Comparison Between Kennedy and Lacey Theories
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Overview of Kennedy's Theory
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we begin with G.L. Kennedy's theory. Can anyone tell me what you remember about it?

I think it's about how channels can maintain equilibrium based on water flow and sediment.

Exactly! Kennedy's theory focuses on maintaining equilibrium specifically in terms of sediment transport being balanced with sediment supply. His key equation is V = m(y)^0.64. Can someone explain the terms used in this equation?

V is the mean velocity, m is the critical velocity ratio, and y refers to the flow depth.

Great job, Student_2! Remember, this theory has its limitations, primarily that it's not generalizable beyond specific regions like the Punjab system. So, keep that in mind as we transition to Lacey's theory.
Overview of Lacey's Theory
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let's explore Lacey's theory. What do you all know about it?

I think it's broader and more commonly used in different canal systems.

That's right, Student_3! Lacey's theory incorporates comprehensive geometry - depth, width, and slope, which allows it to adapt to various conditions. Key aspects include the silt factor and equations for velocity and area. Can anyone provide a specific equation from Lacey’s theory?

The velocity equation is V = (140 * Qf)^(1/2).

Well done, Student_4! This shows how Lacey's theory not only considers depth but also the influence of sediment size through the silt factor, making it more versatile.
Key Differences Between the Theories
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's recap some critical differences between the two theories. How does Kennedy's approach differ from Lacey's?

Kennedy focuses only on the depth and is more theoretical, while Lacey includes full geometry and is empirical.

Spot on! Kennedy's theory is limited to sediment suspended by bed eddies, while Lacey incorporates the silt factor, making it applicable to a variety of alluvial conditions. Why do you think these differences matter?

I guess it affects how engineers design channels in different environments.

Exactly! Understanding these distinctions ensures that engineers choose the right model for predicting channel behaviors.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The section details the methodologies and assumptions behind Kennedy's semi-theoretical approach and Lacey's empirical theory, noting key differences such as sediment considerations and applicability across various conditions. The discussion emphasizes the transition from Kennedy’s focus on depth-related modeling to Lacey’s comprehensive geometry, making it applicable to broader scenarios in canal design.
Detailed
Comparison Between Kennedy and Lacey Theories
The theories of G.L. Kennedy (1895) and R.L. Lacey (1930) provide differing frameworks for understanding regime channels. Kennedy's theory is primarily semi-theoretical, relying on depth-related metrics and observations from the Upper Bari Doab Canal. It focuses on the critical velocity in suspension but does not account for sediment concentration or movement explicitly, making its applicability limited to regions similar to the Punjab canal system.
In contrast, Lacey's theory is empirical and encompasses a broader approach, taking into account a full range of geometrics—depth, width, and slope—while explicitly incorporating the silt factor. This makes Lacey's theory more versatile and applicable to various Indian alluvial canals, providing a robust framework for hydraulic engineers. The comparison highlights the evolution of thought in understanding sediment transport and channel stability, marking a critical transition in hydraulic engineering practices.
Youtube Videos




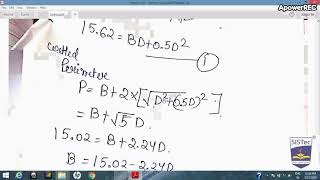




Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Type of Theory
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Kennedy's Theory: Semi-theoretical
- Lacey's Theory: Empirical
Detailed Explanation
Kennedy's theory is described as semi-theoretical because it is based on a combination of theoretical principles and specific observations. This means it relies on some established scientific ideas but is not fully grounded in widely applicable theory. In comparison, Lacey's theory is empirical, meaning that it is based on practical observations and experimental data from real canal systems. This makes Lacey's findings more broadly applicable in different contexts.
Examples & Analogies
Think of Kennedy's theory like a recipe where you have some guidelines but also have to guess some measurements based on experience, while Lacey's theory is like a well-tested recipe that has been refined through numerous trials to create a consistent and delicious dish.
Sediment Consideration
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Kennedy's Theory: Only eddy-based suspension included
- Lacey's Theory: Silt factor explicitly considered
Detailed Explanation
In Kennedy’s theory, sediment movement is simplified to the concept of suspension caused by eddies, which are swirls created by the flow of water. This means it focuses only on how sediment stays suspended in the water without considering other factors influencing sediment transport. On the other hand, Lacey’s theory takes a more comprehensive approach by explicitly including the silt factor, which accounts for the sediment size and type. This allows for a more detailed understanding of how different sediments behave in flowing water.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine trying to carry different types of balls through water. For Kennedy's theory, it's like only considering how a basketball floats in the water, while Lacey's theory takes into account all ball types—including tennis balls, which sink differently—demonstrating the importance of various sizes and weights in water transport.
Channel Geometry Consideration
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Kennedy's Theory: Only depth-related
- Lacey's Theory: Full geometry (depth, width, slope)
Detailed Explanation
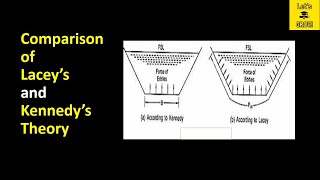
Kennedy's theory focuses solely on the flow depth of the channel, meaning it doesn't fully account for other geometrical features such as width and slope. This limitation makes the theory less flexible and applicable to different channel shapes. Lacey's theory, in contrast, examines the entire geometry of the regime channel, which includes the relationship between depth, width, and slope. This holistic approach allows for more precise predictions of channel behavior under varying conditions.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a swimming pool where Kennedy's theory looks only at how deep the water is, ignoring how wide or sloped the sides are, whereas Lacey's theory evaluates all these dimensions to understand how the pool holds water and how it might spill over during a rain, giving a complete picture.
Applicable Conditions
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Kennedy's Theory: Primarily for Punjab canal system
- Lacey's Theory: More general for Indian alluvial canals
Detailed Explanation
Kennedy's theory was developed specifically based on the conditions in the Punjab canal system, which means it might not apply well in other contexts with different soil, water flow, or sediment conditions. Lacey's theory is designed to be more adaptable and is applicable to a variety of alluvial canal systems across India, making it more useful for engineers dealing with diverse environments.
Examples & Analogies
If Kennedy's theory is like a specialized tool designed for a specific type of job—like a wrench that only works on particular bolts—Lacey's theory is like a multi-tool that can be applied in various situations, making it versatile and widely accepted in engineering practices.
Key Concepts
-
Kennedy’s Theory: Focuses on depth-related calculations and is semi-theoretical.
-
Lacey’s Theory: Empirical with a comprehensive geometric approach, incorporating the silt factor.
Examples & Applications
Kennedy's equation V = m(y)^0.64 illustrates the depth dependence of sediment transport.
Lacey's equation for velocity incorporates both discharge and sediment factor, making it more adaptable.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Kennedy's semi in-depth flow, Lacey's shapes for all to know.
Stories
Imagine two engineers walking along a canal. Kennedy looks closely at depth, while Lacey sees the entire landscape, adjusting his calculations to fit various terrains.
Memory Tools
K for Kennedy = 'K' for specific, L for Lacey = 'L' for all encompassing.
Acronyms
K and L
Keep in mind Kennedy is limited (K)
while Lacey is logical (L) for varied canals.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Regime Channel
An alluvial channel that maintains dynamic equilibrium between flowing water and sediment load.
- Empirical Theory
A method based on observations and experiments rather than purely theoretical models.
- SemiTheoretical
An approach that combines theoretical assumptions with empirical observations.
- Silt Factor
A coefficient that relates sediment size to hydraulic radius in channel design.
- Critical Velocity Ratio (m)
A parameter in Kennedy's theory representing the critical velocity for sediment transport.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
