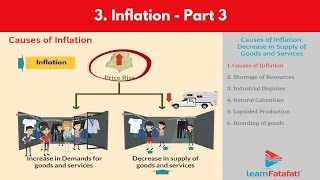
Causes of Inflation
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Increase in Demand
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's start by discussing the first cause of inflation: an increase in demand. Can anyone tell me what might cause an increase in demand?

Maybe if people's incomes go up, they'll buy more things?

Exactly! Higher incomes can lead to greater consumer spending. This is often referred to as demand-pull inflation. What else might contribute to increased demand?

Population growth could also increase demand!

Absolutely! More people mean a higher demand for goods and services. Increased government spending is another factor that may stimulate demand. Let’s recap: increased demand, higher incomes, and population growth can drive inflation. Remember the acronym D-P for 'Demand-Pull'.
Increase in Cost of Production
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's move on to our second cause: an increase in the cost of production. Can someone give me examples of what might cause these costs to rise?

Maybe when wages go up?

Exactly right! Higher wages can increase the cost for employers. What about other factors?

Raw material costs might also go up, right?

Correct! Rising costs of fuel and materials can lead businesses to increase their prices as well. It’s important to remember that both wages and raw materials contribute to what we call cost-push inflation.
Supply Chain Disruptions
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Next, let's discuss supply chain disruptions. What can cause these disruptions?

Things like natural disasters or strikes?

Yes! Natural disasters can halt production, while strikes can limit supply from workers, both leading to shortages and potentially higher prices. This underscores how interconnected our economy is.

What about import restrictions?

Great point! Import restrictions can also limit the supply of goods and drive prices up. Remember the phrase S-S-D for 'Supply-Side Disruptions'.
Monetary Factors
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let’s discuss monetary factors. How do these influence inflation?

If there’s too much money in circulation, that can lead to people spending more?

Correct! When there’s excess money supply or low interest rates, it means more money is available to be spent, which can result in inflation. Remember the acronym M-E for 'Monetary Effects'.
Deficit Financing
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Finally, let’s look at deficit financing. What does that mean for inflation?

If the government prints more money to cover its debts, it can cause inflation, right?

Exactly! When a government prints money to fund deficits, it increases the money supply without increasing the production of goods and services, leading to inflation. This can be remembered with the acronym D-M for 'Deficit-Money'.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The causes of inflation are multifaceted, stemming from both demand-side and supply-side factors. Key drivers include an increase in aggregate demand due to factors such as income growth, restrictions in supply due to natural disasters or labor strikes, rising costs of production, and monetary policies that lead to higher money supply. Understanding these causes is crucial for diagnosing and addressing inflation.
Detailed
Detailed Summary
Inflation is a complex economic event driven by various factors that influence the general price level of goods and services. The following are the key causes of inflation:
- Increase in Demand: Inflation often occurs when consumer demand exceeds supply. This situation can arise from increased household incomes, population growth, or increased government spending, leading to excess demand for goods and services.
- Increase in Cost of Production: Rising production costs, including wages, raw materials, and fuel prices, can lead businesses to increase their prices to maintain profitability.
- Supply Chain Disruptions: Events such as natural disasters, strikes, and import restrictions can disrupt supply chains, leading to shortages and price increases.
- Monetary Factors: An increase in the money supply or low-interest rates can lead to more money chasing the same amount of goods, causing inflation.
- Deficit Financing: When governments print more money to cover budget deficits, it can lead to inflation as more currency is in circulation without a corresponding increase in goods and services.
Understanding these causes is vital for policymakers aiming to control inflation and stabilize economic conditions.
Youtube Videos







Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Increase in Demand
Chapter 1 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Increase in Demand
○ Due to higher income, population growth, or government spending
Detailed Explanation
An increase in demand for goods and services occurs when consumers have more money to spend. This can happen due to higher wages, a growing population that leads to more consumers, or increased government spending on services and infrastructure. When demand exceeds the available supply, prices tend to rise, contributing to inflation.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a popular new restaurant opening in a small town. If many people receive raises or hundreds of new residents move in, there will be more customers wanting to dine at this restaurant than there are tables available. As a result, the restaurant may raise its prices, reflecting the increased demand.
Increase in Cost of Production
Chapter 2 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Increase in Cost of Production
○ Higher wages, raw material costs, fuel prices
Detailed Explanation
When the cost of producing goods increases, companies often pass these costs on to consumers in the form of higher prices. This can happen due to rising wages if workers demand more pay, or due to increases in the cost of raw materials and fuel. As production becomes more expensive, businesses may charge more for their products, leading to inflation.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a bakery that makes bread. If the price of flour drastically increases or if the workers demand higher pay, the bakery's costs go up. To maintain profit margins, the bakery may raise the price of its bread, which contributes to overall inflation in the goods market.
Supply Chain Disruptions
Chapter 3 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Supply Chain Disruptions
○ Natural calamities, strikes, or import restrictions
Detailed Explanation
Supply chain disruptions occur when there are obstacles in delivering goods from producers to consumers. This can result from natural disasters like floods, labor strikes that halt production, or government-imposed restrictions on imports. When goods cannot reach the market easily, their availability decreases and prices tend to rise.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a factory that gets its components from multiple suppliers. If there's a flood that impacts one supplier, that factory might not be able to produce enough products. With fewer products available, the price for the goods with higher demand might increase significantly, leading to inflation.
Monetary Factors
Chapter 4 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Monetary Factors
○ Excess money supply or low interest rates
Detailed Explanation
When a government or central bank increases the money supply too much or keeps interest rates very low, consumers and businesses have easier access to loans and cash. This can lead to more spending, which, when combined with limited supply, results in increased demand and rising prices. Consequently, an excessive amount of money chasing a finite amount of goods can trigger inflation.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a town where a new bank opens and offers loans at almost no interest. Loans are taken out rapidly by residents, who spend the money on various consumer goods. If the stores run out of popular items because of the sudden influx of money, they will need to raise prices, resulting in inflation.
Deficit Financing
Chapter 5 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Deficit Financing
○ Government printing more money to cover budget deficits
Detailed Explanation
Deficit financing occurs when a government spends more money than it collects in revenue, leading to the need to borrow or print more money to cover the gap. When more money enters the economy without equivalent increases in goods and services, inflation may occur as the value of currency diminishes due to oversupply.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a scenario where a city government wants to fund a new park but lacks enough funds. If they decide to print more money to finance this project without any increase in local economic output, the surplus money could lead to inflation, increasing the cost of goods and services in that area.
Key Concepts
-
Increase in Demand: Higher demand due to increased personal income or population can lead to inflation.
-
Cost of Production: Rising production costs, including wages and materials, can contribute to inflation.
-
Supply Chain Disruptions: Issues like natural disasters or strikes can limit goods supply, raising prices.
-
Monetary Factors: An excessive money supply and low-interest rates may lead to inflation.
-
Deficit Financing: Government-induced inflation by printing more money to cover budget deficits.
Examples & Applications
In an economy experiencing rapid growth, consumers may start to buy more cars, leading to increased demand and higher prices.
After a hurricane, the disruption to oil supply can lead to increased fuel prices, contributing to inflation.
If a country’s central bank increases the money supply significantly, prices of everyday goods may rise as consumers have more cash to spend.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
When demand is high and supply's a mess, prices will rise, that’s any guess!
Stories
Imagine a market where everyone craves the newest gadget, but the store has only a few. Prices soar as everyone wants what they can’t easily get—that’s demand-pull inflation in action!
Memory Tools
Remember the acronym D-S-M-D for 'Demand, Supply, Money, Deficits' to recall the main causes of inflation.
Acronyms
Use the acronym PIE to remember
'Production costs
Increased demand
Economic factors' as key causes of inflation.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- DemandPull Inflation
Inflation caused by an excess demand for goods and services exceeding supply.
- CostPush Inflation
Inflation resulting from an increase in the cost of production factors like wages and raw materials.
- Supply Chain Disruptions
Interruptions in the supply chain that lead to shortages of goods, potentially causing price increases.
- Monetary Factors
Economic indicators resulting from the money supply and interest rates that can influence inflation.
- Deficit Financing
The practice of funding government spending by borrowing or creating more money, which can lead to inflation.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
