Exosphere
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to the Exosphere
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're going to explore the exosphere, the outermost layer of our atmosphere. Who can tell me where the exosphere starts?

Isn’t it above 500 km?

That's correct! It starts at about 500 kilometers and goes up to about 10,000 kilometers. What do you think happens in this layer?

Is that where satellites orbit?

Exactly! The exosphere is where most satellites are located. Can anyone think of why satellites prefer to be in this part of the atmosphere?

Because the air is really thin, right? That means less resistance!

Yes, less atmospheric drag allows satellites to maintain their orbits more easily. Great job!

So remember, the exosphere is very thin, yet very important for satellite operations!
Characteristics of the Exosphere
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's discuss what the exosphere is made of. Can anyone tell me about the gases found in this layer?

I think it’s mostly hydrogen and helium?

That’s right! The exosphere primarily contains hydrogen and helium, along with trace amounts of other gases. Why is the particle density so low?

Because it's the outermost layer? There are not many particles up there?

Exactly! It's extremely thin. Now, what about the temperature in the exosphere? Does anyone remember what it can reach?

I think it can get really hot, like thousands of degrees!

Yes! It can reach up to 2,500 °C, but because there are so few particles, the heat is not felt as we would expect. Great participation today!
The Importance of the Exosphere
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Finally, let’s talk about why the exosphere is important. Can anyone think of its significance?

It’s where satellites orbit, so it’s crucial for communication.

Absolutely! Communication satellites rely on this layer. Do you think there are any other scientific benefits?

Maybe studying cosmic rays?

Yes! The exosphere helps us understand cosmic radiation and how it interacts with Earth's atmosphere. Each of these aspects is vital for both technical and scientific advancements.

So, remember: The exosphere is thin, contains mainly hydrogen and helium, and is critical for satellite operation!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
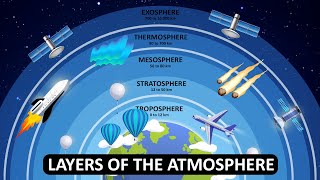
The exosphere, the final layer of the atmosphere, begins above 500 km and gradually merges into outer space. This layer has very low density, allowing satellites to orbit, and it plays a crucial role in communications and atmospheric science.
Detailed
Exosphere Overview
The exosphere is the outermost layer of Earth's atmosphere, extending from approximately 500 km above sea level to about 10,000 km, gradually merging into space. Unlike the denser layers of the atmosphere, the exosphere is characterized by an extremely thin atmosphere with very low particle density. Key features of the exosphere include:
- Satellite Orbits: This layer is where various satellites, including communication satellites, orbit the Earth. The sparse air allows these satellites to function without significant atmospheric drag.
- Gradual Transition: The boundary between the exosphere and outer space is not distinctly defined; instead, the atmosphere gradually becomes thinner, which can make it difficult to pinpoint where the exosphere ends.
- Composition: The exosphere contains mainly hydrogen and helium, with other trace elements existing in minimal quantities.
- Temperature: Although the temperature can reach thousands of degrees Celsius, the low density means that there are very few particles, thus providing little heat transfer.
The exosphere plays a significant role in various Earth sciences and our understanding of atmospheric processes, including those affecting satellite communications and the study of cosmic radiation.
Youtube Videos







Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Overview of the Exosphere
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The Exosphere is the outermost layer of the atmosphere, situated above 500 km.
Detailed Explanation
The Exosphere represents the highest layer of Earth's atmosphere, starting at approximately 500 kilometers above the earth's surface. Unlike the layers below it, the Exosphere is where the atmosphere becomes extremely thin, and there’s very little air. This layer gradually transitions into outer space, making it a unique part of our atmosphere.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the Exosphere like the top of a tall mountain where the air gets thinner and thinner until it becomes almost impossible to breathe. Just like how higher altitudes on Earth have less air pressure and fewer oxygen molecules, the Exosphere has very few air molecules compared to the layers below it.
Characteristics of the Exosphere
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The air in the Exosphere is extremely thin, and it is where satellites orbit the Earth.
Detailed Explanation
In the Exosphere, the density of air is so low that the few air molecules present are spaced out significantly. This means that jets and other aircraft cannot fly here; instead, this is where satellites and space stations orbit Earth due to the weak gravitational pull at this altitude. Satellites rely on this layer to maintain their paths around our planet, making the Exosphere important for communication and weather forecasting.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine how a balloon floats in the air. When inflated, it stays buoyant because there are enough air molecules inside pushing against the surrounding air. In the Exosphere, however, there are so few air molecules that it’s like trying to keep a balloon afloat in a vacuum. Only specially designed spacecraft can operate in this thin atmosphere.
Transition to Space
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The Exosphere gradually merges into outer space.
Detailed Explanation
As one ascends past the Exosphere, there is no distinct boundary marking the end of the atmosphere and the beginning of space. The transition is smooth, making it challenging to pinpoint where Earth’s atmosphere is definitively over. This gradual merging indicates that the Exosphere is a crucial area where earthly influences dissipate, and the conditions of outer space begin to prevail.
Examples & Analogies
Consider the merging of two colors - when painting, you might blend blue into green, creating a gradient rather than a sharp line. Similarly, there isn’t a clear-cut end to the Exosphere; it gradually transitions into the emptiness of space, just as colors blend and flow from one into the next.
Key Concepts
-
The Exosphere: The outermost layer of the atmosphere, important for satellite orbits.
-
Composition: Primarily made of hydrogen and helium with very low density.
-
Temperature: Can reach very high temperatures, but low density limits heat transfer.
-
Importance: Critical for satellite operation and scientific understanding.
Examples & Applications
Satellites like GPS and communication satellites orbit in the exosphere to minimize atmospheric drag.
The exosphere's thin atmosphere allows for fewer obstacles for satellites, enabling effective communication.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In the exosphere so high, satellites float and fly. Thin air and gases light, reach for stars, a wondrous sight.
Stories
Imagine a rocket reaching for space, leaving behind the heavy atmosphere. It glides smoothly through the exosphere, where satellites dance in the thin air, free from resistance, just like birds in the sky.
Memory Tools
Use the acronym HHS – High altitude, High temperatures, Satellites orbit here to remember the key features of the exosphere.
Acronyms
EAT
Exosphere Affects Technology—reminding us how this layer is crucial for communication and satellites.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Exosphere
The outermost layer of Earth's atmosphere, beginning at about 500 km and extending into space.
- Satellite
An object placed in orbit around the Earth or another planet for the purposes of communication, weather monitoring, or scientific observation.
- Cosmic Radiation
High-energy radiation that originates outside the Solar System and may have significant impacts on technology and life.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
