Storage
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Skin Storage
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're discussing an important function of the skin: storage. Can anyone tell me what the skin stores, particularly in the hypodermis?

Does it store fat?

Exactly! The hypodermis stores fat, which is crucial for several functions. Let's explore those functions.

Why is fat storage important for energy?

Great question! The fat is an energy reserve that provides energy during times when you might not be eating enough. Remember, we can think of fat as 'fuel' for the body.
Functions of Stored Fat
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let's talk about the key functions of stored fat. Can anyone identify one?

Maybe it's for insulation?

Yes! Fat provides insulation, helping your body maintain its temperature. It reduces heat loss, especially in cold conditions.

What about protection? Does it help with that too?

Absolutely! The fat acts as a cushion, protecting organs and tissues from mechanical damage. So, remember – fat is crucial not just for energy but also for insulation and protection!
Review and Recap
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

To wrap up our discussion on storage, what are the three main functions of the fat stored in the skin?

Energy reserve, insulation, and cushioning!

Perfect! Remember that the hypodermis serves as a vital layer for more than just superficial functions. It has deep importance for your body’s energy balance, temperature regulation, and protection against injury.

Can you give us a quick way to remember these functions?

Sure! Just think of the word 'E.I.C.' – Energy, Insulation, Cushioning. It’s a handy mnemonic!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
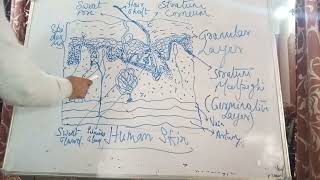
The storage function of the skin is crucial as it primarily involves the storage of fat in the hypodermis layer. This fat serves as an energy reserve, insulation, and cushioning for the body.
Detailed
Detailed Summary
The skin, specifically its hypodermis (or subcutaneous layer), plays a vital role in storing fat. This fat deposits serve three main functions:
- Energy Reserve: The fat stored in the hypodermis acts as a reservoir of energy that the body can utilize during times of need, such as during extended periods without food.
- Insulation: The layer of fat insulates the body, helping to regulate temperature by reducing heat loss in cold environments.
- Cushioning: The fat also provides cushioning to help protect underlying structures, such as muscles and bones, from physical injuries and shocks.
Hence, the storage function of skin is integral not only for energy but also for maintaining body temperature and protecting vital organs.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Storage of Energy and Insulation
Chapter 1 of 1
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Stores fat in the hypodermis as an energy reserve and insulation.
Detailed Explanation
The skin, specifically the hypodermis layer, plays a crucial role in storing fat. This fat serves two main purposes: it acts as an energy reserve and helps insulate the body. The hypodermis, also known as the subcutaneous layer, is where the body stores excess energy in the form of fat. When the body requires energy, it can convert this stored fat into usable energy. Additionally, fat acts as a barrier to prevent heat loss, keeping our bodies warm in cold environments.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the fat stored in the hypodermis like a battery. Just as a battery stores energy for future use, the body stores fat to provide energy when needed. Also, if you imagine wearing a thick jacket in winter, the insulation from the fat under your skin helps to keep you warm, just like the jacket does.
Key Concepts
-
Hypodermis: The innermost layer of skin that stores fat.
-
Energy Reserve: Stored fat acts as an energy source for the body.
-
Insulation: Fat helps to maintain body temperature by reducing heat loss.
-
Cushioning: Stored fat protects underlying tissues from physical damage.
Examples & Applications
During a period of fasting, the body uses stored fat from the hypodermis for energy.
In winter, the insulating layer of fat helps maintain body warmth.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Skin so warm beneath, fat will stay, protecting body, come what may.
Stories
Once in a winter wonderland, a bear named Fuzzy stored fat in the hypodermis to keep warm and protected while he hibernated, proving how essential fat is for survival during tough times.
Memory Tools
E.I.C. – Energy for fuel, Insulation to keep warm, Cushioning for protection.
Acronyms
FAT – Fuel for energy, A barrier of warmth, and Tissue protection.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Hypodermis
The innermost layer of skin, composed of fat and connective tissue that provides insulation and cushioning.
- Fat Storage
The process by which excess energy is stored in the form of fat within the body, particularly in the hypodermis.
- Energy Reserve
Stored fat that the body can use for energy during times of need.
- Insulation
The ability of the stored fat to reduce heat loss and help maintain body temperature.
- Cushioning
The protective function of stored fat that helps absorb shocks and protect underlying organs and tissues.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
