Automobile Suspension Systems
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Function of Suspension Systems
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're going to discuss the function of automobile suspension systems. Can anyone tell me what you think the primary role of a suspension system is?

I think it helps in absorbing shocks from the road.

Exactly! The suspension system absorbs shocks from road irregularities. It also helps maintain tire contact with the road to enhance vehicle control and ride comfort. Remember the acronym 'SCR' for Suspension: Shock absorption, Contact maintenance, and Ride comfort.

Does that mean a better suspension leads to better driving experience?

Absolutely! A well-designed suspension system significantly affects how comfortable and controlled the ride feels. Let's think about what happens in different terrains and how the suspension compensates.
Key Components of Suspension Systems
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's explore the key components of a suspension system. What do you think the main elements are?

Are springs one of the components?

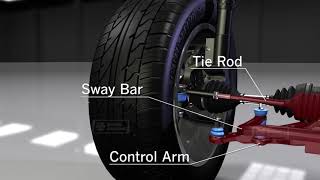
Absolutely! Springs, including coil, leaf, and torsion bar types, are vital. And we have dampers, which are often shock absorbers, control arms, bushings, and stabilizer bars. Remember the mnemonic 'SDS-CBS' for Springs, Dampers, Control arms, Bushings, and Stabilizer bars.

How does each part contribute to performance?

Great question! Springs absorb energy from impacts, dampers control the spring motion, and the other components help in geometry and stability of the system, ensuring overall performance.
Design Considerations
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let’s focus on design considerations. What do you think engineers need to consider when designing a suspension system?

They should think about comfort and shock absorption?

Correct, but there's more! Engineers consider natural frequency, damping ratio, load distribution, and geometry like MacPherson strut and double wishbone setups. Each aspect affects how the system interacts with the vehicle dynamics.

Why is the damping ratio important?

Great question! The damping ratio helps control the oscillations of the suspension. Too much or too little can lead to poor performance. It's essential for maintaining stability and comfort.
Applications of Previous Topics
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Lastly, how do you think concepts from our earlier modules, like stress analysis and vibrations, apply to suspension systems?

I guess they relate to how much stress components can handle?

Exactly! Understanding stress and how materials respond to vibrations helps in designing durable, efficient suspension systems. The use of springs and dampers is a direct application of our prior knowledge.

Can we also consider fatigue in this context?

Yes! Fatigue is a critical factor, particularly for components that experience repeated stress. This is vital in ensuring long-lasting performance in vehicles.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The automobile suspension systems are essential mechanical systems designed to absorb shocks from road irregularities, maintain tire contact, and enhance ride comfort. The section delves into key components such as springs and dampers and discusses design considerations and their applications in the automotive realm.
Detailed
Automobile Suspension Systems
The automobile suspension system is a crucial mechanical system that serves several functions: absorbing shocks caused by road irregularities, maintaining contact between the tires and the road for improved control, and enhancing ride comfort for passengers.
Key Components
The primary components of the suspension system include springs (which can be coil, leaf, or torsion bar), dampers (typically shock absorbers), as well as control arms, bushings, and stabilizer bars. Each of these components plays a vital role in ensuring the efficient operation of the suspension system.
Design Considerations
When designing suspension systems, engineers consider various factors, including natural frequency and damping ratio, load distribution, and suspension geometry (e.g., MacPherson strut or double wishbone setups). These elements directly contribute to the performance and integrity of the system under various driving conditions.
Applications of Earlier Topics
This section also connects to prior topics like springs, dampers, stress analysis, vibrations, and fatigue, showcasing how these concepts apply to real-world suspension systems.
Understanding automobile suspension systems enhances one's knowledge of mechanical design and demonstrates the integration of theoretical knowledge into practical applications.
Youtube Videos





Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Function of Suspension Systems
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Absorb shocks from road irregularities
● Maintain tire contact with road
● Enhance ride comfort and vehicle control
Detailed Explanation
The primary functions of automobile suspension systems are to absorb shocks created by uneven road surfaces, ensure that the vehicle's tires stay in contact with the road for better grip and control, and improve overall ride comfort for passengers. By absorbing impacts from bumps and potholes, the suspension prevents excessive movement of the vehicle's body, which can lead to discomfort and loss of control.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine riding a bike over a bumpy path. If your bike has a good suspension system (like shock-absorbing tires), you’ll feel the bumps less and can pedal smoothly across the uneven surface. A car's suspension works similarly, smoothing out the ride for passengers and ensuring better handling.
Key Components of Suspension Systems
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Springs (coil, leaf, torsion bar)
● Dampers (shock absorbers)
● Control arms, bushings, stabilizer bars
Detailed Explanation
Suspension systems are made up of several key components. Springs, which can be coil, leaf, or torsion bars, help support the weight of the vehicle and absorb shocks. Dampers, commonly known as shock absorbers, control the speed of the springs' motions, preventing excessive bouncing. Control arms link the wheels to the vehicle’s frame, allowing for smooth movement, while bushings act as cushions that reduce noise and vibration. Stabilizer bars help reduce body roll during turns, making the vehicle more stable.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a trampoline: the springs on it allow for bouncing, similar to how the vehicle's springs allow for vertical movement. The dampers act like a friend holding your shoulders to prevent you from bouncing too high and losing balance. This combination keeps the ride enjoyable and safe.
Design Considerations in Suspension Systems
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Natural frequency and damping ratio
● Load distribution
● Suspension geometry (MacPherson strut, double wishbone)
Detailed Explanation
When designing suspension systems, several factors must be considered. The natural frequency indicates how quickly the system can respond to shocks, while the damping ratio measures how quickly the system stabilizes after an impact. Proper load distribution across all components is essential for maintaining balance and performance. Lastly, the geometry of the suspension, such as whether it uses a MacPherson strut or a double wishbone design, affects how the wheels move relative to the vehicle’s body and impacts handling characteristics.
Examples & Analogies
Consider how a playground swing set works. The angle (geometry) of the swing arm affects how high the swing can go and how quickly it swings back. In cars, the design of their suspension geometry influences how they handle bumps and turns, much like that swing set influences your ride.
Applications of Earlier Topics
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Use of springs, dampers, stress analysis, vibrations, and fatigue
Detailed Explanation
The concepts learned in earlier topics such as the properties of materials (springs), the function of dampers, and analyses of stress and vibrations play a crucial role in the design and functioning of suspension systems. Understanding how these components interact and how they are affected by factors like fatigue (wear over time) helps engineers create safer, more effective suspension systems. This knowledge ensures that vehicles can perform well under various conditions.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine building a small bridge out of popsicle sticks. You need to consider how much weight it can hold (stress), how it will bend or sway in the wind (vibration), and how it will hold up over time (fatigue). Similarly, engineers must account for these factors when designing suspension systems to ensure they are safe and durable.
Key Concepts
-
Function of Suspension: Absorbs shock, maintains tire contact, enhances comfort.
-
Key Components: Springs, dampers, control arms, and their roles.
-
Design Considerations: Damping ratio, natural frequency, geometry, load distribution.
-
Applications of Previous Concepts: Use of springs, dampers, and stress analysis in suspension design.
Examples & Applications
A vehicle navigating a rough road demonstrates the shock-absorbing capability of springs.
The importance of damping can be observed when a car takes a sharp turn; a well-designed suspension maintains stability.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Springs and dampers, oh what a pair, keep you comfy, lighten your care.
Stories
Once upon a time, a car called Comfort found springs and dampers to ride on bumpy roads and keep its passengers happy.
Memory Tools
SDS-CBS: Springs, Dampers, Control arms, Bushings, Stabilizer bars.
Acronyms
SCR
Shock absorption
Contact maintenance
Ride comfort.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Springs
Mechanical components that compress or extend to absorb shocks from road irregularities.
- Dampers
Hydraulic or mechanical components that control the motion of springs and absorb energy.
- Control Arms
Linkage that connects the suspension system to the vehicle chassis, allowing for wheel movement.
- Damping Ratio
A measure of how oscillations in a system decay after a disturbance.
- Suspension Geometry
The arrangement and angle of suspension components affecting vehicle handling.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
