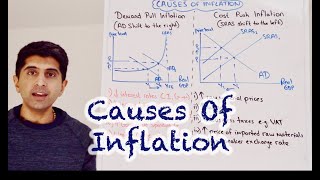
Demand-Pull Inflation
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Demand-Pull Inflation
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today we are discussing demand-pull inflation. Can anyone tell me what that might mean?

Is it when demand for things is greater than the supply?

Exactly! Demand-pull inflation happens when there's excessive demand for goods and services in the economy. This means producers can't keep up with the buying power of consumers.

So, if everyone wants to buy a new car, it could cause car prices to go up?

That's a perfect example! If car manufacturers can't produce enough cars to meet demand, the price of those cars will rise. Remember, this is like a teeter-totter—if one side, demand, goes up without supply increasing, prices will increase too.
Causes of Demand-Pull Inflation
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's explore what can cause demand-pull inflation. What are some factors that could increase demand?

Higher incomes might boost demand, right?

Yes! When people earn more, they tend to spend more, which pushes demand higher. Any other factors?

Government spending can also contribute, particularly when funds are invested in large projects.

Exactly! Increased government spending, especially in infrastructure, can lead to more jobs and higher consumer spending, leading to demand-pull inflation.

What about population growth?

Good point! An increasing population means more demand for goods and services. Each of these factors plays a crucial role in driving demand-pull inflation.
Implications of Demand-Pull Inflation
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's talk about the implications of demand-pull inflation. What might happen to consumers when prices rise?

Their purchasing power decreases, right?

Exactly! As prices rise, consumers can buy less with the same amount of money. This can create hardship, especially for those on fixed incomes—think about retirees, for example.

And for businesses?

For businesses, while they might initially benefit from higher prices, sustained inflation could lead to increased costs, especially if wages and materials also rise. It can create an unpredictable economic environment.

So, it’s a cycle that could lead to economic instability?

Exactly! If inflation becomes too high or uncontrolled, it can hamper economic growth and lead to uncertainty in investment. Understanding this cycle is essential for effective economic policy.

So, we need to balance demand and supply to maintain price stability?

Correct! Balancing demand and supply is key in managing inflation.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section explores demand-pull inflation, highlighting how it arises from increased consumer demand that outpaces the economy's ability to produce goods and services, thus causing prices to rise. It discusses the implications of this type of inflation on the economy.
Detailed
Detailed Summary
Demand-pull inflation occurs when demand for goods and services in an economy surpasses supply, leading to increased prices. This imbalance can stem from several factors, including higher consumer spending due to increased incomes, government expenditure on various projects, or burgeoning populations. As demand continues to rise without a corresponding increase in supply, businesses will raise prices to balance their inventory levels. Consequently, this inflation affects the purchasing power of consumers and can lead to economic instability if left unchecked.
Overall, understanding demand-pull inflation is crucial for policymakers and economists as it plays a significant role in shaping monetary and fiscal strategies aimed at stabilizing prices and promoting sustainable economic growth.
Youtube Videos







![Inflation | [ ICSE Economics Class 10] | Chapter 13 | One Shot](https://img.youtube.com/vi/bgFXx8y39yE/mqdefault.jpg)
Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Definition of Demand-Pull Inflation
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Demand-Pull Inflation: Caused by excess demand over supply.
Detailed Explanation
Demand-Pull Inflation occurs when the demand for goods and services exceeds their supply. This imbalance leads to an overall increase in prices. In simple terms, when many people want to buy a product, but there isn’t enough of that product available, sellers often increase the prices to balance out demand with supply.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a popular concert with a limited number of tickets. If thousands of fans are trying to buy tickets, but only a few are available, ticket prices will likely soar. This situation illustrates Demand-Pull Inflation where the high demand (thousands of fans) outstrips the limited supply (few tickets).
Causes of Demand-Pull Inflation
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Demand-Pull Inflation is often driven by factors such as increased consumer spending, government expenditure, and investment.
Detailed Explanation
There are several key drivers of Demand-Pull Inflation. These include increased consumer spending due to rising incomes, increased government spending on public services and infrastructure, and higher levels of investment by businesses. Each of these factors boosts overall demand in the economy, often leading to price increases when supply does not keep pace.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a city that has just announced a new sports team. The announcement might lead to people spending more on merchandise, tickets, and local businesses. This surge in spending increases demand across various sectors. Since the supply of team merchandise and seats at games is limited, prices may begin to rise, demonstrating Demand-Pull Inflation.
Effects of Demand-Pull Inflation
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
When Demand-Pull Inflation occurs, it can lead to various economic consequences such as increased costs of living and potential wage inflation.
Detailed Explanation
The occurrence of Demand-Pull Inflation often leads to a general increase in the cost of living, as consumers have to pay higher prices for goods and services. Additionally, workers may demand higher wages to keep up with soaring prices, leading to a wage-price spiral, where wages and prices push each other higher.
Examples & Analogies
Think about a scenario where the prices of groceries have risen due to increased demand. If families notice they have to spend more on food, they might ask for higher wages at work to maintain their living standards. This cycle can continue, with prices and wages both rising, creating an economic environment filled with uncertainty.
Key Concepts
-
Demand-Pull Inflation: Inflation that results from increased demand for goods/services exceeding supply, leading to higher prices.
-
Purchasing Power: The ability of consumers to buy goods and services; decreases as demand-pull inflation rises.
-
Government Expenditure: Increased spending by the government can lead to demand-pull inflation through stimulating demand.
-
Consumer Spending: An increase in consumer spending leads directly to higher demand, influencing demand-pull inflation.
Examples & Applications
An example of demand-pull inflation is during a booming economy where workers receive raises, leading to more spending on luxury goods and services. This increased demand can drive up prices.
Another instance is government initiatives like stimulus checks or tax cuts, which inject money into the economy, increasing consumer spending and thus pushing prices higher.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
When demand shoots up high, prices soar to the sky!
Stories
Imagine a bakery on a busy street. One day, a famous chef opens nearby, attracting many customers. Demand for pastries at the bakery skyrockets, but the baker can't keep up with orders, so they raise prices. This is demand-pull inflation in action.
Memory Tools
D.I.S.C. for factors of demand-pull inflation: Demand Increase, Supply Constant.
Acronyms
P.E.T. for impacts
Prices up
Earnings static
Tough for consumers.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- DemandPull Inflation
A type of inflation that occurs when demand for goods and services exceeds their supply.
- Purchasing Power
The amount of goods and services that can be bought with a unit of currency.
- Economic Stability
A condition in which the economy experiences constant growth and low inflation.
- Consumer Spending
The total amount of money spent by households on goods and services.
- Government Expenditure
Spending by the government on goods and services that is intended to create economic growth.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
