Ecological Succession
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Definition and Importance of Succession
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're discussing ecological succession, which refers to the natural process of change in species composition in an ecosystem over time. It's important because it shows how ecosystems evolve.

So, does that mean ecosystems are always changing?

Exactly! Ecosystems can fluctuate and adapt due to environmental changes. A helpful way to remember this is the term 'succession' which implies 'following after'.

What kinds of places undergo this change?

Great question! There are two main types: primary and secondary succession. Let's explore those next.
Primary Succession
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Primary succession starts in lifeless areas. Can anyone give me an example of where this might occur?

What about a volcanic eruption site?

Exactly! After a volcanic eruption, you might find bare rock. Pioneers like lichens can colonize these areas first, paving the way for more complex species. Just remember: 'Pioneers Prepare the Path!'

How long does primary succession take?

It can take hundreds to thousands of years! Eventually, this process leads to a stable climax community.
Secondary Succession
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s discuss secondary succession. This happens in areas that have been disturbed but where soil and some organisms still remain. What can you think of that might cause such a disturbance?

A forest fire?

That's right! Unlike primary succession, secondary succession usually happens much faster because the soil is already there. Remember, 'Soil Speeds Recovery!'

How long does that normally take?

It can take years to decades, depending on the ecosystem's nature and the disturbance's severity.
Significance of Succession
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Why do we study ecological succession? It helps us understand how ecosystems recover from disturbances, informing conservation and restoration efforts.

Does that mean we can help ecosystems recover faster?

Exactly! By understanding the processes, we can implement more effective conservation strategies.

So, it's all about balance and resilience?

Very much so! Ecosystems thrive on balance, and succession is a crucial part of that.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section highlights the significance of ecological succession, defining it as a gradual, natural process of change in species diversity. It describes two major types: primary succession in lifeless areas and secondary succession following disturbances.
Detailed
Ecological Succession
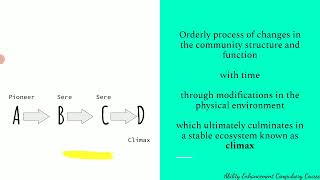
Ecological succession refers to the gradual process in which ecosystems change and develop over time, leading to a shift in species composition. This fundamental ecological concept emphasizes that ecosystems are not static; they evolve through a series of stages, ultimately resulting in a stable community. The major types of ecological succession are:
- Primary Succession: This occurs in previously uninhabited environments, such as areas formed by volcanic eruptions or exposed rock after glacial retreats. It begins with pioneer species, like mosses and lichens, that can survive in harsh conditions. Over time, these organisms modify the environment, enabling more complex plants to establish, leading to a mature ecosystem.
- Secondary Succession: This type of succession occurs in areas that have been disturbed but still retain some soil and organisms, such as after a forest fire or flood. The recovery process is usually faster than primary succession because the soil is already present, allowing plants and animals to recolonize the area more quickly.
Understanding these processes is vital for conservation efforts and managing natural resources, as they illustrate how ecosystems can recover from disturbances and adapt to changes.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Definition of Ecological Succession
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Definition: Natural, gradual process of change in the types of species in an ecosystem
Detailed Explanation
Ecological succession is the process through which ecosystems change and develop over time. It involves a gradual replacement of one set of species by another. This change is often triggered by events such as natural disasters or the introduction of new species, which alters the environment and creates opportunities for new species to thrive.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a forest after a big storm: initially, there are only broken trees and open spaces. Over time, small plants and grasses might start to grow in these spaces, followed by bushes and eventually, young trees. Just like how a community may change and grow after a major event, ecosystems too go through this cycle of change.
Types of Ecological Succession
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Types:
○ Primary Succession: Occurs in lifeless areas (e.g., lava flow, bare rock)
○ Secondary Succession: Occurs in disturbed areas (e.g., after forest fire or flood)
Detailed Explanation
There are two main types of ecological succession: primary and secondary. Primary succession happens in an area where there were originally no organisms, such as on bare rock after a volcanic eruption. This process starts with pioneer species, like lichens, that can survive in harsh conditions. On the other hand, secondary succession occurs in areas where an ecosystem has been disturbed but soil and seeds still exist, such as after a forest fire. The recovery happens faster in secondary succession because the soil already contains nutrients and seeds from existing plants.
Examples & Analogies
Think of primary succession like starting a new garden in a completely empty space with no soil or plants. You begin from scratch. In contrast, secondary succession is like renovating an existing garden after a storm that knocked over some plants but left the soil intact. You can replant and quickly restore it to its former beauty.
Key Concepts
-
Ecological Succession: The gradual process of change in species composition in an ecosystem.
-
Primary Succession: Succession occurring in lifeless areas.
-
Secondary Succession: Succession following disturbances in areas with existing soil.
Examples & Applications
A lava field left by a volcanic eruption is an example of a site for primary succession.
An area that experienced a forest fire and regrows over time is an example of secondary succession.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Pioneers on land, make it grand, with soil in hand, new life will stand!
Stories
Once upon a time, a barren land waited for its heroes — the pioneer species — who arrived to plant the first seeds and invite a thriving ecosystem!
Memory Tools
Remember 'Press out Slow' for 'Primary Succession creates slowly in Lifeless areas'.
Acronyms
POSS for 'Pioneer, Ocean, Soil, Species' in ecological succession.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Ecological Succession
The natural, gradual process of change in the types of species in an ecosystem.
- Primary Succession
The type of succession that occurs in lifeless areas, such as after a lava flow or glacial retreat.
- Secondary Succession
The type of succession that occurs in areas that have been disturbed, where soil and some organisms still exist.
- Pioneer Species
The first species to colonize previously uninhabited environments.
- Climax Community
The stable and mature stage of an ecosystem that undergoes little change in species composition.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
