Inequality of Income and Wealth
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding Income Inequality
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today we're exploring income inequality. Can anyone define what this means?

Isn't it about how some people have a lot of money while others have very little?

Exactly! It refers to the uneven distribution of income among different groups in society. Why do you think this might happen?

Maybe because of differences in education? Some people go to better schools than others.

Yes, education plays a crucial role. Higher education often leads to better job opportunities. Let’s remember 'EDU' for 'Education Drives Up' income. Now, what other factors could contribute to income inequality?

I think it could be due to who controls resources, right?

Great point! Monopoly over resources can definitely widen the gap. Recap: Education and resource control are key factors of income inequality.
Effects of Income and Wealth Inequality
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now that we understand the causes, what do you think are the consequences of income inequality?

It might cause social unrest, right? People could get really upset.

Exactly! Social unrest can occur when people feel economically marginalized. Can anyone think of another impact?

I remember that if there’s too much wealth disparity, it can hurt the entire economy.

Right! When a significant portion of the population lacks purchasing power, national welfare declines. Let’s keep these impacts in mind!
Solutions to Income Inequality
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's shift our focus to solutions. What strategies can we use to reduce income inequality?

Progressive taxation could be a solution, right? Higher earners paying more tax?

Yes! Progressive taxation is a way to redistribute wealth. What else can we do?

Implementing social welfare schemes to help those in need makes sense.

Absolutely! Social welfare programs can improve quality of life. Remember: 'TAX WELFARE' for Tax and Welfare solutions to inequality!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Inequality of income and wealth in India refers to the uneven distribution among different sections of society. The section explores causes such as varying education levels, monopoly control over resources, and regional disparities, alongside the effects of social unrest and reduced national welfare, while presenting solutions like progressive taxation and social welfare schemes.
Detailed
Inequality of Income and Wealth
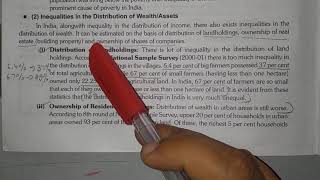
Inequality of income and wealth signifies the uneven distribution of financial resources and opportunities among different social classes in India. This disparity is primarily driven by several key factors, including:
- Differences in Education and Skills: Individuals with higher education and skill sets tend to secure better-paying jobs, exacerbating the income gap.
- Monopoly Control Over Resources: When a few entities or individuals control critical resources, it limits opportunities for the broader population.
- Urban-Rural Divide: A significant economic divide exists between urban and rural areas, with urban regions generally having better access to education and job opportunities.
The effects of this inequality can lead to serious social consequences including:
- Social Unrest: When significant portions of the population feel disenfranchised economically, it can lead to protests and discontent.
- Reduced National Welfare: Income inequality can hinder overall economic growth, as a large number of people may not have the purchasing power to contribute to the economy.
To combat these issues, potential solutions could include:
- Progressive Taxation: Implementing a tax system that increases tax rates for higher income levels can help redistribute wealth.
- Redistribution Policies: Formulating policies aimed at redistributing wealth and resources can help alleviate inequality.
- Social Welfare Schemes: Implementing governmental programs that support the economically disadvantaged can help improve their quality of life and opportunities.
Youtube Videos






Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Definition of Income and Wealth Inequality
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Meaning: Uneven distribution of income among different sections of society.
Detailed Explanation
Income and wealth inequality refers to how income and assets are not evenly distributed across different groups within a society. This means that some individuals or families have a lot of money and resources, while others have very little. Inequality can affect people's quality of life and opportunities for advancement.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a pie divided among friends. If one friend gets a bigger slice compared to the others, they have more pie to enjoy, representing greater resources. Similarly, in society, some people have larger shares of income and wealth, while others have only small portions.
Causes of Inequality
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Causes:
○ Differences in education and skills
○ Monopoly control over resources
○ Urban-rural divide
Detailed Explanation
There are several reasons why income and wealth inequality occurs. First, differences in education and skills can create a gap; those with higher education can get better-paying jobs, while others may struggle. Second, when a few companies dominate the market (monopoly), they control prices and profits, leading to greater wealth for them compared to others. Lastly, the urban-rural divide often means that people living in cities have access to better jobs and resources than those in rural areas.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a race where some runners have special shoes that make them faster, while others run barefoot. The ones with the shoes (more education and skills) have an advantage. Similarly, a few big companies, like a monopolist, can outpace smaller businesses, leading to unequal wealth distribution.
Effects of Inequality
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Effects:
○ Social unrest
○ Reduced national welfare
Detailed Explanation
Inequality can lead to serious consequences for society. Social unrest refers to the tensions and conflicts that arise when people feel they are treated unfairly, which can lead to protests and instability. Reduced national welfare means that the overall health and well-being of the society decrease; when only a few people have wealth, it can lead to inadequate services and opportunities for the larger population.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a community park where only a few get to enjoy it fully while others are barred from entering. If people feel unfairly treated, they might cause trouble or demand changes. This represents how inequality could lead to conflicts and lower the overall happiness of the community.
Solutions to Income and Wealth Inequality
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Solutions:
○ Progressive taxation
○ Redistribution policies
○ Social welfare schemes
Detailed Explanation
To address income and wealth inequality, different measures can be taken. Progressive taxation means that those who earn more pay a higher percentage of their income in taxes, which helps redistribute wealth. Redistribution policies can include government initiatives that ensure wealth is shared more evenly, such as funding education or healthcare for those in need. Social welfare schemes provide support to low-income individuals and families, helping them improve their living conditions.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a cake where a baker decides to slice the biggest pieces for those who need more nutrition. By taxing richer individuals at higher rates, the government can make the income cake more equitable, filling the needs of the less fortunate, just like feeding everyone ensures they can share in the cake and thrive.
Key Concepts
-
Income Inequality: Uneven distribution of income among different social groups.
-
Wealth Inequality: Disparities in the distribution of assets.
-
Progressive Taxation: Taxation system wherein higher earners pay a larger percentage of taxes.
-
Social Unrest: Discontent arising from economic disparity.
-
Redistribution Policies: Government strategies aimed at reducing wealth inequalities.
Examples & Applications
A teacher earns a significantly higher salary than a factory worker, highlighting income inequality.
A city may have luxurious areas while the outskirts face economic hardship, illustrating wealth inequality.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
When income's not spread, it's a cause of dread.
Stories
Imagine two neighborhoods, one wealthy and one struggling. Their fortunes divide their access to opportunities.
Memory Tools
Use 'I-RISE' to remember: Income Inequality Worries, Instigates Social unrest, & Requires Solutions like Employment schemes.
Acronyms
W.E.S.T. for Wealth, Education, Social unrest, Taxes to remember factors in income inequality.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Income Inequality
The uneven distribution of income among different groups in society.
- Wealth Inequality
The unequal distribution of assets among individuals in an economy.
- Progressive Taxation
A tax system where tax rates increase as income increases.
- Monopoly
A market structure where a single seller or entity dominates.
- Social Welfare
Programs designed to assist those in financial need.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
