Food Chains and Food Webs
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Food Chains
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're going to talk about food chains! Can anyone tell me what a food chain is?

Is it something to do with food and eating?

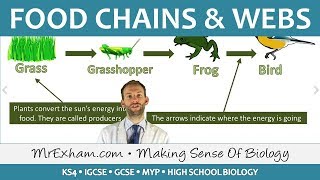
Exactly! A food chain is a linear sequence that shows how energy moves from one organism to another in the ecosystem. It's like a story of who eats whom! For example, consider this food chain: Grass → Grasshopper → Frog → Snake → Hawk. Each of these organisms play a role in the chain!

So, the grass is at the beginning because it makes its own food?

That's right! Grass is a producer. This leads us to remember the acronym 'P-C-D' for Producers, Consumers, and Decomposers. Can anyone name what a primary consumer is in our example?

The grasshopper!

Great job! And what comes after the grasshopper?

The frog!

Perfect! The food chain illustrates how energy flows in a straightforward manner. Let’s summarize: food chains start with producers and move through consumers.
Understanding Food Webs
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now that we understand food chains, let's talk about food webs. How do you think they differ from food chains?

Is it like a bunch of food chains combined?

Exactly! A food web is a network of interconnected food chains. It shows the complex feeding relationships in an ecosystem. For instance, a rabbit doesn't just eat grass, it might also eat vegetables or fruits, and it can be eaten by different predators.

So, every animal could be part of many chains?

Correct! This complexity is important because it illustrates how resilient ecosystems can be. If one species is removed, others can still maintain the balance. Can anyone think of a real-life example?

Like if we remove wolves from an area, the deer population grows too much, affecting plants?

Exactly, that's a great example of a disturbed food web! Let's summarize our discussion: food webs provide a richer picture of ecosystem interactions.
Significance of Food Chains and Webs
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Why do you think understanding food chains and food webs is important in ecology?

It helps us see how everything is connected?

Exactly! Understanding these concepts helps us comprehend energy flow in ecosystems and the impact of changes in populations, like when humans disrupt habitats.

So, if we pollute or cut down trees, it affects everything?

That's right! Ecosystems depend on the balance between producers, consumers, and decomposers. It helps us realize the importance of conservation efforts.

And it shows why we should care about biodiversity!

Absolutely! So to recap, food chains and food webs are fundamental to understanding ecosystem dynamics.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
In this section, food chains are defined as linear sequences that illustrate who eats whom in an ecosystem, while food webs represent a complex network of interconnected food chains that demonstrate feeding relationships among organisms. Both concepts are vital for understanding energy flow in ecosystems.
Detailed
Food Chains and Food Webs
In this section, we explore the concepts of food chains and food webs, both critical for understanding the dynamics of ecosystems.
Food Chains
A food chain is a linear sequence that depicts how energy and nutrients flow from one organism to another in an ecosystem. This sequence typically starts with producers, which create their own energy through photosynthesis, and flows to various levels of consumers, leading up to higher-level predators. For instance, a simple food chain might illustrate the flow as:
- Grass (Producer) → Grasshopper (Primary Consumer) → Frog (Secondary Consumer) → Snake (Tertiary Consumer) → Hawk (Quaternary Consumer).
Each step in this chain represents a trophic level, showcasing the feeding relationships that sustain life.
Food Webs
Conversely, a food web comprises a complex network of interconnected food chains. It depicts how various organisms are related and emphasizes the intricate and often overlapping feeding relationships in an ecosystem. This broader perspective is critical as it accounts for the reality that most animals consume more than one type of food and have multiple predators.
Importance
Understanding food chains and webs is essential for studying energy flow through ecosystems and the interactions among species, highlighting the balance of ecosystems and the role of biodiversity.
Youtube Videos







Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Understanding the Food Chain
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Food Chain: A linear sequence showing who eats whom in an ecosystem
○ Example: Grass → Grasshopper → Frog → Snake → Hawk
Detailed Explanation
A food chain is a straightforward way to visualize how energy and nutrients flow through an ecosystem. It starts with producers, like grass, which create their own food through photosynthesis using sunlight. The grass is eaten by herbivores, such as grasshoppers. Then, those herbivores are prey for carnivores, like frogs. This continues up the chain to higher-level consumers, like snakes, and finally to apex predators, such as hawks. Each step in this chain is called a trophic level, where energy is transferred from one organism to another.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a food chain like a relay race. The grass represents the first runner who starts the race by using sunlight to grow. Each subsequent organism passes the baton of energy and nutrients, culminating in the hawk at the finish line, representing the top of the food chain.
Exploring the Food Web
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Food Web: A network of interconnected food chains showing complex feeding relationships
Detailed Explanation
A food web expands on the idea of a food chain by demonstrating how various organisms are interconnected through multiple feeding relationships. While a food chain is linear, a food web is much more complex and illustrates how different food chains overlap and interact. This means that an organism can be part of several food chains, being a predator in one and prey in another. This complexity allows ecosystems to be more resilient, as the disruption of one species may not completely ruin the ecosystem because other food sources and relationships exist.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a food web as a city map with various roads (food chains) connecting different neighborhoods (organisms). While you can travel directly from one neighborhood to another using one road, there are also many alternative routes. If one road is blocked (a species disappears), other routes still allow traffic (energy flow) to continue, keeping the city (ecosystem) functioning.
Key Concepts
-
Food Chain: A linear sequence showing feeding relationships among organisms.
-
Food Web: A complex web of interconnected food chains within an ecosystem.
-
Trophic Level: The position of an organism within a food chain.
-
Producers, Consumers, and Decomposers: Key roles in energy flow.
Examples & Applications
Example of a food chain: Grass → Grasshopper → Frog → Snake → Hawk.
Example of a food web: A community where rabbits eat grass, and also are food for hawks, while plants provide food for caterpillars, eaten by birds.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In our food web, everyone plays; producers make, consumers graze. Decomposers break down what decays, in the circle of life, nature stays!
Stories
Once in a lush forest, grass greeted a hungry grasshopper, who was caught by a curious frog. The frog was savored by a swift snake, while a watchful hawk saw the snake as a meal. This web of feeding creates balance.
Memory Tools
Remember 'P-C-D' for Producers, Consumers, and Decomposers in food chains.
Acronyms
FOOD for 'F'ood chains, 'O'rganisms, 'O'ptimal energy flow, and 'D'ynamics of ecosystems.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Food Chain
A linear sequence that shows who eats whom in an ecosystem.
- Food Web
A complex network of interconnected food chains showing the relationships among organisms.
- Producers
Organisms, like plants, that make their own food through photosynthesis.
- Consumers
Organisms that obtain energy by consuming other organisms; includes herbivores, carnivores, and omnivores.
- Trophic Level
Each level in a food chain; the position of an organism in relation to energy flow.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
