Variation of Metallic and Non-Metallic Character
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Definition of Metallic and Non-Metallic Character
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today we're going to talk about two critical concepts in chemistry: metallic character and non-metallic character. Can anyone tell me what metallic character means?

Is it about how easily an element can lose electrons?

Exactly! Metallic character is the tendency of an element to lose electrons and form positive ions. What about non-metallic character?

Is that the tendency to gain electrons?

Very good! Non-metallic character indicates the tendency to gain electrons and form negative ions. This is crucial for understanding chemical reactivity. Remember, 'Need More' - Non-metals tend to 'Need' electrons more.

Got it! So metals lose and non-metals gain?

Exactly right! Let's move on to trends across periods. Why do you think metallic character changes as we move across a period?
Trends Across a Period
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

When we look across a period from left to right, metallic character decreases. Can anyone give me an example?

Sodium decreases as we move towards chlorine, right?

Exactly! Sodium is a metal with high metallic character, while chlorine is a non-metal with high non-metallic character. Remember the acronyms 'M1-M2' for Metals decreasing Metallic character and 'N1-N2' for Non-metals increasing Non-metallic character. Why does this trend happen?

Is it because nuclear charge increases and pulls electrons closer?

Precisely! This increased nuclear charge enhances the attraction between protons and electrons, making it harder for metals to lose electrons. Let's now explore what happens down a group.
Trends Down a Group
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

As we move down a group, what happens to metallic character?

It increases!

Correct! Why do we see that trend?

I think it’s because new electron shells are added, making it easier for metals to lose electrons.

Spot on! And how about non-metallic character?

That decreases, right?

Exactly! It's all about the balance between the number of shells and the effective nuclear charge holding the electrons. Let's summarize what we've learned in today's session.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The section outlines the concepts of metallic and non-metallic character, illustrating how these properties vary across a period and down a group. Metallic character is associated with the tendency to lose electrons, while non-metallic character indicates a tendency to gain electrons.
Detailed
Variation of Metallic and Non-Metallic Character
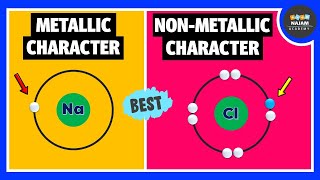
In this section, we explore the concepts of metallic and non-metallic characters in elements of the periodic table. Metallic character is the tendency of an element to lose electrons and form positive ions, whereas non-metallic character describes the tendency to gain electrons and form negative ions.
Trends Observed:
- Across a Period: Moving from left to right across a period, metallic character decreases and non-metallic character increases. For example, sodium (a metal) has a more significant metallic character than chlorine (a non-metal).
- Down a Group: Moving down a group in the periodic table, metallic character increases while non-metallic character decreases. This trend is observable as you compare alkali metals (like lithium) with halogens (like fluorine).
Understanding these trends is essential for predicting the properties and reactivity of various elements, which is foundational for the study of chemistry.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Defining Metallic and Non-Metallic Character
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Metallic character: Tendency to lose electrons and form positive ions.
● Non-metallic character: Tendency to gain electrons and form negative ions.
Detailed Explanation
Metallic character refers to how easily an element can lose electrons and form positive ions or cations. Elements that easily lose electrons are considered to have high metallic character. In contrast, non-metallic character describes an element's tendency to gain electrons to form negative ions or anions. Elements with high non-metallic character typically attract electrons more readily than they lose them.
Examples & Analogies
Think of metallic character like a person who easily shares their toys (losing electrons), while non-metallic character is like a person who prefers to borrow toys from others (gaining electrons). Just like some people are more open to sharing than others, elements behave differently when it comes to their cosmic exchanges of electrons.
Trends Across a Period
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Trends:
○ Across a period: Metallic character decreases, non-metallic character increases.
Detailed Explanation
As we move from left to right across a period in the periodic table, the metallic character of elements decreases. This is because elements have more protons and a stronger positive charge in their nuclei, which attracts electrons more effectively. Consequently, these elements are less likely to lose electrons. On the other hand, the non-metallic character increases as we move from metals to non-metals in a period, since non-metals are more likely to gain electrons.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a team of friends in a relay race. The friends on the left are quick to pass the baton (lose electrons), while as you move to the right, the friends are more focused on receiving the baton and running with it (gaining electrons). The closer you get to the finish line, the more the teammates want to hold onto the baton, reflecting the increasing non-metallic character.
Trends Down a Group
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
○ Down a group: Metallic character increases, non-metallic character decreases.
Detailed Explanation
When you move down a group in the periodic table, the metallic character of the elements increases. This is primarily due to the addition of new electron shells. As more electron shells are added, the outermost electrons are further from the nucleus and experience less attraction from the positively charged protons. This makes it easier for these elements to lose electrons, hence displaying stronger metallic character. Conversely, the non-metallic character decreases, since these elements are less inclined to gain electrons due to their weaker attraction.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a large crowd of people at a concert. The front rows (representing upper groups) have people who are eager to be involved (gain electrons), while the back rows (representing lower groups) are more carefree and willing to let loose (lose electrons). The excitement diminishes with distance from the stage, much like how non-metallic character decreases down the groups in the periodic table.
Key Concepts
-
Metallic Character: Tendency to lose electrons and form positive ions.
-
Non-Metallic Character: Tendency to gain electrons and form negative ions.
-
Period Trend: Across a period, metallic character decreases while non-metallic character increases.
-
Group Trend: Down a group, metallic character increases while non-metallic character decreases.
Examples & Applications
Sodium has a higher metallic character than chlorine, while chlorine has a higher non-metallic character.
Moving down the alkali metals from lithium to cesium, metallic character increases.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Metals are bold, they lose with ease; Non-metals are shy, they want to seize.
Stories
Imagine a battle with metals on one side raising swords to attack (losing electrons) while non-metals on the other side shyly wait, hoping someone will hand them a shield (electrons).
Memory Tools
M-L for Metals Losing and N-G for Non-metals Gaining.
Acronyms
M&N
for Metallic (loses) and N for Non-Metallic (gains).
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Metallic Character
The tendency of an element to lose electrons and form positive ions.
- NonMetallic Character
The tendency of an element to gain electrons and form negative ions.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
