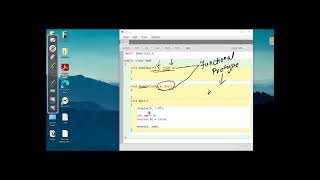
Actual and Formal Parameters
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
In this section, we explore the difference between formal parameters, which are placeholders in a function definition, and actual parameters that are the real values supplied to a function when it is invoked. Understanding this distinction is essential for effectively using functions in programming.
Detailed
Actual and Formal Parameters
In programming, particularly within functions, we encounter two types of parameters: formal and actual parameters. Formal parameters are declared in the function signature; they act as variables that accept values when the function is invoked. On the other hand, actual parameters are the real values that are passed to these formal parameters during the function call.
Key Points:
- Formal Parameters: These are listed in the function definition. For example, in
void greet(String name),nameis a formal parameter used to receive the input whengreetis called. - Actual Parameters: These come into play when the function is called with specific values. For instance, calling `greet(
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Formal Parameters
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Formal parameters: Defined in the function declaration.
Detailed Explanation
Formal parameters are the variables that are declared in the function definition. They act as placeholders that receive values when the function is called. For instance, if we define a function to add two numbers, we can say add(int a, int b). Here, a and b are the formal parameters that are specified in the function declaration. They help the function know what data it will work with.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine you are baking cookies. The recipe calls for ingredients (like flour and sugar) but does not specify quantities. When you decide how many cookies to make, you fill in those ingredient amounts. In this scenario, the recipe is like the function definition, and the ingredient quantities represent the formal parameters.
Actual Parameters
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Actual parameters: Passed when the function is called.
Detailed Explanation
Actual parameters are the real values that are passed to the function when it is called. Using our previous example, if you call the function add(5, 3), the actual parameters are 5 and 3. These values are inserted into the formal parameters a and b during the execution of the function, allowing the function to perform its task using these specific inputs.
Examples & Analogies
Continuing with the baking analogy, think of the actual parameters as the specific amounts of ingredients you choose when you bake cookies. You might take 2 cups of flour and 1 cup of sugar. These numbers are your actual parameters, which you use to make the cookies based on the recipe.
