Introduction to Electromagnetic Waves
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
What are Electromagnetic Waves?
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're going to learn about electromagnetic waves. Can anyone tell me what they think electromagnetic waves are?

Are they like regular waves in the ocean?

Not quite! While they are called waves, electromagnetic waves consist of oscillating electric fields and magnetic fields. They don’t need material to travel. So, they can even move through the vacuum of space!

How do they actually move? Like how fast?

Great question! Electromagnetic waves travel at the speed of light, which is approximately 3 × 10^8 meters per second. That’s incredibly fast! You can think of 'C' as in 'Chase the light' to remember this speed.

Why are they important, though?

Electromagnetic waves are essential in modern communication systems. Without them, we wouldn't have radio, television, or even cell phones! They’re crucial in many fields, like medical imaging too.

So, to summarize, electromagnetic waves are waves made of electric and magnetic fields that travel through space at light speed and support critical technologies.
Importance of Electromagnetic Waves
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now that we know what electromagnetic waves are, let’s talk about why they matter. Can anyone think of where we might encounter them in our daily lives?

I see them in my radio and TV!

Exactly! They enable broadcasting in radio and TV. We depend on them for wireless technologies too, like smartphones. Now, did you know that electromagnetic waves also help in medical imaging?

Really? How does that work?

X-rays are a type of electromagnetic wave that helps us look inside the human body. They also play a role in radar systems used in weather forecasting.

So, they’re everywhere!

You got it! My memory aid for this is to think of "EM—Everywhere in Media and Medicine." So, to summarize, electromagnetic waves are vital in communication, medical imaging, and more.
Electric and Magnetic Fields in Electromagnetic Waves
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s dive deeper into what electromagnetic waves are made of. Can someone explain what we mean by electric and magnetic fields?

I think electric fields are related to electricity, right?

That's right! An electric field is a region around charged particles that exerts a force on other charges. The magnetic field, on the other hand, is produced by moving charges, like those in a wire carrying current. Together, they form electromagnetic waves! A mnemonic device for this is E-M-F—Electric-Magnetic Fusion.

But how do they interact?

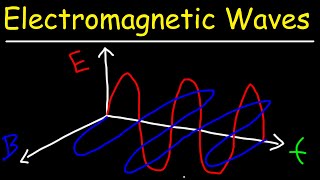
They oscillate in such a way that they are always in sync and perpendicular to each other. That’s why we say electromagnetic waves are transverse waves! In essence, as the electric field rises, the magnetic field does too, creates a rhythmic ‘dance’ of fields.

So they always move together?

Correct! Always in phase! So to recap, electromagnetic waves consist of electric and magnetic fields that oscillate perpendicular to each other and propagate through space.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Electromagnetic waves propagate through space as oscillating electric and magnetic fields and do not require a medium for travel. These waves are pivotal in modern technology, underpinning communication systems such as radio and television, while also playing significant roles in medical imaging, radar, and remote sensing.
Detailed
Introduction to Electromagnetic Waves
Electromagnetic waves are a type of wave that propagate through space, characterized by oscillating electric and magnetic fields. A crucial aspect of these waves is that they can travel through a vacuum, meaning they do not require a medium like air or water to move. This unique property allows them to traverse the vast emptiness of space at the speed of light, approximately 3 × 10^8 m/s.
These waves arise due to the interaction between electric and magnetic fields and are fundamental to numerous modern technologies. For instance, they underlie communication systems such as radio, television, mobile phones, and satellite transmissions. Additionally, electromagnetic waves are integral to advancements in medical technologies, including X-ray imaging and radar systems, making their understanding vital for students in physics and engineering.
Youtube Videos





Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Definition of Electromagnetic Waves
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Electromagnetic waves are waves that propagate through space, consisting of oscillating electric and magnetic fields. These waves do not require a medium to travel, meaning they can move through a vacuum (space).
Detailed Explanation
Electromagnetic waves are a type of wave that travels through space and are composed of two varying fields: electric fields and magnetic fields. Unlike sound waves, which require air or some other medium to travel, electromagnetic waves can move through the empty space of a vacuum, which is crucial for telecommunications and other modern technologies.
Examples & Analogies
Think of electromagnetic waves like light from a flashlight. When you turn on a flashlight, the light travels through the air (or even in space) without needing anything to help it along. The electric field could be thought of as a wave moving up and down, while the magnetic field is like a wave moving sideways. Together, they allow the light (an electromagnetic wave) to travel through the darkness.
How Electromagnetic Waves Are Generated
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Electromagnetic waves are a result of the interaction between electric and magnetic fields. These waves travel at the speed of light (c=3×10^8 m/s) in a vacuum.
Detailed Explanation
Electromagnetic waves are created when electric charges accelerate, causing changes in electric and magnetic fields that propagate outward. This propagation occurs at an astonishing speed, specifically the speed of light in a vacuum, which is approximately 300,000 kilometers per second. This remarkable speed allows electromagnetic waves to cover vast distances quickly, which is essential for things like radio waves reaching our devices.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine throwing a stone into a still pond. The stone creates waves that travel outward from where it hits the water. In a similar way, when an electric charge moves or accelerates, it generates waves that travel through space. You can think of the speed of light as the fastest rollercoaster ride, zipping past the world around it!
Importance of Electromagnetic Waves
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
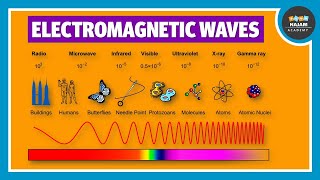
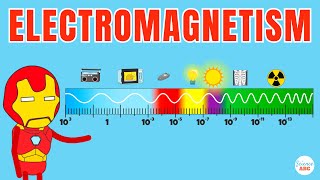
Electromagnetic waves are fundamental to modern communication systems, including radio, television, cell phones, and satellite transmissions. They also play a crucial role in many technologies such as radar, medical imaging (X-rays), and remote sensing.
Detailed Explanation
Electromagnetic waves are integral to a wide variety of communication technologies we use in everyday life. For instance, radio waves enable us to listen to music on the radio, and microwaves are used in weather forecasting. Additionally, in medicine, X-rays help doctors see inside the human body without surgery. These applications highlight how versatile and essential electromagnetic waves are for numerous fields.
Examples & Analogies
Consider how we use smartphones. When you make a call, your voice is transformed into an electromagnetic wave that travels to a cell tower. The tower then sends it to the recipient’s phone. This is similar to sending a postcard through the mail—your message travels through various channels to reach someone far away.
Key Concepts
-
Electromagnetic Waves: Waves made by oscillating electric and magnetic fields that don't need a medium to travel.
-
Speed of Light: The speed at which electromagnetic waves travel in a vacuum.
-
Electric Field: A region of space around electric charges where they exert forces on other charges.
-
Magnetic Field: A field produced by moving electric charges that interacts with other moving charges.
Examples & Applications
Electromagnetic waves are utilized in mobile phones for wireless communication, allowing us to transmit voices and texts.
Medical imaging uses X-rays, a type of electromagnetic wave, to visualize the internal structure of the body.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
To remember electromagnetic waves, light travels high, through electric and magnetic fields, they never shy.
Stories
Imagine a brave knight named Electra riding on a horse made of light, accompanied by her shield of magnetism, journeying through the kingdom of communication.
Memory Tools
EM—Everywhere in Media and Medicine, to remember the applications of electromagnetic waves.
Acronyms
C—Chase the light, to help memorize the speed of light.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Electromagnetic Waves
Waves that propagate through space with oscillating electric and magnetic fields.
- Speed of Light
The speed at which electromagnetic waves travel in a vacuum, approximately 3 × 10^8 m/s.
- Electric Field
A region around a charged particle where it exerts a force on other charges.
- Magnetic Field
A field produced by moving electric charges that exerts a force on other moving charges.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
