrigated by a unit discharge of water over a specific period. Remember the formula: D = Area / Discharge.

So, if we have a higher duty, does that mean we are using water more efficiently?

That's correct! A higher duty reflects more effective use of water. Let's summarize: Duty indicates the efficiency of water use in irrigation.
Understanding Delta (Δ)
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's talk about Delta. Can someone explain what Delta represents in irrigation?

Delta is the total depth of water a crop requires during the base period, right?

Exactly! And to calculate it, we use the formula: Δ = (8.64 × B) / D, where B is the base period in days and D is the duty. Why do you think it's important to know Δ?

It helps in understanding the total water needed, which can aid in planning our irrigation better.

Wonderful! By knowing Delta, we can manage our water resources more effectively.
Duty and Delta Relationship
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now that we understand Duty and Delta separately, how do you think they relate to each other?

If you have a low Duty, then your Delta must be high to meet the crop's water requirements over that period, right?

Exactly! When Duty is lower, Delta increases to compensate for the reduced area being irrigated with available water. This relationship is crucial for optimizing irrigation systems.

So, can adjusting either Duty or Delta improve water management?

Yes, adjusting these parameters allows us to tailor our irrigation strategies effectively. Always remember: balance is key!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section outlines the concepts of Duty (the area irrigated by a specific discharge) and Delta (the water depth needed across a base period). It also provides the equations and context for understanding their interactions and effects on irrigation planning and management.
Detailed
Duty and Delta Relationship
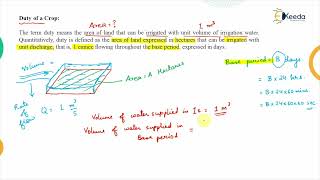
The Duty (D) and Delta (Δ) Relationship in irrigation provides essential insights into how effectively water can be allocated for agricultural practices. Duty (D) is defined as the area that can be irrigated per unit discharge of water over a specified period, with the formula:
D = Area / Discharge
This concept is vital because it indicates the efficiency of water use in the field.
On the other hand, Delta (Δ) refers to the total depth of water necessitated for a crop for the duration of the base period, calculated as:
Δ = (8.64 × B) / D
where B is the base period in days, and D is the duty in hectares per cubic meter. This relationship helps in determining the water requirements for crops over time, thus enhancing irrigation scheduling and management.
Understanding Duty and Delta allows for effective planning and resource allocation, ultimately leading to better agricultural productivity and sustainability.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Duty (D)
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Duty (D)
Amount of land irrigated by a unit discharge of water in a base period.
Area
D =
Discharge
Detailed Explanation
The duty (D) is a crucial concept in irrigation management. It represents the amount of land that can be irrigated by a specific flow of water (discharge) over a defined period called the base period. To calculate duty, you divide the total area of land that needs irrigation by the amount of water flow (discharge) available. This helps farmers and water managers understand how efficiently water is being used to irrigate their crops.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine you have a garden that requires watering. If you have a hose that can deliver water at a rate of 10 liters per minute, and your garden covers an area of 100 square meters, the duty can help you determine how much area you can effectively water with that hose. If you know that with that flow rate, you can adequately water 100 square meters in an hour, it helps you set clear expectations for maintaining healthy plants.
Delta (Δ)
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Delta (Δ)
Total depth of water required by the crop during the entire base period.
Δ = 8.64 × B
Where:
- B = Base period in days
- D = Duty in ha/cumec
Detailed Explanation
Delta (Δ) refers to the total amount of water needed by crops during the entire irrigation cycle, referred to as the base period. The formula for delta shows that it is directly proportional to the number of days the crop is growing during that time. To calculate delta, you can multiply a constant (8.64) by the length of the base period in days. This information is essential for planning and determining irrigation needs, ensuring that crops receive sufficient water throughout their growth stages.
Examples & Analogies
Think of delta as a water supply plan for your farm. If you are growing crops that need water spread out over 30 days, using the delta formula helps you figure out how much water you need to deliver each day to keep the plants healthy. Just like planning a vacation budget over several days, delta helps in budgeting the water required effectively over a growing period.
Key Concepts
-
Duty (D): Amount of land irrigated by a unit discharge over a base period.
-
Delta (Δ): Total water depth required by a crop during the base period.
Examples & Applications
If a field has a Duty of 10 hectares per cubic meter per day, then it can be irrigated effectively with a specific discharge.
For a base period of 15 days and a Duty of 10 hectares/cumec, the Delta can be calculated as Δ = (8.64 × 15) / 10, which equals 12.96 mm.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
For every drop of duty, there's a delta that must flow, to keep the crops growing, and ensure they glow.
Stories
Imagine a farmer named Duty who waters his crops with the perfect amount of water. But one day, he realizes that less water means he needs to find a bigger Delta to meet his crops' needs.
Memory Tools
Remember D for Duty as in 'Drive' and Δ for Delta as in 'Depth' - together they navigate irrigation!
Acronyms
D (Duty) = Area / Discharge and Δ (Delta) = (8.64 × B) / D - remember the formulas to ace irrigation!
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Duty (D)
The amount of land irrigated by a unit discharge of water in a specified period.
- Delta (Δ)
The total depth of water required by the crop during the entire base period.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
