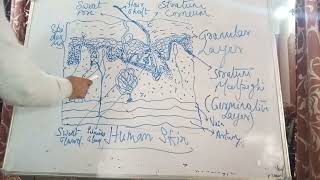
Hypodermis (Subcutaneous layer)
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding the Hypodermis
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're going to discuss the hypodermis, or subcutaneous layer, of the skin. Can anyone tell me what they think this layer does?

Isn't it just the layer where fat is stored?

That's correct! The hypodermis is rich in fat cells, which serve multiple purposes, including insulation. Remember, 'HYP' for 'heat and yellow fat—Protection from the cold.' What do you think would happen if we didn't have this layer?

Wouldn't we get cold easily?

Exactly! It helps to keep our body warm. It also provides cushioning to protect our organs.

So, it’s not just for storage?

Great question! It's also about protection and energy reserves, crucial for our body's functioning.

How does it connect to the other layers?

The hypodermis connects the dermis to underlying tissues, acting as an anchor for the skin. Now, let’s summarize: The hypodermis provides insulation, cushioning, energy storage, and connects our skin to the body.
Significance of Fat in the Hypodermis
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's dive deeper into the fat cells of the hypodermis. Why do we need them?

For energy storage, right?

Correct! This stored fat is a reserve of energy that our body can utilize when needed. Think of it as a 'battery pack' for energy. Who can think of other functions?

Doesn't it also help with cushioning?

Absolutely! It cushions our organs against impact, similar to how a helmet protects the brain. It's vital for protecting us from bruises and injuries. Can someone tell me how this layer contributes to overall health?

It helps regulate body temperature?

Yes, it insulates the body, which keeps us warm in cold weather. Let’s recap: The hypodermis stores energy, provides cushioning, and insulates our body.
Health Implications of Hypodermis
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's talk about health. Why is it important to maintain a healthy hypodermis?

Doesn't it affect our weight and energy levels?

Exactly! If we have too little or too much fat in this layer, it can lead to various health issues. Balance is key for proper function. Can someone explain why excess fat might be problematic?

It can lead to obesity or heart issues.

Right! Obesity can lead to increased inflammation and various health complications. What about too little fat?

It might make us cold or more prone to injuries.

Exactly! Lack of cushioning can lead to damage from impacts. Remember, a healthy hypodermis means a healthy body overall. Let’s conclude: The hypodermis plays a vital role in fat storage and health.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The hypodermis, or subcutaneous layer, is crucial for insulation, cushioning, and energy storage. It consists of fat and connective tissues that help anchor the skin to underlying structures while also serving as a reserve for energy and temperature regulation.
Detailed
Hypodermis (Subcutaneous Layer)
The hypodermis, often referred to as the subcutaneous layer, represents the innermost layer of the skin, lying beneath the dermis. It is primarily composed of loose connective tissue and fat cells, which serve several essential functions:
Functions of the Hypodermis:
- Insulation: The layer of fat helps maintain body temperature by minimizing heat loss.
- Cushioning: It acts as a cushion, absorbing shocks and protecting underlying tissues and organs from impact.
- Energy Reserve: The fat stored in the hypodermis serves as a significant energy reserve for the body.
- Connects Skin to Underlying Structures: It helps attach the skin to the underlying muscles and bones, providing structural support.
An awareness of the hypodermis's role emphasizes the skin's overall function as not only a protective barrier but also a vital player in energy storage and thermal regulation.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Definition of the Hypodermis
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The hypodermis is the inner layer made of fat and connective tissue.
Detailed Explanation
The hypodermis is one of the three main layers of the skin, located beneath the dermis. It is primarily made up of adipose tissue, which is fat that provides insulation and cushioning to the body. This layer serves as an anchor for the skin and helps in maintaining the body's temperature.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the hypodermis like bubble wrap for your skin. Just like bubble wrap protects fragile items during shipping, the hypodermis protects your body by cushioning it and keeping the temperature stable.
Functions of the Hypodermis
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
It provides insulation and cushioning.
Detailed Explanation
The hypodermis plays two key roles: insulation and cushioning. Insulation helps to retain the body heat, keeping you warm in cooler environments. The cushioning effect protects underlying muscles and organs from impact. Without this layer, our internal structures would be more susceptible to injury.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine wearing a thick winter coat. Just as the coat keeps you warm by trapping heat and protecting you from cold weather, the hypodermis keeps your body warm and protects it from physical impacts.
Composition of the Hypodermis
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The hypodermis contains fat and connective tissue.
Detailed Explanation
In addition to fat, the hypodermis also consists of connective tissue. This tissue supports and binds other tissues and organs in the body together. The combination of fat and connective tissue allows the hypodermis to effectively serve its functions in insulation, cushioning, and structural support.
Examples & Analogies
Consider how a good bed mattress has both soft padding and a sturdy framework. The soft padding (fat) provides comfort, while the framework (connective tissue) gives it structure. Together, they ensure you have a good night's sleep without hurting your back.
Role in Energy Storage
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The hypodermis stores fat as an energy reserve.
Detailed Explanation
The hypodermis serves as a storage area for excess energy in the form of fat. When the body consumes more calories than it needs for immediate energy, the excess is converted into fat and stored in this layer. This stored fat can later be used as an energy source when the body needs it, such as during exercise or periods of fasting.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the hypodermis like a battery pack for your body. Just as a battery stores electricity for later use, the hypodermis stores energy in the form of fat that your body can use when necessary.
Key Concepts
-
Hypodermis: The layer providing insulation, cushioning, and energy storage beneath the skin.
-
Subcutaneous Tissue: The layer that connects the skin to the underlying structures and stores fat.
Examples & Applications
The hypodermis protects your organs by cushioning them from impacts, such as when you fall.
It helps keep your body warm by storing fat, especially important in cold weather.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In the hypodermis, we store fat, keeping us warm and safe from that!
Stories
Imagine a cozy blanket (hypodermis) wrapped around a fragile object (organs), protecting it from cold and bumps.
Memory Tools
HYPER: Hypodermis Yields Protection, Energy, Reserves.
Acronyms
FICS
Fat Insulates
Cushions
Stores energy.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Hypodermis
The innermost layer of the skin, composed mainly of fat and connective tissue, which provides insulation and cushioning.
- Subcutaneous
Referring to the layer beneath the skin, mainly containing fat and connective tissues.
- Insulation
The process of preventing the loss of heat or energy.
- Cushioning
The act of protecting against physical injury by absorbing impact.
- Energy Reserve
Stored energy in fat cells used by the body when required.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
