Mode
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Mode
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're going to learn about the mode. Can anyone tell me what they think the mode means?

Is it the number that appears the most?

Exactly! The mode is the value that occurs most frequently in a dataset. It's one of the measures of central tendency, just like mean and median.

So, why would we use mode instead of mean or median?

Great question! Mode is especially useful when we have categorical data or when we want to understand the most common item in a dataset.

Can a dataset have more than one mode?

Yes, a dataset can be unimodal with one mode, bimodal with two modes, or multimodal with multiple modes. This helps us see how data is distributed.

So, the mode tells us what is 'popular' in the data?

Exactly! A good way to remember this is: mode is our 'most frequent friend' in the dataset.
Finding Mode
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's look at an example. If we have the dataset 4, 7, 4, 9, 3, what would be the mode?

I think it's 4 because it appears most often.

Right! Now, how about this dataset: 5, 5, 6, 6, 7, 7?

Is that bimodal because 5 and 6 both appear twice?

Exactly! You got it. Remember, if two numbers have the same highest frequency, it's bimodal.

What if all the numbers appear once?

Then we say there is no mode. This reinforces that mode really focuses on frequency.
Applications of Mode
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now that we know what the mode is, can anyone think of situations where knowing the mode would be useful?

In surveys to see what is most popular among people?

Exactly! In surveys or market research, the mode helps determine the most favored option.

Can mode be used in sports, like finding the most common score?

Absolutely! The mode can help coaches identify common scores or performances for strategy.

What about when analyzing test scores?

Yes! In education, knowing the mode of scores can highlight the most common achievement level among students.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The mode is a crucial measure of central tendency that identifies the most common value in a dataset. A dataset may be unimodal (one mode), bimodal (two modes), or multimodal (multiple modes), which provides flexibility in representing datasets with varying distributions.
Detailed
Detailed Summary of Mode
In statistics, the mode is defined as the value that appears most frequently in a dataset. It can be helpful, especially in datasets with categorical variables, where other measures like the mean and median may not apply. There are several key points about the mode:
- Definition: The mode is the number that occurs most often in a set of data points.
- Multiplicity: A dataset can have no mode (if all numbers occur with the same frequency), one mode (unimodal), or multiple modes (bimodal or multimodal).
- Utility: The mode is particularly valuable when analyzing qualitative data where the mean or median is not an appropriate measure of central tendency.
For example, consider the data set: 10, 15, 10, 20, 10, 25, 20, 25, 25. Here, the number 10 occurs three times, while 25 appears three times; hence, is a bimodal dataset with modes of 10 and 25. The understanding of mode enhances the overall comprehension of data distribution in various statistical applications.
Youtube Videos







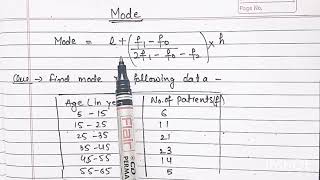


Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Definition of Mode
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Mode is the value that occurs most frequently in a data set.
Detailed Explanation
The mode is defined as the element in a data set that appears most often. It helps identify the most common or popular choice within that data. For instance, if you have a list of students' favorite colors, the mode would be the color that appears the most times in that list. It's useful for understanding trends in data.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a classroom where students are asked their favorite fruit. If 10 students say apples, 5 say bananas, and 2 say oranges, the mode is apples because it is the most frequently chosen fruit.
Modes in Data Sets
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- A data set can have no mode, one mode, or multiple modes.
Detailed Explanation
A data set may exhibit different characteristics regarding the mode: it may have no mode if all values appear with the same frequency, one mode if one value appears more frequently than others, or multiple modes if two or more values share the highest frequency. These cases help us understand the distribution and characteristics of the data set better.
Examples & Analogies
Consider the favorite ice cream flavors of a group of friends: if 5 choose chocolate, 5 choose vanilla, and 5 choose strawberry, there’s no mode since all flavors have the same number of votes. If 10 choose chocolate and 3 choose vanilla, chocolate is the mode. Lastly, if another group has 5 choosing chocolate and 5 choosing vanilla, then there are two modes: chocolate and vanilla.
Example of Finding Mode
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Example: Find the mode of the data: 10, 15, 10, 20, 10, 25, 20, 25, 25.
Solution:
Frequencies:
● 10 occurs 3 times
● 15 occurs 1 time
● 20 occurs 2 times
● 25 occurs 3 times
Modes = 10 and 25 (bimodal)
Detailed Explanation
In the given data set, we identify how many times each number appears. The number 10 appears three times, as does the number 25. Since both have the highest frequency of occurrence, we classify this data set as bimodal, meaning it has two modes: 10 and 25. This example illustrates how to determine the mode by counting the frequency of each value.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a popular music survey where responses indicate favorite artists. If 30 people choose Artist A, 12 choose Artist B, and 30 choose Artist C, Artists A and C are the modes, showing that these two artists are equally favored among the survey participants.
Key Concepts
-
Mode: The number that appears most frequently in a dataset.
-
Unimodal: A dataset with one mode.
-
Bimodal: A dataset with two distinct modes.
-
Multimodal: A dataset with more than two modes.
Examples & Applications
In the dataset 2, 3, 3, 4, the mode is 3.
In the dataset 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, there is no mode.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
To find the mode, just seek and ask, what's the frequent one? that's the task!
Stories
Once in data land, there lived a number that always played with friends the most. Everyone loved it, making it the king of popularity, known as the Mode!
Memory Tools
The 'M' in 'Mode' stands for 'Most Frequent'.
Acronyms
M.O.D.E - Most Often Demonstrating Event.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Mode
The value that occurs most frequently in a dataset.
- Unimodal
A dataset with only one mode.
- Bimodal
A dataset with two modes.
- Multimodal
A dataset with multiple modes.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
