Bounded Model Checking (BMC)
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Bounded Model Checking
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're discussing Bounded Model Checking, or BMC for short. Can anyone tell me what they think BMC means?

Isn't it about checking the design limits to find errors?

Great start! BMC indeed checks for design errors, but it does this within a bounded timeframe, focusing on properties over a limited number of clock cycles.

How does that help us, though?

Excellent question! By bounding the time, it allows us to quickly identify corner cases and bugs early in the design phase.

So we can fix issues before they become bigger problems?

Exactly! That early intervention minimizes potential costs associated with late-stage bug fixes. Let's summarize: BMC verifies properties in a fixed number of cycles, helping detect bugs early.
How BMC Works
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s discuss how BMC actually works. Who can explain the basic process?

Does it check each clock cycle for violations?

Yes! BMC examines a limited number of cycles and checks for specific properties. Can anyone provide an example of a property we might verify?

We could check if a signal stays valid for N cycles?

Exactly! If BMC detects a violation, it presents a counterexample that shows the sequence of events leading to that violation. This helps a lot in understanding and debugging.

So it's like having a roadmap to the error?

That's a perfect way to put it! Now, to recap: BMC explores a design within a specific timeframe, checks properties, and provides counterexamples when violations occur.
Tools for BMC
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s talk about the tools used for BMC. Who knows any tools that support this method?

I've heard of Cadence JasperGold.

Absolutely! JasperGold is one of the well-known tools. Another is Mentor Graphics Questa Formal. Can anyone mention why these tools are pivotal?

They help us incorporate BMC into our workflows.

Correct! These tools make integrating bounded model checking into designs seamless, enhancing our verification process. Let’s finalize this session by summarizing: Tools like JasperGold and Questa Formal utilize BMC to ensure designs meet specified properties effectively.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
BMC explores design properties within a restricted number of clock cycles, useful for early bug detection and ensuring certain conditions are met in designs. It generates counterexamples if violations occur, which aids in debugging.
Detailed
Bounded Model Checking (BMC)
Bounded Model Checking (BMC) is an essential formal verification technique used to identify property violations in a design within a specified time frame or a limited number of clock cycles. The primary advantage of BMC lies in its ability to quickly detect design bugs early in the lifecycle, which helps reduce errors that may otherwise propagate through the design process.
Applications of BMC
BMC is particularly effective for verifying temporal properties, such as ensuring that a condition holds true within a specific number of cycles, such as 'A should always be true within N cycles.' This method is especially relevant during the early stages of design development, where developers seek to catch corner cases that might lead to failures in the final product.
How BMC Works
The BMC process involves exploring a limited scope of design states—specifically, a restricted number of clock cycles. During this exploration, if a property violation is detected, the tool will provide a counterexample; this counterexample outlines the exact sequence of events or states leading to the violation. This feature significantly facilitates debugging and helps developers understand the nature of the flaw, enabling them to implement corrective measures efficiently.
Tools Supporting BMC
Various formal verification tools support BMC capabilities, with notable names including Cadence JasperGold and Mentor Graphics Questa Formal. These tools offer integrated solutions for designers looking to incorporate bounded model checking into their verification workflows.
Youtube Videos

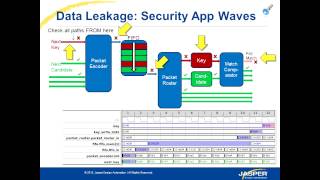

Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Definition and Purpose of Bounded Model Checking
Chapter 1 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Bounded Model Checking (BMC) is a formal verification technique that searches for violations of properties within a bounded time frame. It is particularly useful for detecting corner cases in the design.
Detailed Explanation
Bounded Model Checking (BMC) is a specific method used in formal verification, which focuses on checking if certain properties of a system hold true within a specified time limit. This means that instead of examining all possible behaviors and states of a design, BMC looks only at those that occur within a set number of time intervals (or 'time frames'). The main advantage of BMC is its efficiency in finding issues or 'bugs' that may arise from unique or extreme conditions, known as corner cases.
Examples & Analogies
Think of BMC like testing a car under certain conditions. Instead of driving the car across every possible terrain, you decide to drive it only on smooth roads for specific distances (like 5 kilometers). You want to see if it performs well under these limited but realistic conditions, just like BMC checks only a certain number of clock cycles.
Applications of Bounded Model Checking
Chapter 2 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
BMC is used to find design bugs within a limited scope of time, often during early stages of design or for designs with known temporal properties. It can be applied to verify properties such as "A should always be true within N cycles."
Detailed Explanation
The application of Bounded Model Checking is critical during the early stages of design or when working with systems that operate under specific timing conditions. It can verify whether certain conditions (like a signal being true) are maintained for a given number of cycles. This approach allows designers to catch potential bugs early, hence saving time and resources in later stages of the design process.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine you are baking a cake and want to ensure that it rises properly within 30 minutes in the oven. You check the cake every so often within that time frame (like setting timers at 10, 20, and 30 minutes) to see if it has risen. This is similar to how BMC checks if specific conditions within the design hold true during defined cycles.
Mechanics of Bounded Model Checking
Chapter 3 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
BMC explores a limited number of clock cycles and checks if the specified properties hold within this time window. If a property violation is found within the bounds, the tool generates a counterexample (sequence of events that led to the violation).
Detailed Explanation
In BMC, the process begins with defining a set number of clock cycles to examine. The verification tool then checks if the specified properties are valid within these cycles. If an issue is found—meaning a property that is supposed to hold true does not—the tool generates a counterexample. This counterexample is crucial as it provides a specific sequence of events that demonstrates the failure, helping designers quickly identify and fix the problem.
Examples & Analogies
Think of BMC as a security camera focused on a specific area of a house. If the camera captures an intruder (a property violation) during the time it was set to monitor, it can then show the sequence of events (the footage) that led to identifying the intruder. This provides clear evidence and helps homeowners understand how to enhance their security measures.
BMC Tools
Chapter 4 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Tools: Cadence JasperGold and Mentor Graphics Questa Formal provide BMC capabilities.
Detailed Explanation
To perform Bounded Model Checking, specialized tools are used that can automate the verification process. Cadence JasperGold and Mentor Graphics Questa Formal are examples of such tools. They are designed to efficiently conduct BMC, allowing designers to explore the state space of the design while focusing on specific time frames and properties.
Examples & Analogies
Using a tool for BMC is like using a specialized app on your smartphone that tracks your workouts. Just as the app helps you focus on your fitness goals (like specific exercises over a set timeframe), BMC tools help engineers focus on verifying part of their designs within specific parameters.
Example of BMC
Chapter 5 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
BMC can be used to verify that a finite state machine (FSM) never enters a state where the output is invalid, within a specific number of clock cycles.
Detailed Explanation
An example application of Bounded Model Checking is in the context of a finite state machine (FSM). BMC can check that the FSM does not reach any invalid states within a defined number of cycles, ensuring that the machine operates correctly under expected conditions. This specific verification can help catch errors early in the design process, which could lead to significant issues if left unaddressed.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a traffic light controller as an FSM. BMC ensures that the traffic light cannot simultaneously display both red and green (an invalid state) in the first ten cycles after it is powered on. This is similar to how traffic regulations work; they are designed to prevent dangerous situations to keep drivers and pedestrians safe.
Key Concepts
-
Bounded Model Checking: A verification technique that checks design properties within a specific timeframe.
-
Early Bug Detection: The ability to find and address design bugs at an early stage.
-
Counterexample Generation: Providing specific sequences of events when a property violation is found.
Examples & Applications
Using BMC to ensure that a finite state machine (FSM) never enters an invalid state within three clock cycles.
Verifying a protocol design where a specific signal must remain valid within four cycles.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
BMC’s here to check the space, within cycles we’ll find the trace.
Stories
Imagine you are a detective in a maze. You can only walk a certain number of steps, but you must find any paths that lead you in circles. That's how BMC ensures paths in designs are correct!
Memory Tools
BMC - 'Bounding My Checks.' Remember, we bound our checks to find bugs efficiently!
Acronyms
BMC
Bounded Model Checking - 'B' for Bounded
'M' for Model
'C' for Checking.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Bounded Model Checking (BMC)
A formal verification method that checks properties in a design within a limited number of clock cycles.
- Counterexample
A sequence of states or events that demonstrates a violation of a property during verification.
- Property
A condition or assertion about the expected behavior of a design.
- Temporal Properties
Conditions that must hold true within certain time constraints in the design.
- RTL Verification
A method used to verify the functionality of designs represented at the Register Transfer Level.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
