INTRODUCTION
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Role of Structural Engineers
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Welcome, everyone! Today we’re diving into the exciting world of structural engineering. Can anyone tell me what structural engineers primarily do?

They design buildings, right?

Correct! They do design buildings, but they also work on bridges, dams, and even aerospace vehicles like spacecraft. They collaborate closely with architects, especially for buildings. Why do you think teamwork is important in this field?

Because architects focus on the aesthetic design, while engineers ensure it's safe and functional!

Exactly! The creative vision of architects must integrate with the structural integrity provided by engineers. Think of the acronym 'C.A.S.E.' - Collaboration And Safe Engineering. This sums up their teamwork.

So, what's the difference between engineering for buildings and for infrastructure?

Great question! For infrastructure, structural engineers usually take the lead, while for buildings, they work more as a support role. This distinction is key in project management.

What about aerospace designing?

Aerospace structures have stringent safety requirements and must consider various forces at play during flight. This adds complexity to the design process. In summary, structural engineers ensure all structures are safe and effective, collaborating closely with different specialists.
Environmental Factors in Structural Design
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let's dive into how the environment influences structural design. Can anyone name an environmental factor that could impact a building?

Wind loads?

Exactly! Wind loads and lateral movements are critical to consider. Structures like elevator shafts often incorporate shear walls to resist these lateral forces. Can anyone guess why?

Because they need to stay stable during strong winds or earthquakes?

Correct! Stability is paramount. Let's also discuss sound. How might sound affect structural design?

The shape of the roof could concentrate or disperse sound, right?

Yes! A dome concentrates sound, while a dish roof disperses it. This can significantly impact acoustics in performance venues. Finally, think about natural light. How might we enhance light in deep structures?

Using more openings or a frame design!

Exactly! Remember the mnemonic 'S.L.A.C.K.' - Sound, Light, and Clearance Keep design dynamic. Understanding these factors ensures the structure's longevity and functionality.
Structural Analysis Requirements
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's focus on structural analysis. What do you think are the fundamental requirements that need to be met during this analysis?

They must be strong enough to support loads?

Correct! Strength is key. The stresses must not exceed critical values. Alongside strength, we also must consider stiffness and stability. Why are these factors important?

To prevent deformation that could lead to cracks or failure?

"Exactly! Preventing buckling or cracking ensures the structure remains safe over time. Let's break these down:
Load Transfer Elements
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s delve into how load transfer works in structures. Can anyone name a type of load transfer element?

Beams for flexural loads?

Yes! Beams handle flexural loads. What about axial loads?

Cables and trusses!

Great! Remember the phrase 'The Four Types of Loads - Axial, Flexural, Shear, Torsional.' Each transfer method is essential to structural integrity. Why do you think understanding these loads is important?

It helps engineers design safe structures that can hold different forces!

Exactly! It’s about ensuring structures are safe and reliable under expected loads. Always refer to the '4 L.T.E. Rules' - Loading, Transfer, Element performance, and Rules for safety!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
In this section, the roles of structural engineers in the design and analysis of buildings, infrastructures, and aerospace vehicles are discussed. It highlights the importance of environmental factors in design, load transfer elements, and the necessity of structural analysis to ensure safety and functionality.
Detailed
Introduction to Structural Engineering
Structural engineering plays a pivotal role in the design and construction of various structures, including architectural edifices, bridges, and vehicles. Engineers in this field collaborate closely with architects for buildings, focus on civil infrastructures such as dams and pipelines, and ensure safety in aerospace and marine structures.
The environmental context significantly affects structural design, requiring consideration of factors such as lateral loads (due to wind or earthquakes), sound interaction with structures, natural light provision, systems for utilities, and framing preferences based on clearance requirements.
Moreover, understanding structural analysis is crucial. This entails determining internal forces—axial, shear, flexural, torsional—and adhering to fundamental requirements: strength, stiffness, and stability. Engineers must constantly analyze and redesign to address serviceability and failure probabilities, especially in existing infrastructures requiring rehabilitation.
Ultimately, comprehensive evaluation and iterative design processes ensure structures fulfill safety and usability standards.
Youtube Videos







Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Role of Structural Engineers
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Structural engineers are responsible for the detailed analysis and design of:
1. Architectural structures: Buildings, houses, factories. They must work in close cooperation with an architect who will ultimately be responsible for the design.
2. Civil Infrastructures: Bridges, dams, pipelines, offshore structures. They work with transportation, hydraulic, nuclear and other engineers. For those structures, they play the leading role.
3. Aerospace, Mechanical, Naval structures: aeroplanes, spacecrafts, cars, ships, submarines to ensure the structural safety of those important structures.
Detailed Explanation
This chunk outlines the main responsibilities of structural engineers in various fields. They are crucial for designing and analyzing different types of structures. For example, in architectural structures like buildings, they collaborate with architects who visualize the design, ensuring the safety and feasibility of the construction. Similarly, for civil infrastructures such as bridges, they take the lead role in ensuring these structures can withstand the forces they encounter. This includes collaborating with various other engineers depending on the specific structure type, like transportation or hydraulic engineers. In aerospace, mechanical, and naval applications, they focus on ensuring safety in critical structures like airplanes and ships.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a structural engineer as a skilled part of a team, much like a chef in a restaurant. Just as a chef must understand how to use different ingredients and techniques to create a safe and delicious meal, a structural engineer must understand materials and physics to create safe and functional buildings and bridges. They are the experts who make sure everything holds together, much like how a chef makes sure all the elements of a dish complement each other.
Collaboration in Structural Engineering
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
They must work in close cooperation with an architect who will ultimately be responsible for the design.
Detailed Explanation
This chunk emphasizes the importance of collaboration between structural engineers and architects. While architects focus on the aesthetics and functionality of a building, structural engineers ensure that the design can be constructed safely and will remain stable over time. This partnership is essential because the architect's vision must be feasible; thus, the structural engineer analyzes whether the proposed designs can withstand various forces, such as gravity, wind, and earthquakes.
Examples & Analogies
Consider building a new playground. The architect proposes fun and exciting features like slides and climbing frames. However, the structural engineer checks if the proposed materials will be strong enough to support the slides and if the structures can withstand the weight of children playing on them. Just as a successful playground design needs both creative ideas and safety considerations, architectural projects also require the combined efforts of both architects and structural engineers.
Types of Structures Designed by Engineers
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Architectural structures: Buildings, houses, factories.
- Civil Infrastructures: Bridges, dams, pipelines, offshore structures.
- Aerospace, Mechanical, Naval structures: aeroplanes, spacecrafts, cars, ships, submarines.
Detailed Explanation
This chunk categorizes the different types of structures that structural engineers analyze and design. Architectural structures encompass residential and commercial buildings, which play vital roles in urban development. Civil infrastructure refers to large-scale projects like bridges and dams, which are essential for transportation and water management. Lastly, aerospace, mechanical, and naval structures include vehicles and vessels designed for air and sea travel, emphasizing the safety of both passengers and cargo.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a city as a puzzle, where each type of structure is a piece that fits together. The architectural structures (like buildings and homes) form the residential and commercial areas, while civil infrastructures (like bridges and roads) connect these pieces together, allowing people to move about the city easily. Lastly, the aerospace and naval structures are like the flying and floating pieces that let us travel beyond the borders of the city, linking our world.
Key Concepts
-
Structural Engineers: Professionals tasked with ensuring safety and integrity in various constructed structures.
-
Environmental Constraints: Factors such as wind, sound, and natural light that influence structural design choices.
-
Structural Analysis: The process of evaluating internal forces and deformations within a structure under specified loads.
-
Load Transfer Elements: Components within structures that facilitate the distribution of loads.
Examples & Applications
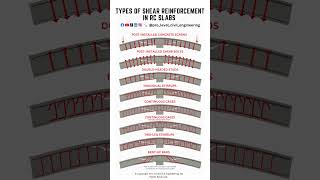
A shear wall used in high-rise buildings to resist lateral forces from wind.
The use of trusses in bridges to efficiently distribute weight over large spans.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
To keep structures standing tall, stability is the call.
Stories
Imagine a bridge built strong, with beams that bear the weight all along.
Memory Tools
Remember 'S.S.S.' - Strength, Stiffness, Stability for safe foundations.
Acronyms
C.A.S.E. - Collaboration And Safe Engineering highlights teamwork.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Structural Engineering
A branch of civil engineering concerned with the design and analysis of structures that support or resist loads.
- Shear Wall
A wall that resists lateral forces, commonly used to stabilize structures against wind or seismic activity.
- Stability
The ability of a structure to maintain equilibrium without collapsing or undergoing excessive deformation.
- Load Transfer Elements
Structural components that help distribute external loads throughout a structure.
- Serviceability
The ability of a structure to perform its intended function without significant deformation or failure during its service life.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
