Contingency Theories
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Contingency Theories
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Welcome, everyone! Today, we're diving into contingency theories of leadership. Can anyone tell me what they think contingency means in this context?

Does it mean that something is dependent on something else?

Exactly! In leadership, this means the effectiveness of a leadership style depends on the context. For example, a leader might be effective in one situation, but not in another. Let's explore some specific theories that illustrate this.

What are some of those theories?

Great question! We will discuss Fiedler’s Contingency Model, Hersey and Blanchard’s Situational Leadership Theory, and Path-Goal Theory. Let's start with Fiedler's model.
Fiedler’s Contingency Model
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

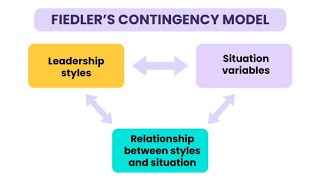
Fiedler’s Contingency Model suggests that a leader's effectiveness is tied to their style and the favorableness of the situation. Have you heard of the LPC scale?

I think I've heard about it. What does it measure?

The LPC scale measures how a leader views their least preferred coworker. Based on this, we can determine if a leader is task-oriented or relationship-oriented. What do you think might affect situational favorableness?

Maybe how well the team members get along with the leader?

Yes! Leader-member relations, task structure, and position power are key factors. Let’s move on to Hersey and Blanchard’s theory.
Hersey and Blanchard’s Situational Leadership Theory
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Hersey and Blanchard suggest that leaders must adapt their styles according to followers' readiness. What are the four styles they identify?

I remember telling, selling, participating, and delegating!

Spot on! Can someone explain the telling style?

That’s the one where the leader gives clear instructions but has a low relationship focus.

Correct! And as readiness increases, leaders should shift towards selling, participating, and then delegating as appropriate.
Path-Goal Theory
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Lastly, let’s explore Path-Goal Theory. This theory emphasizes how leaders can help their subordinates achieve goals. What does this involve?

It’s about clearing the path for followers to reach those goals?

Exactly! Leaders provide support and guidance depending on the situation. What are the four styles that can be applied?

Directive, supportive, participative, and achievement-oriented!

Well done! Remember, the choice of style is influenced by the task and follower’s needs. This adaptability is critical in effective leadership.
Recap and Key Takeaways
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

To wrap up, we’ve covered Fiedler’s Contingency Model, Situational Leadership Theory, and Path-Goal Theory. Why are these theories important in leadership?

They show us that we should change our leadership style based on the situation and our followers.

Exactly! Adapting our approach can lead to better communication and team effectiveness. Great insights today, everyone!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section details various contingency theories, including Fiedler’s Contingency Model, Hersey and Blanchard’s Situational Leadership Theory, and Path-Goal Theory, emphasizing how specific circumstances influence the suitability of different leadership styles.
Detailed
Contingency Theories
Contingency theories suggest that there is no single best way to lead. Instead, a leader's effectiveness is contingent upon factors such as the situation, the follower's needs, and the leader's style. The main theories included in this section are:
- Fiedler’s Contingency Model: This theory posits that a leader’s effectiveness is determined by their individual style and the favorability of the situation for that style. The Least Preferred Co-worker (LPC) scale is used to assess leaders' styles and situational variables include leader-member relations, task structure, and position power.
- Hersey and Blanchard’s Situational Leadership Theory: This model emphasizes that leaders must adapt their style based on the readiness or maturity of their followers. It identifies four leadership styles: telling (high task, low relationship), selling (high task, high relationship), participating (low task, high relationship), and delegating (low task, low relationship).
- Path-Goal Theory (Robert House): This theory focuses on how leaders can help their subordinates achieve goals by clearing paths and providing the support needed. It identifies different styles based on situational needs including directive, supportive, participative, and achievement-oriented leadership.
Understanding these theories helps future leaders in engineering and business contexts to apply the right leadership approach based on the situation, ensuring better team performance and satisfaction.
Youtube Videos







Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Overview of Contingency Theories
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
These theories suggest that the effectiveness of a leadership style depends on the context.
Detailed Explanation
Contingency theories of leadership imply that no single leadership style is the best in all situations. Instead, the effective leadership style varies based on different factors in the environment. Leaders must evaluate their surroundings and the needs of their teams to determine the most suitable approach to leadership.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a coach leading a sports team. Depending on the strengths and weaknesses of the players, as well as the specific opponent they're facing, the coach may choose a more aggressive or conservative strategy. This adaptability is similar to how leaders must change their styles based on contextual factors.
Fiedler’s Contingency Model
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
a. Fiedler’s Contingency Model
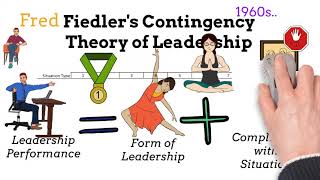
- Leadership effectiveness = Leader’s style + Situational favorableness.
- Uses LPC (Least Preferred Co-worker) scale.
- Situations vary by leader-member relations, task structure, and position power.
Detailed Explanation
Fiedler's model posits that the success of a leader hinges on two primary components: the leader's inherent style and the favorability of the situation they are in. The LPC scale helps identify a leader's style by asking them to reflect on their least preferred coworker. Situational favorableness considers the dynamics between leaders and their team members, the clarity of the task at hand, and the power or authority the leader holds.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a project manager who is great at motivating a team in a supportive environment but struggles when the team dynamics are strained. Fiedler’s model helps to understand that it's not just the manager's style but also the situation they are in that determines their effectiveness.
Hersey and Blanchard’s Situational Leadership Theory
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
b. Hersey and Blanchard’s Situational Leadership Theory
- Emphasizes adapting style to followers' readiness.
- Four styles:
- Telling (high task, low relationship)
- Selling (high task, high relationship)
- Participating (low task, high relationship)
- Delegating (low task, low relationship)
Detailed Explanation
Hersey and Blanchard's theory focuses on the readiness level of followers as the key factor in determining how a leader should behave. The four leadership styles range from telling, where the leader provides specific instructions, to delegating, where the leader gives full responsibility to the team. This highlights the importance of customizing the leadership approach based on the needs and development level of team members.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a teacher who has students of varying abilities. For a student who struggles with material, the teacher might use the 'telling' style to provide clear directives. In contrast, for a student who is more proficient, the teacher may adopt a 'delegating' style, allowing the student to work independently.
Path-Goal Theory
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
c. Path-Goal Theory (Robert House)
- Leaders clear the path for subordinates to achieve goals.
- Leadership styles vary based on situation:
- Directive
- Supportive
- Participative
- Achievement-Oriented
Detailed Explanation
Path-Goal Theory suggests that a leader's role is to help their team members reach their goals by providing the necessary direction and support. The leader can adopt different styles based on what is most effective for the specific situation and the needs of the team members. For example, a directive style might be needed for complex tasks, while a supportive style could be more effective in fostering team morale.
Examples & Analogies
Visualize a mentor guiding a group of interns. If the interns are new and unfamiliar with their tasks, the mentor might take a directive approach, laying out clear steps. However, if the interns have prior knowledge and confidence, the mentor may shift to a supportive style, encouraging collaboration and problem-solving among them.
Key Concepts
-
Contingency Theories: Leadership effectiveness depends on context.
-
Fiedler’s Model: Relies on LPC scale and three situational variables.
-
Situational Leadership: Adapts to follower readiness with four styles.
-
Path-Goal Theory: Leaders assist followers by selecting appropriate styles.
Examples & Applications
In a high-pressure project, a task-directed leader may be effective initially, but as the team grows more competent and confident, a relationship-focused approach may yield better results.
A tech manager using the Path-Goal Theory may provide detailed instructions (directive style) during the early phases of a project, then switch to a supportive style once team members have gained sufficient knowledge.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
To lead with the best, know the quest; adapt your style, don’t just guess.
Stories
Once there was a leader named Fiedler who only led well when team members liked him and when there were clear tasks. He learned that adapting to the situation made him a better leader.
Memory Tools
Remember the four styles of situational leadership with 'TSPD': Telling, Selling, Participating, Delegating.
Acronyms
Use 'LPC' to recall Least Preferred Co-worker, a measure in Fiedler’s model.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Contingency Theories
Theories that assert that the effectiveness of a leadership style depends on the situational context.
- Fiedler's Contingency Model
A model that evaluates leadership effectiveness based on leader's style and situational favorableness using the LPC scale.
- Least Preferred Coworker (LPC) Scale
A tool used to determine a leader's orientation by assessing their feelings toward their least preferred coworker.
- Situational Leadership Theory
A theory suggesting that leaders must adapt their style according to followers' readiness.
- PathGoal Theory
A theory that focuses on how leaders can assist their subordinates in achieving goals by varying their leadership style.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
