Structures and their Surroundings
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Major Movements
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today we're diving into major movements! Can anyone tell me why it's critical to consider forces like wind and earthquakes in structural design?

I think it’s to make sure buildings don’t collapse during strong winds or seismic activity?

Exactly! We often use shear walls in elevator shafts to resist these lateral loads. They’re strong and efficient. Can anyone share what a shear wall does?

A shear wall helps to support vertical loads and also resist lateral forces.

Great! These walls provide structural integrity under various conditions. Remember the acronym 'CABS': Columns, Anchors, Beams, Shear walls, which helps us recall the main components for stability!

So, CABS helps with understanding the major supports?

Exactly! And if we don't account for these forces, we risk instability. Any other thoughts on this?

It's interesting how much planning is needed to just keep structures standing.

Absolutely! In summary, shear walls are a key solution for managing lateral forces caused by movements like wind and earthquakes.
Sound and Structure Interaction
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's discuss sound and structure! What happens with sound in a dome roof compared to a dish roof?

I think a dome roof focuses sound, maybe creating echoes?

Correct! It can concentrate sound, which might not be ideal in an auditorium. Conversely, what does a dish roof do?

It diffuses the sound, making it more evenly spread throughout the space.

Well said. Remember, 'Dome Equals Direction', while 'Dish Diffuses Noise'. These phrases can help you remember their effects.

So the roof shape can really change the acoustics of a building?

Yes, it significantly affects sound quality. A good rule of thumb is to always think about the purpose of the space when designing its roof.

I’ll remember to consider acoustics when designing!

Great! It's important to think about sound dynamics in any structural design.
Natural Light Considerations
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

How does natural light influence our structural design choices?

I think if we don't have enough light, it can affect the space’s functionality.

Exactly! A flat roof might block light, while a folded plate can enhance it. Who remembers the complexities involved in these designs?

The analysis for different designs can be complex, right?

Correct! Remember the phrase 'Folded Invites the Light'. This helps in recalling how certain shapes can improve lighting.

What about buildings with shear walls and not enough openings?

They can significantly limit natural light. We must balance structural strength with adequate light.

That's a crucial design element!

Absolutely! Every element must work together for both safety and functionality.
Integration of Building Services
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

What role do services like HVAC and electrical systems play in structural design?

They help with the comfort and functionality of the space, right?

Exactly! They can dictate the type of floor system we choose. Can anyone elaborate?

If there are many ducts, we might need a raised floor for better airflow.

Good observation! Remember, 'Function Forms Floor'. This helps in thinking about how functionality can shape our designs.

So it’s not just about how the structure looks, but how it works too?

Precisely! All elements from aesthetics to services to interactions must align for a successful design.

That makes perfect sense!
Net Clearance and Framing
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Finally, let’s discuss net clearance! Why is it crucial in framing?

It helps to ensure that the space is usable and practical for its intended function.

Absolutely! If the clearance isn’t right, it can restrict movement and usability. Who remembers the impact this has on design choices?

It can dictate the type of framing used, right?

Exactly! Keep in mind 'Clearance Captures Comfort'. It can help reinforce the importance of this consideration in design.

I see how all these factors work together now!

Yes, design is a collaborative effort between numerous factors. In summary, net clearance must be treated with care to ensure effective use of space.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Structural design must consider various environmental factors that affect the way structures are built and function. Key constraints include major movements such as wind and earthquakes, sound interactions with different roof types, the need for natural lighting, and the integration of services like HVAC and electrical systems.
Detailed
Structures and their Surroundings
Structural design is heavily influenced by environmental factors that can dictate aspects of its architecture and functionality. This section outlines several key constraints in structural design:
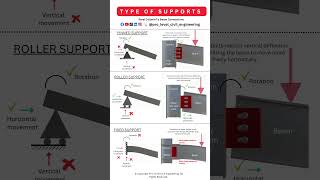
- Major Movements: Structural components must withstand forces from movements, such as the lateral loads imposed by wind or seismic activity. For instance, elevator shafts are often designed as shear walls to handle these lateral forces effectively.
- Sound Interaction: The way sound interacts with structural elements can vary. A dome roof can concentrate sound, potentially creating echo, while a dish roof works to diffuse sound, providing a balanced acoustic environment.
- Natural Light: The design must also consider the inflow of natural light. A flat roof may lead to insufficient lighting, whereas a folded plate design may enhance illumination—albeit with a more complex analysis process. Similarly, buildings with shear walls might limit openings, reducing natural light, while framed designs allow more light to enter.
- Building Services: The technical systems within a structure, like HVAC ducts and conduits for electrical or communication cables, directly influence the choice of flooring systems, thereby affecting overall design and functionality.
- Net Clearance: The unobstructed space between columns must be accounted for as it determines the type of framing utilized in the structure. This clearance is crucial for ensuring that the space is usable and practical for its intended function.
In conclusion, understanding these environmental constraints is vital for engineers to create safe, functional, and efficient structures.
Youtube Videos







Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Impact of Major Movements
Chapter 1 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Major movements: For example, elevator shafts are usually shear walls good at resisting lateral load (wind, earthquake).
Detailed Explanation
Major movements refer to external forces or factors, like wind or earthquakes, that exert pressure on structures. To counteract these lateral loads, elevator shafts are often designed as shear walls. Shear walls are vertical structural elements that help stabilize buildings by resisting side-to-side forces.
Examples & Analogies
Think of shear walls like the backbone of a person; just as a backbone supports the body and keeps it upright against various forces, shear walls keep the building steady during strong winds or earthquakes.
Interaction of Sound and Structure
Chapter 2 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Sound and structure interact:
- A dome roof will concentrate the sound
- A dish roof will diffuse the sound
Detailed Explanation
The design of a structure can significantly affect how sound behaves inside it. A dome roof, with its curved shape, will cause sound waves to converge at a focal point, making certain areas louder. In contrast, a dish-shaped roof disperses sound waves, resulting in a more uniform distribution of sound throughout the space.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine playing music under a dome versus in an open field. Under the dome, the sound echoes and amplifies, creating a richer experience, while in the open space, the music may seem softer and spread out.
Natural Light Considerations
Chapter 3 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Natural light:
- A flat roof in a building may not provide adequate light.
- A folded plate will provide adequate lighting (analysis more complex).
- A bearing and shear wall building may not have enough openings for daylight.
- A frame design will allow more light in (analysis more complex).
Detailed Explanation
Natural lighting is essential for the aesthetic and energy efficiency of a structure. Flat roofs may block light penetration, whereas folded plate designs can enhance light entry. Buildings with bearing and shear walls may lack adequate openings for windows, while frame designs can create more opportunities for natural light through extensive openings, though they require more complex analysis for structural integrity.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a flat-roofed house versus a house with many windows and a sloped roof. The flat-roofed house may feel dark and stuffy, while the other is bright and inviting, emphasizing how roof shape influences light.
Conduits and Ducts
Chapter 4 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Conduits for cables (electric, telephone, computer), HVAC ducts, may dictate type of floor system.
Detailed Explanation
The integration of electrical cables and HVAC ducts within a building's design can influence the choice of flooring systems. Certain flooring types may need to accommodate these systems for efficient installation and operation, while others may not. Proper planning ensures that these conduits do not interfere with the structural integrity and aesthetics of the building.
Examples & Analogies
Think about how you arrange furniture in a room around cables and power outlets. Just as you need to plan your layout to avoid tangled cords, structural engineers must design floor systems with the necessary space for conduits and ducts.
Clearance Between Columns
Chapter 5 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Net clearance between columns (unobstructed surface) will dictate type of framing.
Detailed Explanation
The distance between columns, or net clearance, is essential in determining the framing type used in a structure. If the clearance is large, a different frame design may be required to safely support the load compared to structures with closer column placements. This design consideration impacts both functionality and aesthetics.
Examples & Analogies
Picture an open space like a gym; if the columns are too close together, it may break the room's functionality and movement flow. When designing a building, engineers think similarly about how columns can impact the layout and efficiency of spaces.
Key Concepts
-
Shear Walls: Essential for resisting lateral loads.
-
Sound Interaction: Different roof shapes affect acoustics.
-
Natural Light: Critical for functionality and ambiance.
-
Building Services: Influence structural design and layout.
-
Net Clearance: Vital for usability and structural integrity.
Examples & Applications
In earthquake-prone areas, shear walls are commonly used in tall buildings to provide stability.
A dish roof design can enhance the sound quality for spaces used for performances, allowing clearer acoustics.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Shear walls stand tall, resisting the wind’s call.
Stories
Once upon a time in a windy town, buildings learned to wear shear walls like armor to prevent them from falling down in storms.
Memory Tools
Use 'LACE' - Lateral forces, Acoustics, Clearing space, and Efficient light - to remember crucial aspects of structural design.
Acronyms
SAND - Structures and Natural light dictate Design.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Shear Wall
A structural wall designed to resist lateral forces acting on a building.
- Dome Roof
A roof shape that curves outward, often amplifying sound within the structure.
- Dish Roof
A roof shape that curves inward, designed to diffuse sound effectively.
- Natural Light
Light that comes from the sun, which is essential for reducing energy consumption and improving interior environments.
- Net Clearance
The unobstructed space between columns that affects the design and function of a structure.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
