Meiosis
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Meiosis
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today we're exploring meiosis! This is a remarkable process where a single cell undergoes division to produce gametes. Can anyone tell me why this process is crucial for sexual reproduction?

Is it because it results in sperm and egg cells that can combine to create new life?

Exactly! These gametes are haploid, meaning they have half the number of chromosomes compared to somatic cells. What's the chromosome number for human gametes?

They have 23 chromosomes.

Great! So when they combine during fertilization, what happens to the chromosome number?

It goes back to 46 chromosomes!

Correct! This is how genetic continuity is maintained across generations. Remember, meiosis creates diversity, which is key for evolution.
Stages of Meiosis
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's dissect the stages of meiosis. Who can describe what happens during Meiosis I?

In Meiosis I, homologous chromosomes pair up and can exchange segments through crossing over, right?

Absolutely! This crossing over is vital for genetic variability. What follows after this pairing?

Then they are separated into two cells.

Correct! And after Meiosis I, what do we call the cells that result?

They are haploid cells.

Exactly! Next, we proceed to Meiosis II without further DNA replication. Who can tell me the outcome of this second division?

It creates four haploid gametes!

Spot on! This process is crucial for genetic diversity and the continuous evolution of species.
Significance of Genetic Variation
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's focus on the significance of genetic variation created by meiosis. Why is this variation so important?

It helps adapt populations to changing environments!

Exactly! The genetic diversity arising from meiosis promotes adaptability. Can anyone think of an example in nature where this might be beneficial?

In species that face diseases, having a variety of genetic traits can mean some individuals are resistant!

Right! This diversity can determine survival in the face of challenges like pathogens or climate changes. It truly underscores the power of meiosis!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
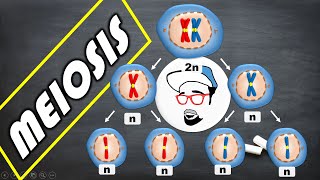
Meiosis occurs in reproductive organs and involves two rounds of division, resulting in four genetically diverse haploid cells. This chapter explores its stages, significance in genetics, and how it introduces variation among gametes.
Detailed
Meiosis
Meiosis is distinct from mitosis and is crucial for sexual reproduction. It occurs in the reproductive organs, where it produces gametes—sperm and eggs in animals, and pollen and ovules in plants. The process consists of two consecutive divisions: Meiosis I and Meiosis II.
In the first meiotic division (Meiosis I), homologous chromosomes pair up and undergo recombination or crossing over, leading to genetic variation. The homologous pairs are then separated into two daughter cells, each containing half the original chromosome number, hence producing haploid cells. In the second meiotic division (Meiosis II), these two cells divide again without further DNA replication, resulting in four unique haploid gametes. The introduction of genetic variability through recombination during Meiosis I is of particular importance as it enhances the evolutionary adaptability of species.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Introduction to Meiosis
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Meiosis
● Occurs in reproductive organs.
● One cell divides twice to form four haploid cells (gametes).
● Introduces variation through recombination.
Detailed Explanation
Meiosis is a type of cell division that specifically occurs in the reproductive organs, such as ovaries and testes. It is distinct from mitosis, as it results in four cells instead of two. These cells are haploid, which means they contain only half the number of chromosomes (one set). In humans, for example, where somatic (body) cells have 46 chromosomes (23 pairs), the gametes produced through meiosis will have just 23 chromosomes. This reduction is crucial for sexual reproduction because when the sperm and egg combine during fertilization, the diploid chromosome number is restored. Additionally, meiosis introduces genetic variation through a process called recombination, where sections of DNA are exchanged between paired chromosomes.
Examples & Analogies
You can think of meiosis like a dance competition where dance couples switch partners. Each couple represents a cell, and by switching partners, the dancers create new combinations of pairs (similar to genetic variation). Just as the new dance pairs might have unique choreography, the resulting gametes from meiosis have different genetic setups.
Stages of Meiosis
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
🔹 Example:
A testis cell with 46 chromosomes undergoes meiosis → each sperm has 23 chromosomes.
Detailed Explanation
To understand how meiosis works, consider how a testis cell with 46 chromosomes goes through the process of meiosis. It first undergoes replication, where each chromosome is duplicated, resulting in pairs. Then, the cell divides twice: the first division separates the chromosome pairs, and the second division separates the sister chromatids, resulting in four unique sperm cells, each with 23 chromosomes. This two-step division allows not only for the halving of the chromosome number but also facilitates genetic diversity through recombination that occurs in the first meiotic division.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a factory producing different types of candy bars. The factory starts with a variety of ingredients (chromosomes). In the first stage, they mix these ingredients to create pairs (duplicate them). Then, in the second stage, they create different combinations of these ingredients to produce unique candy bars (the gametes). Just like the factory ends up with a range of candy variations, meiosis produces sperm or egg cells that contribute genetic diversity.
Key Concepts
-
Meiosis is a two-part cell division process that produces haploid gametes.
-
Meiosis introduces genetic variation through crossing over during Meiosis I.
-
The outcome of meiosis is four genetically unique haploid cells.
Examples & Applications
In humans, meiosis in males results in four sperm cells from one testicular cell, each with 23 chromosomes.
In females, meiosis in the ovaries produces one ovum and three polar bodies that usually degenerate.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Meiosis splits, not once but twice, leading to gametes that are nice.
Stories
Imagine two friends, DNA and Proteins, teaming up during a dance of Meiosis. They swap dance partners (crossing over), creating new and diverse dance styles among the gametes!
Memory Tools
MFG - Mitosis For Growth, Meiosis For Gametes.
Acronyms
MEIOSIS - Making Every Individual Original and Special through division.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Haploid
Cells that contain one complete set of chromosomes (n).
- Gametes
Reproductive cells, such as sperm and eggs, that are produced through meiosis.
- Crossing Over
The exchange of genetic material between homologous chromosomes during meiosis.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
