Composition of the Atmosphere
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Overview of Atmospheric Gases
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we will explore the composition of the atmosphere. Can anyone tell me what the main gases are?

I think nitrogen and oxygen are the biggest parts?

Correct! Nitrogen makes up about 78% of the atmosphere, while oxygen is roughly 21%. That means these two gases vastly outnumber the others. Does anyone know why nitrogen is important?

Maybe because it helps keep the air stable?

Exactly! Nitrogen is inert, which is vital because it keeps the atmosphere from burning up. Let's remember it as 'N for Nitrogen, neutral and nurturing'.

What about oxygen? Why is it so important?

Oxygen is essential for cellular respiration and supports combustion. Think of it as 'O for Oxygen, offering life!'

So far, we have learned that nitrogen and oxygen are the major components. But can someone tell me what argon is?

Isn't it one of the noble gases?

Yes! Argon is about 0.93% of our air and is chemically inert. Now, let’s summarize: The primary gases are Nitrogen, Oxygen, and Argon. Great job, everyone!
Trace Gases and Their Impact
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Next, let's talk about trace gases. Who can name a few?

Carbon dioxide?

Yes! Carbon dioxide makes up only 0.03% of the atmosphere but is pivotal for life due to photosynthesis. Can anyone explain why it's called a greenhouse gas?

Oh, it traps heat in the atmosphere!

Exactly! That’s why we have to be careful with increasing CO2 levels from human activities. Let’s remember it as 'C for Carbon, capturing warmth'.

What about water and dust? Why do they matter?

Good question! Water vapour and dust are crucial for cloud formation and precipitation. Think of it as 'Wet and Dusty, weather must be'! They can vary significantly in concentration.

So those help with the weather, right?

Exactly! So to summarize, while trace gases are minor in volume, they play major roles in our environment!
Importance of Atmospheric Composition
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Finally, let’s discuss the significance of the atmosphere's composition. Why do you think it matters?

It’s important for life!

Absolutely! The mix of gases supports life processes and helps regulate the climate. Can anyone think of other impacts?

It protects us from solar radiation?

Yes! The atmosphere acts like a shield against harmful solar radiation and meteoroids. Think of it as 'Air's Armor'.

What would happen without these gases?

Without them, life as we know it would be impossible. The atmosphere helps maintain temperature and supports weather patterns.

So, to recap: the atmosphere's gases are crucial for life, temperature regulation, and protection. Well done today, everyone!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
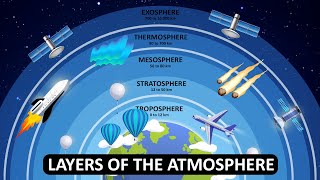
The atmosphere consists of approximately 78% nitrogen, 21% oxygen, 0.93% argon, and smaller amounts of carbon dioxide and trace gases. Water vapour and dust play critical roles in weather phenomena, including cloud formation and precipitation, making the composition of the atmosphere crucial for sustaining life on Earth.
Detailed
Composition of the Atmosphere
The Earth's atmosphere is made up of a mixture of gases that are vital for life and various environmental processes. The principal components include:
- Nitrogen (N₂): Comprising 78% of the atmosphere, nitrogen is inert and serves primarily to dilute oxygen and prevent rapid combustion.
- Oxygen (O₂): At 21%, oxygen is critical for cellular respiration in living organisms and supports combustion.
- Argon (Ar): This noble gas makes up 0.93% of the atmosphere and is chemically inert, contributing to atmospheric balance.
- Carbon Dioxide (CO₂): Although it constitutes only 0.03%, carbon dioxide is essential for photosynthesis and plays a significant role in the greenhouse effect.
- Others (trace gases): Include gases like neon and helium in minuscule amounts.
- Water Vapour and Dust: These two constituents vary in concentration and are vital for weather phenomena, including cloud formation and precipitation. Water vapour is significant in regulating temperature and weather dynamics.
Understanding the composition of the atmosphere is crucial not only for recognizing its role in supporting life but also for understanding weather patterns, climate change, and environmental policies.
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Overview of Atmospheric Gases
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Gas Percentage by Volume
Nitrogen (N₂) 78%
Oxygen (O₂) 21%
Argon (Ar) 0.93%
Carbon Dioxide (CO₂) 0.03%
Others (Neon, Helium, etc.) Trace amounts
Detailed Explanation
The atmosphere is composed mostly of nitrogen, which makes up 78% of the air we breathe. Oxygen follows, making up 21%. The remaining gases include argon, carbon dioxide, and trace amounts of other gases like neon and helium. These components are vital for various life-supporting processes on Earth.
Examples & Analogies
You can think of the composition of the atmosphere like a cake. Nitrogen is the largest layer, the cake's sponge, providing the bulk. Oxygen adds flavor, while argon and carbon dioxide are like the icing, adding special touches to keep everything balanced.
Importance of Water Vapour and Dust
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Note: Water vapour and dust are crucial for cloud formation and precipitation.
Detailed Explanation
While nitrogen and oxygen are the most abundant, water vapour and dust play essential roles in the atmosphere. Water vapour is necessary for cloud formation, and without it, we wouldn't have rain. Dust particles act as nuclei for water droplets, enabling precipitation.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine making a snow globe. The water inside is like the water vapour in the atmosphere, essential for creating the snowy effect. Without the small flecks of glitter (dust), the snow wouldn’t fall and gather, just like rain wouldn’t form without dust particles in the air.
Key Concepts
-
Composition of the Atmosphere: The atmosphere comprises mainly nitrogen, oxygen, argon, with trace gases including carbon dioxide, essential for sustaining life.
-
Role of Water Vapour: Water vapour and dust are crucial for processes like cloud formation and precipitation, impacting weather and climate.
-
Significance of Trace Gases: Though present in small amounts, trace gases like carbon dioxide play major roles in heat retention and photosynthesis.
Examples & Applications
The air we breathe is primarily composed of nitrogen and oxygen, necessary for human and animal survival.
Photosynthesis in plants utilizes carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, illustrating the essential role of trace gases.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Nitrogen and oxygen, in the air they play, / Argon’s here to quietly stay!
Stories
Once in a golden cloud, nitrogen traveled free, / Oxygen and argon danced in perfect harmony, / But the tiny CO2 sparking much liveliness, / Together they create life's rich universe.
Memory Tools
N (Nitrogen) 78%, O (Oxygen) 21%, A (Argon) 0.93%. Remember 'NOA' for atmospheric giants!
Acronyms
For breathing and burning, remember the 'NOBLE'
for Nitrogen
for Oxygen
for Burning (combustion)
for Lighter (argon)
for Essential (carbon dioxide).
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Atmosphere
A layer of gases surrounding the planet, essential for sustaining life.
- Nitrogen
A largely inert gas constituting 78% of the atmosphere, preventing rapid combustion.
- Oxygen
A vital gas for respiration and combustion, making up 21% of the atmosphere.
- Argon
A chemically inert noble gas constituting 0.93% of the atmosphere.
- Carbon Dioxide
A trace gas essential for photosynthesis, comprising 0.03% of the atmosphere.
- Trace gases
Gases present in the atmosphere in very small amounts but significant for environmental processes.
- Water Vapour
Water in gaseous form, critical for weather formation and processes.
- Dust
Small solid particles that contribute to weather and air quality.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
