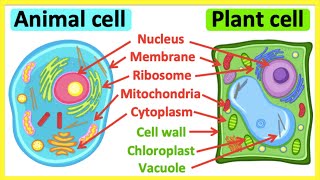
Differences between Plant Cell and Animal Cell
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Cell Wall Presence
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're going to talk about the differences between plant and animal cells. One major difference is that plant cells have a cell wall. Can anyone tell me why that might be important?

I think it helps them stay rigid and maintain their shape!

Exactly! The cell wall provides structure and protection. Now, what about animal cells? What do they have?

Animal cells don’t have a cell wall; they just have a cell membrane!

Correct! The cell membrane is flexible, allowing for movement and shape change in animal cells. Remember, 'Cell Wall is a Plant Call!'—a mnemonic to help you remember that only plant cells have this structure.

So, animal cells can move around more easily?

Yes! And we will discuss other unique features of these cells as we go along.

To wrap up, plant cells have a rigid cell wall while animal cells do not. This is one of the key differences that affect how they function.
Chloroplasts
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Another difference is that plant cells contain chloroplasts. Can someone tell me what chloroplasts do?

They help in photosynthesis, right?

Correct! Chloroplasts contain chlorophyll and are crucial in converting sunlight into energy. Can anyone tell me if animal cells have chloroplasts?

No, they don’t have chloroplasts!

Exactly! Animal cells obtain energy by consuming other organisms instead of through photosynthesis. Remember, 'Chloroplasts are for Plants!' to recall this difference.

So to summarize, chloroplasts are essential for plants to capture sunlight and are absent in animal cells.
Vacuoles
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Next, let's talk about vacuoles. Plant cells generally have a large central vacuole, while animal cells have smaller vacuoles or none at all. Why do you think that is?

I guess they need to store a lot of water and nutrients for photosynthesis.

Yes! The central vacuole helps maintain turgor pressure in plants. Animal cells, on the other hand, may have several small vacuoles that store substances like waste or nutrients. Remember the saying 'Plant Vacuoles are Big, Animal Vacuoles are Small!'

What happens if plant vacuoles get empty?

Great question! If plant vacuoles lose water, the plant can wilt. It's really important! To wrap up this session, large vacuoles are a standout feature of plant cells, while animal cells typically have small vacuoles.
Cell Shape Differences
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's discuss the shape of these cells. Plant cells tend to be rectangular, while animal cells are usually round. Why might that be?

I suppose the shape helps plants stay firm?

Exactly! A rectangular shape suits their function in maintaining structure. Animal cells, which are round, are more flexible and can change shape to perform different functions. Remember the saying 'Rectangular Plants, Round Animals!'

Can that make a difference in how they move or interact?

Very much so! Their shapes affect how they grow, interact, and perform their functions. In summary, plant cells maintain a fixed rectangular shape, while animal cells are more irregular and flexible.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Plant and animal cells differ in key structural elements such as the presence of a cell wall and chloroplasts in plant cells, while animal cells have centrosomes. This section highlights these distinctions, influencing their functions and overall characteristics.
Detailed
In this section, we examine the differences between plant cells and animal cells, two fundamental types of eukaryotic cells. Plant cells are characterized by features such as a rigid cell wall made of cellulose, chloroplasts for photosynthesis, and large central vacuoles. In contrast, animal cells lack these structures and instead possess centrosomes to facilitate cell division. Understanding these differences is vital as they underpin the varied functions and adaptations of these cells within their respective organisms. This comparison not only clarifies the unique properties of each cell type but also emphasizes their roles in the broader context of biological systems.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Presence of Cell Wall
Chapter 1 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Feature: Cell Wall
- Plant Cell: Present
- Animal Cell: Absent
Detailed Explanation
Plant cells have a rigid outer layer called the cell wall, which provides extra support and protection. In contrast, animal cells lack this cell wall and instead have a flexible plasma membrane that allows for different shapes and structures.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the plant cell like a house with strong walls that keep it standing tall, while the animal cell is like a balloon that can change shape easily when you squeeze it.
Presence of Chloroplasts
Chapter 2 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Feature: Chloroplasts
- Plant Cell: Present
- Animal Cell: Absent
Detailed Explanation
Chloroplasts are organelles found only in plant cells that contain chlorophyll, which is essential for photosynthesis. This is the process that allows plants to convert sunlight into food. Animal cells do not have chloroplasts since they obtain energy by consuming other organisms.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine that chloroplasts are like solar panels on the roof of a plant's house, converting sunlight into energy, while animals are like households that rely on grocery stores for their meals.
Size and Presence of Vacuoles
Chapter 3 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Feature: Vacuoles
- Plant Cell: Large, central
- Animal Cell: Small or absent
Detailed Explanation
In plant cells, vacuoles are large and usually central, helping to maintain turgor pressure, which keeps the plant upright. On the other hand, animal cells may have small vacuoles or none at all, as they do not need to store large amounts of water or nutrients in the same way.
Examples & Analogies
You can think of a plant cell's vacuole like a water reservoir that stores water to keep a garden lush, while an animal cell is like a small lunchbox that carries snacks rather than large quantities of food.
Cell Shape
Chapter 4 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Feature: Shape
- Plant Cell: Regular (rectangular)
- Animal Cell: Irregular (round)
Detailed Explanation
Plant cells have a fixed, regular shape often described as rectangular due to the presence of the rigid cell wall. In contrast, animal cells have a variable, irregular shape, allowing them to fit together in different ways based on their function within the organism.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the plant cell as a box of cookies that are neatly arranged and all the same shape, whereas animal cells are like a mixed bag of candies, each having different shapes and sizes.
Centrosomes
Chapter 5 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Feature: Centrosome
- Plant Cell: Absent (has centrosomes without centrioles)
- Animal Cell: Present (with centrioles)
Detailed Explanation
Centrosomes are present in animal cells and play a crucial role in cell division. They contain structures called centrioles. In plant cells, while centrosomes may be present, they lack centrioles, reflecting differences in how these cells divide and organize during the cell cycle.
Examples & Analogies
You can think of the centrosome as a construction crew: in animal cells, they have specialized workers (centrioles) to efficiently divide and manage building tasks, while in plant cells, they may have the equipment but lack the specialized crew.
Key Concepts
-
Cell Wall: A structure unique to plant cells providing rigidity and protection.
-
Chloroplast: An organelle necessary for photosynthesis found only in plant cells.
-
Vacuole: A storage area that is large in plant cells and small or absent in animal cells.
-
Centrosome: A structure present in animal cells that plays a crucial role in cell division.
-
Cell Shape: Plant cells are generally rectangular while animal cells are round.
Examples & Applications
In plant cells, the presence of a cell wall allows them to maintain structure and grow tall while standing firm against gravity.
Animal cells, lacking cell walls, can adapt their shape, such as when white blood cells change to engulf pathogens.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Plant cells stand tall, with walls and green, / Animal cells are round, flexible, and lean.
Stories
In a garden, there were two friends: Penny the Plant and Annie the Animal. Penny had a strong wall and loved the sun, while Annie enjoyed running around and changing shape.
Memory Tools
Remember PAVCC: Plants have a Wall, Chloroplasts, and large Central vacuoles, Animal cells are flexible.
Acronyms
PAC
Plant cells have a Wall
Animal cells are flexible.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Cell Wall
A rigid outer layer present in plant cells that provides structure and protection.
- Chloroplast
An organelle in plant cells that contains chlorophyll and facilitates photosynthesis.
- Vacuole
A storage sac within cells; large in plant cells and smaller or absent in animal cells.
- Centrosome
An organelle found in animal cells that is involved in cell division.
- Eukaryotic Cells
Type of cells that have a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles; includes plant and animal cells.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
