Conclusion
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Overview of Electromagnetic Waves
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we are discussing electromagnetic waves. Can anyone tell me what they are?

Are they the waves with electric and magnetic fields?

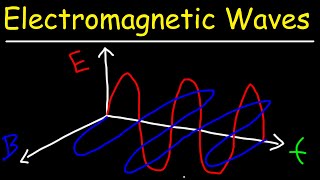
Exactly! They are waves that propagate through space, consisting of oscillating electric and magnetic fields. They don't need a medium, which means they can travel through a vacuum too. I like to remember this by the acronym 'EM' for Electromagnetic.

So they travel at the speed of light? That's fast!

Yes! Electromagnetic waves travel at approximately 3×10^8 meters per second in a vacuum. Can anyone think of a technology that uses electromagnetic waves?

Televisions and radios use them for communication!

Correct! Their applications are indeed vast, impacting our daily lives significantly.
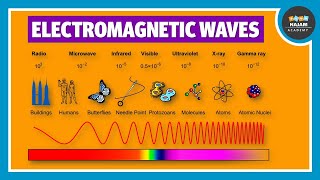
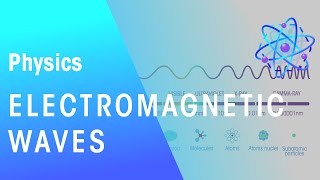
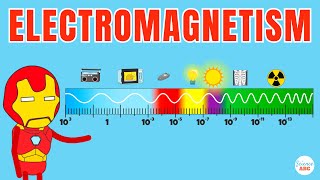
Electromagnetic Spectrum
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let's dive into the electromagnetic spectrum. Can anyone tell me what it includes?

It includes radio waves, microwaves, and visible light, right?

Yes! The spectrum ranges from radio waves with the longest wavelengths to gamma rays with the shortest. Can anyone guess where visible light fits in?

It's in the middle since we can see it!

Exactly! Visible light ranges from about 400 to 700 nanometers. It's fascinating how each type has unique applications and behaves differently depending on its wavelength and frequency.
Propagation of Electromagnetic Waves
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, how do electromagnetic waves propagate? Can they travel through different materials?

They travel fastest in a vacuum, but slow down in other materials, right?

Exactly! Their speed reduces depending on the refractive index of the material. Can anyone explain what refraction means?

It's when waves bend as they enter a new medium, isn't it?

Correct! Reflection and diffraction are other key concepts in wave propagation as well.
Applications of Electromagnetic Waves
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's talk about applications. What are some common technologies that utilize electromagnetic waves?

X-rays for medical imaging!

Exactly! X-rays are a significant application, along with microwaves in ovens, and radio waves in telecommunications. Each type has its important role!

And infrared is used in remote controls!

Great observation! Understanding these applications shows how deeply interconnected electromagnetic waves are with technology we use every day.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section summarizes the fundamental characteristics and significance of electromagnetic waves, emphasizing their oscillating electric and magnetic fields, the electromagnetic spectrum, and their varying propagation speeds in different mediums. Understanding these concepts is crucial for grasping their immense applications in communication, medicine, and daily life.
Detailed
Conclusion
Electromagnetic waves are waves formed by oscillating electric and magnetic fields, essential for the transmission of energy across various mediums. Their unique properties enable propagation through both vacuums and materials, allowing diverse applications in sectors like communication systems (radio, television, mobile phones), medical imaging (X-rays), and more. The electromagnetic spectrum encompasses several types of waves—including radio waves, microwaves, infrared radiation, visible light, ultraviolet radiation, X-rays, and gamma rays—each exhibiting distinct behaviors based on their wavelength and frequency. The ability of electromagnetic waves to travel at different speeds in varying mediums is also pivotal for understanding phenomena such as refraction and reflection. Thus, a comprehensive grasp of these elements is crucial in the application and development of modern technologies.
Youtube Videos





Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Summary of Key Points
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Electromagnetic waves are oscillating electric and magnetic fields that travel through space, with applications ranging from communication to medical technologies.
Detailed Explanation
This chunk summarizes the central concept of electromagnetic waves. These waves are not just theoretical; they comprise oscillating electric and magnetic fields that can move across space. Their significance is immense, as they enable various technologies we use daily, like communication systems (think radio and TV) and medical devices (like X-rays and MRI machines). The use of the term 'oscillating' refers to the back-and-forth movement of electric and magnetic fields.
Examples & Analogies
You can think of electromagnetic waves like waves on a string, where the string itself oscillates up and down while the wave travels along it. However, unlike a string that needs something to hold it up, electromagnetic waves can travel without needing a medium like air or water, even through the vacuum of space!
The Electromagnetic Spectrum
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The electromagnetic spectrum includes radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, X-rays, and gamma rays, each with different uses depending on their wavelength and frequency.
Detailed Explanation
This chunk introduces the electromagnetic spectrum, which is the complete range of electromagnetic waves grouped based on their wavelengths and frequencies. Each type of wave within this spectrum has unique characteristics and applications. For example, radio waves have long wavelengths and are used for communication, while gamma rays have very short wavelengths and are utilized in medical treatments like cancer radiation therapy. The further you go along the spectrum from radio waves to gamma rays, the more energy the waves carry, and thus, the potential applications evolve significantly.
Examples & Analogies
A simple way to visualize the electromagnetic spectrum is to imagine a rainbow. Each color of light represents a different wavelength. In the same way that each color can create different feelings or ideas (like how blue can feel calming while red can feel energizing), each type of electromagnetic wave serves specific purposes in technology and medicine.
Propagation of Electromagnetic Waves
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Electromagnetic waves can propagate through a vacuum and different materials, with their speed depending on the medium.
Detailed Explanation
This chunk discusses how electromagnetic waves travel. They can move through empty space (a vacuum) and also through various materials. However, the speed of electromagnetic waves isn't constant—it changes based on the material they are passing through. For instance, they move faster in a vacuum than in a medium like glass or water. This variance is important in practical applications, as the medium can affect how well signals transmit in technologies like mobile phones and optical fibers.
Examples & Analogies
Think of it like running on different surfaces. If you were to sprint on a smooth track (like a vacuum), you’d run fast, but if you were to run on sand (like in glass or water), it would slow you down. Similarly, electromagnetic waves travel faster through a vacuum than through materials like air or water.
Key Concepts
-
Electromagnetic waves consist of oscillating electric and magnetic fields.
-
The electromagnetic spectrum ranges from radio waves to gamma rays, representing different wavelengths and frequencies.
-
Electromagnetic waves can propagate through vacuum and different materials, with varying speeds.
Examples & Applications
X-rays used in medicine for imaging.
Radio waves used in broadcasting and communication technology.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
From radio to gamma, waves in a stream, they travel through space, just like a dream.
Stories
Imagine a race between electromagnetic waves. Radio waves are taking their time, enjoying the long ride, while gamma rays are zipping through, reaching their destination in a flash.
Memory Tools
Remember the acronym 'RIVUXG' for the electromagnetic spectrum: Radio, Infrared, Visible, Ultraviolet, X-rays, Gamma rays.
Acronyms
EM for Electromagnetic, as they everywhere roam; vacuum's their friend, in any stark home.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Electromagnetic Waves
Waves comprising oscillating electric and magnetic fields that can propagate through vacuum or material.
- Electromagnetic Spectrum
The range of all types of electromagnetic radiation arranged by frequency or wavelength.
- Refractive Index
A measure of how much the speed of light is reduced in a medium compared to vacuum.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
