Effects of Pollution
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Health Problems Due to Pollution
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Welcome, class! Today we’re discussing the effects of pollution on our health. Can anyone think of a health problem caused by pollution?

Asthma! I heard that air pollution can trigger it.

Exactly! Air pollutants can cause and worsen asthma. Remember, we can use the acronym ‘AIR’ to recall some health problems: Ashtma, Infections, and Respiratory diseases. What about other issues?

I think bronchitis is another one.

Good point! Chronic exposure to air pollution often leads to bronchitis. Lastly, who can tell me an example of a skin disease related to pollution?

Perhaps dermatitis due to polluted water?

Correct! Pollution can cause various skin diseases. To summarize, pollution can lead to asthma, bronchitis, and skin issues.
Environmental Damage
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Isn't it caused by air pollutants like sulfur dioxide that mix with rain?

Yes! Acid rain forms when those pollutants react with water in the atmosphere. It can harm forests and water bodies. Can someone explain the consequences of ozone layer depletion?

It allows more UV rays to reach the Earth, which can cause skin cancer.

Right! Increased UV radiation has serious health implications. Overall, pollution leads to significant environmental damage including acid rain and ozone layer depletion.
Global Warming
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Next, let's discuss global warming. How do you think pollution is linked to this issue?

Greenhouse gases, like CO2, trap heat in the atmosphere.

Exactly! Increased levels of greenhouse gases from pollutants result in higher global temperatures. Thus, pollution fuels global warming.
Loss of Biodiversity
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Finally, let’s explore loss of biodiversity. What happens when pollution affects habitats?

Many species might go extinct because they cannot adapt to the polluted environments.

Absolutely! Pollution leads to habitat destruction, which can drive species to extinction. In summary, pollution significantly contributes to loss of biodiversity, affecting ecosystems.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The harmful effects of pollution on health include respiratory diseases and skin conditions. Furthermore, pollution contributes to environmental degradation such as acid rain and decreased biodiversity, as well as exacerbating global warming due to greenhouse gas emissions.
Detailed
Effects of Pollution
Pollution has widespread impacts on both human health and the environment. The adverse effects can be categorized into health problems, environmental damage, global warming, and loss of biodiversity.
Health Problems
Pollution causes numerous health issues, including:
- Asthma: Respiratory problems can arise due to air pollutants.
- Bronchitis: Prolonged exposure to air pollution leads to chronic bronchitis.
- Skin Diseases: Contaminants in water and air can result in skin irritations and diseases.
Environmental Damage
The environmental consequences of pollution include:
- Acid Rain: Pollutants like sulfur dioxide contribute to acid rain, damaging forests, lakes, and soil.
- Ozone Layer Depletion: Air pollutants can break down ozone molecules, leading to increased UV radiation at the Earth's surface.
Global Warming
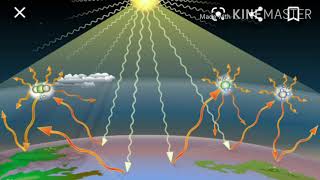
Pollution contributes significantly to global warming through greenhouse gases, which trap heat in the atmosphere, leading to rising global temperatures.
Loss of Biodiversity
Pollution leads to habitat destruction and poses a significant threat to wildlife, resulting in species extinction and loss of biodiversity. This loss disrupts ecosystems and leads to further environmental instability.
In summary, pollution has critical impacts on health, the environment, climate, and biodiversity, demanding immediate attention and action for mitigation.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Health Problems
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Health Problems: Asthma, bronchitis, skin diseases.
Detailed Explanation
Pollution can lead to various health issues in humans. For instance, breathing in polluted air can trigger asthma attacks or worsen bronchitis, both of which are conditions that affect the lungs and breathing. Additionally, pollutants can cause skin diseases, indicating that our body can react negatively when exposed to contaminated environments.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a person who lives near a busy highway. They frequently breathe in exhaust fumes full of harmful chemicals. Over time, this exposure may lead them to develop asthma. It's similar to how eating spoiled food can make you sick; exposure to pollutants can harm your health.
Environmental Damage
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Environmental Damage: Acid rain, ozone layer depletion.
Detailed Explanation
Pollution not only harms individual health but also damages our environment. Acid rain occurs when pollutants in the air combine with rainwater, making it acidic. This can harm plants, aquatic life, and even buildings. Ozone layer depletion refers to the thinning of the ozone layer due to substances like chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), which protect us from harmful ultraviolet rays from the sun. Without a healthy ozone layer, more UV radiation reaches Earth, increasing health risks.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the ozone layer as a sunscreen for the planet. If the sunscreen is damaged, more sunlight can penetrate through, potentially leading to sunburns—both for people and for natural ecosystems.
Global Warming
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Global Warming: Increase in earth’s temperature due to greenhouse gases.
Detailed Explanation
Global warming is primarily caused by an increase in greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide (CO2) and methane (CH4), which are released into the atmosphere through pollution from industries and vehicles. These gases trap heat from the sun and lead to a gradual rise in Earth’s temperature, resulting in climate change.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine Earth as a greenhouse where plants grow. When you add more layers of glass (like greenhouse gases), the heat gets trapped inside, making it warmer. Similarly, more greenhouse gases lead to a warmer planet, affecting weather patterns and habitats.
Loss of Biodiversity
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Loss of Biodiversity: Habitat destruction and species extinction.
Detailed Explanation
Pollution contributes significantly to the loss of biodiversity, which refers to the variety of life in a given ecosystem. As pollution destroys natural habitats—like oceans, forests, and wetlands—many species find it difficult to survive, leading to their extinction. This disruption affects entire ecosystems, as each species plays a role in maintaining balance.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a balanced diet where each food group is important for health. If you remove vegetables (like a species going extinct), it can lead to deficiencies and health issues in your body (the ecosystem). Just like that, losing species disrupts the balance needed for ecosystems to thrive.
Key Concepts
-
Health Problems: Pollution leads to asthma, bronchitis, and skin diseases.
-
Environmental Damage: Acid rain and ozone layer depletion are significant issues caused by pollution.
-
Global Warming: Greenhouse gases from pollution contribute to global temperature rise.
-
Loss of Biodiversity: Pollution contributes to habitat destruction and species extinction.
Examples & Applications
A rise in asthma cases during smoggy days highlights the effects of air pollution.
Acid rain damaging forests and lakes affects entire ecosystems, leading to loss of aquatic life.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Pollution's effects are no bliss, from health to the world, let’s not miss.
Stories
Imagine a small village facing health issues like asthma because of the factory nearby. As the air became polluted, the forest was affected too, with trees dying and animals leaving. This is what happens when pollution is unchecked.
Memory Tools
For pollution effects, remember H.E.G.L.: Health issues, Environmental damage, Global warming, Loss of biodiversity.
Acronyms
P.E.G. - Pollution's Effects on Global warming.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Pollution
The introduction of harmful substances or contaminants into the environment.
- Health Problems
Adverse effects on human health due to exposure to pollutants.
- Acid Rain
Rainfall that is unusually acidic due to pollutants in the atmosphere.
- Ozone Layer Depletion
Reduction of the ozone layer due to the breakdown of ozone molecules.
- Global Warming
The gradual increase in the Earth's temperature due to greenhouse gas emissions.
- Biodiversity
The variety of life in the world or in a particular habitat.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
